Design of a mechanical testing device for ESEM for Bone fracture healing assessment

Design of a mechanical testing device for ESEM
for
Bone fracture healing assessment
Participants
• Project Sponsor
• Dr. Stephen Doty, Hospital of Special Surgery
• Project Advisors
• Luis Cardoso, Ph.D and Marom Bikson Ph.D from The
Biomedical Engineering Department at City College
• Stewart Russell, Ph.D
• Students
• Rasha Aaskar
• Gaurav Aggarwal
• Cristina Alexandrescu, Team Leader
• Francisco Saenz
Table of Contents
• Introduction
– Project Goals
– Clinical Need
– Physiology of Bone
Healing
• Background
– Current Testing Methods for Assessing Healing
• Concept Development
– Design Specifications
– Constraints
– Existing Products
• Concept Design
– Universal External Testing
Stage
– Concept 1: Piezo Actuator
– Concept 2: DC Electric Motor
– Advantages & Disadvantages
• Conclusion
Project Goals
• Develop a device that is capable to:
– Perform mechanical testing on fractured bone during the healing process
– Allow placement inside the ESEM for microscopic analysis
Clinical Need
• Understand the mechanisms of fracture healing
– Evaluation of the mechanical properties
– Microscopic assessment of the tissue composition
• Analyze the effects of different treatments in the fracture repair process
– Increase in rate of healing
– Improve the strength of the fracture site
• Improve patient’s quality of life
Physiology of Bone
Healing
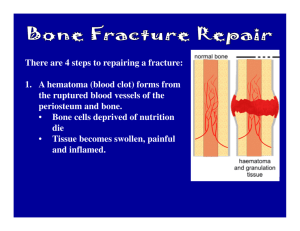
• Inflammation
– Occurs immediately after fracture
– Mechanical stability is achieved by presence of hematoma
– Callus forms by bridging the fracture site
» Takes 2-3 days
• Reparation
– Callus size increases to unite fracture site and reduce bone motion
– Callus begins mineralization and eventually matures into lamellar bone --> bony union occurs
» Takes 4-12 weeks
•Remodeling
–Characterized by Wolff’s Law
–Fully restore anatomical configuration of bone
»Takes 6 months to 1 year in adults
Current Testing Methods for
Assessing Fracture Healing
• Qualitative methods
– Radiography
– Densitometry
• Quantitative methods
– Mechanical testing
• Three point bending
• Four point bending
• Torsion
These tests measure:
– Stiffness
– Ultimate load
– Work to failure
– Ultimate displacement
Hiltunen et al
Design Specifications
• Testing Method
– Four point bending inside the ESEM
• Components
– A motor that applies a chosen range of forces
– Sensors to measure:
• Displacement
• Force Applied
• Materials
– 440C Stainless Steel
– UHMWPE
– Rubber
– Copper Tubing
• Design should allow easy visualizations of bone callus for microscopic analysis
• The Data Acquisition will initially be done via Lab View and NI DAQ Hardware
Parameters
Workable Area
Length
Depth
Value
20 cm
8 cm
Height 10 cm
Internal Environmental Conditions
Type of Atmosphere
Temperature
Partial ~ 4000 Pa
25 Degrees Celsius
Measurement Feedback Scales
Force
Displacement
0 ~ 30 newtons
0 ~ 3 mm
Accuracy
Force 1 micro-newton
Displacement 0.01 mm
Force Lost Due to Components (Gears, shafts, couplers, etc.)
To The Bone 0.01 newtons
Constraints
• ESEM
– Minimal alterations to microscope
– Electromagnetic and environmental conditions
– Workable space inside the chamber
• Device Components
– Satisfy ESEM constraints
– Must be sturdy and secured inside the chamber
• Testing Conditions
– Bone hydration
Initial Concepts of
Internal Testing System
• Modification of existing stage gear system
– Requires excessive modification of the ESEM
• Use of the external port of the ESEM
– Requires the creation of a Vacuum seal
– Modification of the port assembly of the ESEM
These two concepts might result in damage of the ESEM and are too expensive to be pursued.
Existing Products
• There exist devices that meet the design criteria and overcome the imposed constraints
– Prices range from
$10,000-30,000
– Encompass all testing methods
– Customized software applications
Courtesy of www.gatan.com
Therefore…
• Existing commercial devices provide an immediate solution to the original design specifications
• However these systems are too expensive
• These challenges can be overcome by building an external device as opposed to an internal one. The external testing system will:
– Be a cheaper alternative to commercial devices
– Perform the most relevant testing method for fracture healing studies
– Specifically designed for testing of mouse bones
– Be portable for usage in multiple microscopes
– While having a self locking mechanism to maintain deformation
– Be used as a prototype for preliminary studies to determine clinical relevance
– Be safe for the ESEM
• No fragmentation of bone
• No alterations
• No EMF
Concept Designs
• Test system:
– Accommodates motors and linear actuators
– Minimizes alterations to the stage design.
• Criteria:
– Cost
– Accuracy
– Size
– Locking Mechanism
Universal External
Testing Stage
Interface for bone (consisting of hardened liquid polymer [polyethylene] and metal coupler). Applies four point bending force.
Z
Y
X
Load Cell
Physical stage constructed of Stainless Steel or polyethylene with maximum size of 20 x 8 x
10 cm
LVDT
Motor / Actuator
Concept 1
Piezo Actuator
• Composed of a ceramic material that expands and contracts in response to an applied electrical voltage
• Advantages
– Self locking when power is removed
– Rapid response
– High resolution
– Not subject to mechanical tear and wear
– Eliminates the need for an external LVDT
Piezo Actuator
(cont’d)
• Disadvantages
– Brittle
– Repeatability errors due to hysterisis and creep
– Higher costs of roughly $500
• An electrical motor converts electrical energy to mechanical energy using principles of magnetism to propel the armature
Concept 2
DC Electric Motor
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Electric_motor_cycle_1.png
• Advantages
DC Electric Motor
(cont’d)
– If operated only outside it would not create EMF inside the ESEM
– Very Inexpensive
• Costs can be less than
$100
• Disadvantages
– Constant power must be applied to maintain load
– Special locking clamps would be needed to maintain deformation
– Repeatability errors due to hysterisis and creep
– Requires external load and displacement sensor
– Requires design of gear system for linear displacement
External Testing System
• Advantages
– No EMF inside ESEM
– No possible damage to the ESEM
– No particle creation inside the ESEM from fracturing
– External testing system with the possibility to test inside, with appropriate shielding
– Cost effective in manufacturing
– Less need for shielding
• Disadvantages
– Power needs to be removed while imaging in the ESEM for no EMF generation
– Possibility of losing deformation during movement
Conclusion
• The risk of modification with an internal system, and the costs of existing devices has lead to the development of an external testing system
• Our design will provide an alternative solution to the sponsor’s original design specifications while still meeting the requirements of the device