Constructivism
advertisement

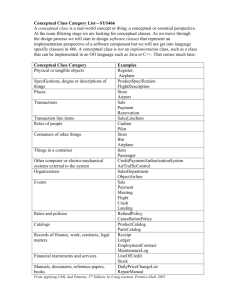
Current Event #2: Constructivism Lee 1/6 Miha Lee Professor Rivas SED 600 18 April 2007 Conceptual change using multiple interpretive perspectives: Two case studies in secondary school chemistry By Allan G. Harrison & David F. Treagust From Instructional Science vol.29: 45–85, 2001. Harrison and Treagust (2001) conducted a case study of two students as they learned chemistry taught by the first author in an Australian high school. Alex and Dan were followed throughout the whole academic year (36weeks) and were observed and interviewed for their understanding of atomic structures. Finally, the researchers concluded that the understanding the conceptual change requires multiple approaches toward the interpretation of learning, involving “social and motivational factors, ontological issues, modeling ability, intellectual development”(p.45). This study attempted to explore alternative explanations for why given the same learning environment why some students learn but others do not. To answer the interesting question, two students were chosen with an explicit purpose of supporting their assertion that students’ scores on standard tests and examinations are unreliable indicators of conceptual understanding. In this sense, the participants, Alex and Dan, were chosen because they were apparently similar in terms of the achievement on the tests, but very different in light of the Current Event #2: Constructivism Lee 2/6 quality of understanding. This is a purposeful sampling for in-depth case study. Purposeful sampling is the dominant strategy in qualitative research. Purposeful sampling seeks information-rich cases that can be studied in depth (Hoepfl, 1997). When the researcher introduced the participants, I could tell the intention of this study; they questioned the scores on the tests as an indicator of learning and understanding. However, the question to be asked is how the researchers knew these students developed very different quality of conceptual understanding prior to conducting the research. The answer to this question was that this was the follow-up study after the first author’ doctoral dissertation. They used the same data in order to answer the different research question. As a result, there are some flaws in this study that need to be addressed before the reader can fully accept the validity of the conclusions. The researchers insisted that the social and motivational factors were the main influence that caused the difference in the conceptual development of two students. However, there was no supportive evidence such as quotations from the interviews. They just described the personality and background in the student profile. In addition, one student, Dan, was from Singapore and he moved to Australia at the beginning of this research. They explained that his prior educational curriculum in science was suitable prerequisites for the Western Australian chemistry course, but I think his different cultural background could affect his learning process, and thus his conceptual development. Despite any perceived flaws in this study, the topic and interpretation of conceptual change were very interesting and useful to me. The target concept of Current Event #2: Constructivism Lee 3/6 this research was the atomic structure that is invisible and thus has many diverse forms of models depending on the purpose of the scientists. In fact, understanding of the nature of various atomic models, including ball and stick, electron shells, and electron clouds, is the fundamental goal of teaching and learning chemistry. Accordingly, the first author taught chemistry in a traditional way except that every metaphor, analogy and model was discussed in detail with the students; the researchers monitored the understanding and use of the analogical models of atoms and molecules. To determine the depth of the conceptual changes from prior knowledge to desired knowledge, the researchers employed three tools with regard to epistemology: conceptual status, modeling level, and intellectual ability. I summarized and compared three epistemological tools in the following table. To confirm the status of concept, the other tools are used. Because modeling levels are derived from the way students describe, explain and use models, the levels provide information about conceptual status, and thus modeling level changes may provide useful evidence for conceptual change. Conceptual status, modeling level and intellectual ability seem to be interrelated to allow their use as ‘triangulation of measures for conceptual change’. There may be other way to evaluate and interpret the conceptual change, but these three ways are sufficient enough to show the complexity and difficulty of assessing conceptual understanding. This multiple epistemological approach to measure the depth of conceptual understanding informed me how to assess student’s learning. Current Event #2: Constructivism Conceptual status Intelligible: A Lee 4/6 Modeling level new Intellectual ability Dualism Level 1: Students who Students in conception is sensible and believe that there is a 1:1 categorize understood by a student. correspondence between right-or-wrong, defer to the Conceptual capture models and reality, that is teacher Assimilation of new concept models are small incomplete correct answer, expect to be copies of actual objects. told knowledge who what memorize knows is and right, as the and regurgitate knowledge. Plausible: that plausible in addition means to Level 2: Students who Students the believe that models remain who Multiplism advance accept to and student knowing what the real world entities rather rationalize conception than representations of representations by believing ideas, and a model’s main that everyone is entitled to purpose is communication his/her opinion. They believe rather than idea exploration. that every opinion is equally finds means, the he/she conception believable. valid and diverse context-bound reasonings are just special cases. Level fruitful if it helps the learner satisfied level 3 criteria that students must comprehend solve or models should be multiple; that knowledge is relative research are thinking tools; and can and contextually bound. other suggests problems new 3: Experts manipulated alone directions. be Conceptual exchange modeler Accommodation epistemological needs. to suit by To reach Relativism, Fruitful: the conception is the his/her The unique feature of this paper is the way the data was provided and analyzed in the paper. First, every change in the concept of atom was described by the time progress with the evidences from the pre and posttests. Because the teaching was model-based, the students’ concepts were also measured by drawing and selecting diagrams that represented the concept of atom’s electron Current Event #2: Constructivism Lee 5/6 shells and electron clouds. Those drawings the students made, quotes the students said, and analysis with pedagogical implications at length helped me follow the progress the students made, and made the researchers’ claims reliable. According to this paper, one student pursued deep understanding of concepts and their interrelationships, but the other just sought “the accumulation and reiteration of information in a systematic way” (p.76). The author attributed this result to the social-affective learning factor by interpreting that “for Alex and Dan, different motivational influences seemed to mediate their conceptual development” (p.78). But as I mentioned earlier, this assertion was given without any supporting evidence. Due to sufficient evidence and detailed interpretation, I was convinced that the qualities of conceptual change of two students were quite different. On the contrary, the research seemed to fail to answer the research question: what caused the difference in the quality of student understanding in the same learning environment? If the students’ scores on the tests were not reliable indicator of learning, we should question the validity of the test, not the motivation of learning. Just because a student has high motivation on grade does not mean he/she can get a high score on the test. However, this study suggested that we use multiple interpretive perspectives in order to measure and understand the conceptual change. Like this research, teachers need information collected from independent perspectives by using qualitative ways of assessment. The researchers specifically commented that in the study, a constructivist Current Event #2: Constructivism Lee 6/6 methodology was purposely chosen for the study’s design, data collection and interpretation, and case study writing. They insisted that qualitative aspect of constructivist researches ask for different criteria, replacing reliability by dependability, and objectivity by conformability because each class present a different social and intellectual mix in a new time and place and the teacher’s knowledge evolves as his/her experience grows. In deed, earlier constructivists were interested in the conceptual change only at a level of epistemology, but recent social constructivists are making shifts from individual cognitive structure to various factors that affect conceptual understanding. Thus, constructivists carry out researches with qualitative methods rather than quantitative methods to measure the depth of understanding and identify the factors that affect student learning. In this sense, this case study was a representative example of constructivists’ qualitative researches even though they failed to provide supporting evidence. Also, this study suggested that further investigations are needed to identify the social and affectional factors that mediate student’s learning process. Reference Hoepfl, M. (1997). Choosing qualitative research: A primer for technology education researchers, Journal of technology education, 9(1), 47-63 Harrison. A. G. & Treagust. D. F., (2001), Conceptual change using multiple interpretive perspectives: Two case studies in secondary school chemistry, Instructional Science, 29, 45–85