JSReviewExam#3.doc
advertisement

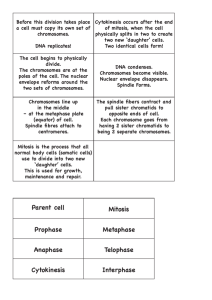
Review Sheet for Exam #3 (Morris Chapters 9 - 12) Dr. Solti This review is meant to serve as a guide to ensure your notes are complete. You will need to be able to do/understand and READ YOUR BOOK! Simply filling out this review sheet will not be enough to earn a good grade. 4 essential elements of communication 4 key steps in cell signaling 4 types of cell signaling terms "ligand" and "ligand-binding site" Cell surface receptor: G-protein coupled (adrenaline signaling in heart muscle), receptor kinase (kinase adds a Pi; phosphatase removes a Pi; mutations called kit), ligand-gated ion channel (between neurons and neuron and muscle cells) Cell-signaling and cancer Know the figure on The Human Life Cycle Bacteria reproduce by binary fission (mitosis) Know the comparison between prokaryote and eukaryote genome Mitosis is a reproducing division (copying) that leads to division of one cell into 2 daughter cells, each with the genetically identical 46 chromosomes. Used to make somatic cells. Have no homologues, no synapsis, no tetrads, no crossing over. Mitosis: division of the nucleus and the chromosomes Cytokinesis: division of the cytoplasm and cell o In animals: occurs by cleavage furrow o In plants: occurs as cell plate Know the definitions of : gene, chromatin, chromosomes, centromere, somatic cell, gamete, haploid, diploid, fertilization Know the figure on The Cell Cycle------one generation of a cell o Mitotic phases- shortest part of cell cycle (only 10%) Mitosis (M) Cytokinesis ( C ) o Interphase phases– nondividing , growth and development (90% of cell cycle) G1 – growth 1 S - DNA synthesis (this is where the sister chromatids are made): remember, “need to multiply to divide” G2 – growth 2 and preparation for division o Nerve and muscle cells stay permanently in G0 once they are developed Know the Stages of Mitosis o Prophase: longest phase of mitosis Condensation/shortening of sister chromatids: in nucleus Formation of mitotic spindle: in cytoplasm (comes from the centrosomes: which are the microtubule-organizing centers) o Prometaphase: Nuclear envelope disintegrates Kinetochore microtubules formed (puppets on a string) o Metaphase: 46 pairs of sister chromatids line up at metaphase plate o Anaphase: Sister chromatids separate and go to opposite poles o Telophase/C Nuclei are reformed Nucleoli are reformed Chromosomes become unobservable chromatin (chromosomes are only observable during mitosis or meiosis) Cytokinesis occurs -1- Review Sheet for Exam #3 (Morris Chapters 9 - 12) Dr. Solti Centromere: where the sister chromatids attach to each other in S phase and detach in Anaphase. If you have 12 centromeres, how many chromsosomes will you have in each daughter cell? 12 Cytokinesis: cleavage furrow in animals by actin microfilaments; cell plate in plants by Golgi body vesicles that turn into cellulose cell wall Know the definitions for: heredity, variation, genetics, DNA, locus, asexual reproduction, somatic cell, gamete, diploid, haploid, fertilization, zygote, karyotype, homologous chromosomes Gamete: sex cell; either sperm or egg; they are haploid, only one set of 23 chromosomes Somatic cells: all other body cells; always diploid; having 2 sets of homologous chromosomes (one set from Mom, and one set from Dad) Meiosis is a reduction division; goes from 1 diploid pre-gamete cell to 4 haploid gametes; occurs in testes/ovaries to make sex cells; leads to genetic variability Know the Stages of Meiotic Cell Division o Meiosis I: to separate homologues and make haploid cells Prophase I: homologues find each other and line up side by side (synapsis) to form a tetrad/bivalent; then they do crossing over of chromatids (chiasmata where they cross over); leads to tremendous variation Metaphase I: 23 tetrads (23 pairs of homologues and their sisters) line up at metaphase plate; tetrads do independent assortment for how they line up; leads to tremendous variation Anaphase I: tetrads split up (homologues separate) Telophase I/Cytokinesis: 2 haploid cells form, but still have sister chromatids attached o Meiosis II: to separate the sister chromatids (identical to mitosis) Prophase II Metaphase II Anaphase II: separate sister chromatids Telophase II/Cytokinesis: now have 4 haploid cells, each with 23 chromosomes If an organism’s liver cells have 500 chromosomes each, how many chromosomes will each sperm cell have? 250 Understand the comparison between Mitosis and Meiosis Genetic variation in meiosis occurs during: Prophase I (crossing over), Metaphase I (independent assortment), random fertilization Female vs. male meiosis DNA damage checkpoints Cancer terminology & cancer Multiple mutation model for cancer development Review of DNA structure Enzymes/Proteins of DNA replication Semiconservative Model for replication Replication occurs 5' to 3' Leading strand vs. lagging strand RNA primer Proofreading Telomeres and telomerase PCR technique Gel electrophoreisis Restriction enzymes and fragments Recombinant DNA and transformation GMOs -2-