Chapter One Outline
advertisement

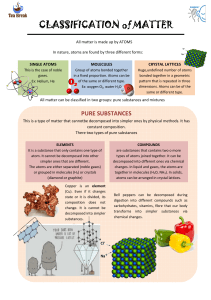
A.P. Chapter One Outline The Nature of Chemistry Chemistry is the science of matter and its transformations from one form to another Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space I. Scientific Methods Hypothesis: an idea that is tentatively proposed as an explanation for some observation and provides a basis for experimentation Observations: something that can be directly perceived through ones senses. A qualitative observation can not be measured numerically A quantitative observation can be measured numerically II. III. IV. V. VI. Identifying Matter: Physical Properties Physical properties can be observed and measured without changing the composition of a substance. Examples include temperature, mass, density, etc. Density is the ratio of an objects mass to its volume; D = m/v Chemical Properties A substances chemical properties describe the kinds of chemical reactions the substance can undergo Chemical reactions are usually accompanied by transfers of energy Substance and Mixtures A heterogeneous mixture is one in which properties in one region are different from properties in another region A homogeneous mixture, or a solution, is completely uniform and consists of two or more substances in the same phase Elements and Compounds Elements are composed of only one kind of atom and cannot be decomposed into two or more substances Compounds are two or more elements chemically combined and can be decomposed States of Matter: Solids, Liquids, and Gases Solids: have rigid shapes, fixed volume, and is relatively incompressible Liquids: has a fixed volume but indefinite shape; is relatively incompressible Gases: have neither a rigid shape or fixed volume VII. VIII. The kinetic-molecular theory states that all matter consists of extremely small particles that are in constant motion. The higher the temperature the greater the speed of the particles The Atomic Theory An atom is the smallest particle of an element that embodies the chemical properties of an element The law of conservation of mass states that there is no detectable change in mass during an ordinary chemical reaction The law of constant composition states that a chemical compound always contains the same elements in the same proportions by mass The Modern Atomic Theory 1. All matter is composed of atoms, which are extremely tiny 2. All atoms of a given element have the same chemical properties 3. Compounds are formed by the chemical combination of two or more different kinds of atoms 4. A chemical reaction involves joining, separating, or rearranging atoms The Chemical Elements Every element has been given a unique name and symbol. The first letter is capitalized, and if there is a second letter it is in lowercase Most elements are metals (they conduct heat and electricity, are lustrous, ductile, and malleable) A molecule is a unit of matter in which two or more atoms are chemically bonded together Allotropes: different forms of the same element in the same physical state at the same temperature and pressure