1406 Guide. Ch 6-11.doc

Study Guide for Biology 1406
Second exam
Dr. Chukwu
Chapter Six
A Tour of the Cell
Define a cell
Differentiate between unicellular and multi-cellular, animal and plant cells
How do we study cell function
What do you mean by fracturnation?
Name the types and parts of the microscope
The three main parts of the cell
Organelles and their functions
The cell cycle, why do cells divide?
The characteristic the plasma membrane
The lipid by-layer and fluid mosaic
What are the parts of the control center of the cell
What are the functions of the plant cell wall
Name the 3 main types of intercellular links Animal cell, what are their functions
What are “The cell theory”
What are the differences between the Eukaryotes & Prokaryotes
Chapter Seven
Membrane Structure and Function
Membrane Transport
What is the plasma membrane made up of
What do you mean by amphipathic
What are the functions of the cholesterol molecules and protein
What is selective permeability
Explain “Diffusion depends on concentration gradients”
What is dynamic equilibrium?
Hydrophobic vs Hydrophobic
What do you mean by passive
What are Osmosis, facilitated transport, dynamic equilibrium, concentration gradient, active transport
Membrane junctions, three types
What are Hypertonic, Hypotonic and Isotonic solutions
Plasma membrane, Phospholipids, amphipathic
What strengthens the fluid mosaic and makes it more stable
What are Diploid and Haploid Number of chromosomes
Where does the gene reside, Sex and body chromosomes
Define mitosis and meiosis
What do yo mean by crossing over
Mother cells vs daughter cells
The Human somatic or Body cells and sex cells, the phases of cell division
What is binary fission?
Tell what is happening at each phase of cell division PMAT, Interphase
What is crossing over, when does this occur
What is Cytokinesis
Differentiate between mitosis and Meiosis
Chapter 8 Metabolism
Metabolism refers to all to the chemical reactions within a cell
These include catabolic and anabolic reactions
Catabolism : this is the chemical reaction that breaks down large substances into smaller ones with the release of energy
Anabolism : this is the systemic chemical reactions in which the products are larger than the reactants, ex aa to protein
Energy coupling: this is the use or transfer of energy generated during catabolism (exergonic reaction) to drive anabolism (endergonic reaction)
Energy
•
Energy is the ability to do work
•
Energy exists in many forms
•
Kinetic energy: this is the energy of motion
•
Potential energy: this is the energy of position
•
Chemical energy: this the energy stored in molecules
•
There are also mechanical, heat and light energy, radient
Energy can be transformed from one form to another
Bioenergetics : this is the study of how organisms manage their energy resources
Thermodynamics : this is the study of the energy transformation that occur in a collection of matter
First law of energy : energy cannot be created or destroyed, but can be transformed or transferred
Second law of energy : every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy
(disorderliness) of the universe
Third law of energy
: the quantity of energy in the universe is constant, but it’s quality is not
Spontaneous VS non-spontaneous process
•
A spontaneous process can take place with out any outside help, ex. The flow of water down the hill
•
A non-spontaneous process cannot occur on it’s own.
Energy is expended for this to take place, ex. Machine pumping water into a water tank tower
What is Free energy :
•
The proportion of the system energy that can perform work when temperature is uniform throughout
What is Exergonic reaction : this is a spontaneous chemical reaction in which there is a net release of free energy
What is Endergonic reaction : this is the type of reaction in which free energy is absorbed from the surrounding ( a non-spontaneous chemical reaction)
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate ): this is the energy source for the cells
It is composed of a nitrogen base adenine, the sugar ribose and three phosphate group
ATP is used in the body cells for anabolic reactions, active transport, nervous conducting and muscle contraction.
ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate): it is similar in structure to ATP except for the phosphate group
ATP has 3p, whereas ADP has 2 phosphate group
ADP is produced when ATP is hydrolyzed
Enzymes
An enzyme is a protein catalyst that speeds up chemical reaction
They regulate the speed at which a chemical reaction occur without affecting the end product of the reaction and without being used up in the reaction
Energy of activation : this is the energy that must be provided to cause molecules to react with one another
Enzymes are substrate specific
•
Wht is a substrate? is a reactant in a reaction controlled by an enzyme
•
Ex. Reactant enzyme
Substrate Product
Sucrase
Sucrose + Water Glucose +Fructose
Factors affecting enzyme activity
•
Temperature : - rate of reaction decreases with rise in temperature
•
Enzyme is denatured beyond optimal temperature
•
Ph : the optimal values ranges from 6 – 8 with a few exception
For pepsin the optimal ph is 2
•
Cofactor : enzyme may be bound tightly to active site as permanent residents
•
Inhibitors: they are mimics
•
Competitive inhibitors reduce the productivity of enzymes
•
Enzymes may block substrates from entering the active site
Chapter 9
What are cellular respiration, mitochondria
The overall process is:
Organic compounds + O2 CO2 + H2O + Energy
Glucose.
C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP + heat)
686 kcal per mole of glucose
What is Phosphorylation
What is Oxidation-reduction reactions, or redox reactions
The three metabolic stages of respiration are ?
In which part of the cell do Glycolysis and krebs cycle occur
How many ATP produced by one mole of glucose?
How many % of ATP is used for work and heat?
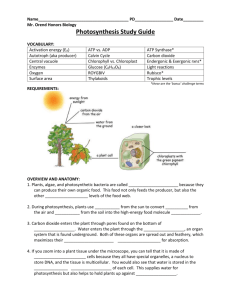
Chapter 10 Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the conversion of light energy to chemical energy which is stored in the form of glucose or other organic compounds
Photosynthesis occur in plants, algae and certain prokaryotes
6CO2 + 12H2O + light energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
Where does photosynthesis occur
Light vs dark cycle
An autotroph is an organism that obtains organic food molecules without eating other organisms
An autotroph is a primary producer or biosphere producer
Autotrophs use energy from the sun or from oxidation of inorganic substances to make organic molecules
Heterotroph s
They are organisms that obtain food molecules by eating other organisms or their by products
They are the biosphere consumers
Decomposers
These are saprotrophic fungus and bacteria that absorb nutrients from non-living organic materials and convert them into inorganic forms (fungi and bacteria)
Plants usually store their food in the form of starch
Photoautotrophs (light – self – feeding)
Almost all autotrophs depend on photosynthesis and the byproduct of photosynthesis for food and oxygen
Chloroplast : the green coloring matter in plants green leaves, stem and fruits
Chloroplast is an organelle found in plants and photosynthetic protists that absorb sunlight and uses it to drive the synthesis of organic compounds from CO2 and H2O
Chlorophyll: this is the pigment in the chloroplast of plants
Chlorophyll is directly involved in light reaction
It converts solar energy into chemical energy
Light reaction is a Redox reaction – the reverse of ATP production
C6H12O6 + 6O2 = 6CO2 + H2O + Energy
Two stages of photosynthesis
Light reaction converts solar energy to chemical energy
Electron and hydrogen are transferred from water to NADP
Oxygen is released in this process
ATP and NADP are produced in the light reaction
A phosphate group is added to ADP (phosphorylation )
No sugar is produced
Carbon fixation
This is the incorporation of carbon into organic compound
This is the beginning of the Calvin cycle
The fixed carbon is reduced by addition of electrons (energy from NDP)
Carbon dioxide is converted to carbohydrate using the ATP generated from the light cycle
Therefore, calvin cycle produces CHO in plants
No light is required (dark reaction
Light cycle: in the thylakoides of the chloroplast
Calvin cycle: in the stoma
Chapter 11 Cell communication
Cells must communicate in order to coordinate their activities in a way that enables the organisms to develop from a fertilizes egg and then survive and reproduce in turn
What is a target cell?
Cell signaling: a method of regulation in all living things
Signaling originating from another cell or from some changed in the organisms physical environment can be received by cells in various forms
Receptors
Cells respond to electromagnetic signals – light
Cells respond to mechanical signals – touch
Cells most often communicate with each other using chemical signals
A signal from cell is converted into specific cellular response in a step called signal transduction pathway
Cells communicate by releasing chemical messengers targeted for cells that may not be immediately adjacent
Intracellular communication
Neural communication
Neurotransmitter: transmits impulse along the nervous system (chemical signal) ex ACH
The impulse diffuse into the nerve cell and passed from one nerve fiber to another across the narrow synaptic cleft (gap)
What is a neurotransmitter, give example
Endocrine communication
Hormone or endocrine signaling
A specialized cell releases the hormone into the blood system which transport it to the target cells; ex. Insulin and the reproductive hormones (gonadotropic - LH, FSH (ICSH)
Paracrine communication :
The product of the cells diffuse into the extracellular fluid (ECF) to affect neighboring cells that may be some distance away
Autocrine communication :
Cells secret chemical messengers that bind to receptors on the same cell
In paracrine signaling, numerous cells can simultaneously receive a response to the molecules of growth factor produced by a single cell on their vicinity (growth factor)
Animal cells may communicate via direct contact between molecules on their surfaces
This is important in embryo development and operation of the immune system
Three stages of cell signaling
Receptor :
The target cell that detects the signal from outside the cell
A chemical signal is detected when it binds to a cellular protein
Molecule binding initiates the process of Transduction
Transduction : converts received signal to a form that can bring about a specific response
This may occur in a single step
Often requires a sequence of changes in a series of different molecules
Response: transduced signal triggers a specific cellular response
Ligand : a molecule that binds specifically to a receptor site of another molecule
***Ethylene*** this is a plant hormone (C2H4) that promote fruit ripening, a hydrocarbon with only six atoms