Eliminating Elective Early Term Deliveries at University Hospital
advertisement

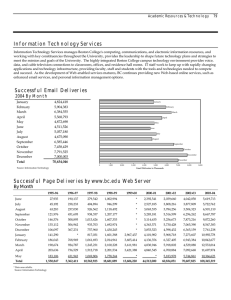
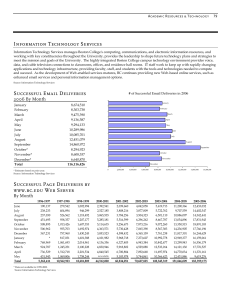
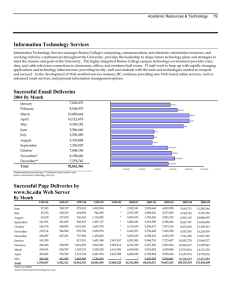
Eliminating Elective Early Term Deliveries at University Hospital Robyn Horsager M.D. Patricia Santiago-Munoz M.D. There was a sharp decline in deliveries occurring after 39 weeks with a concom se in births occurring particularly between 36-38 weeks gestation. ng Change in 1:Distribution of Birth byh Gestational Age: Figure Change in Dist ribut ion of Birt nge in Distribution of Birth by Gestational Age: United States, 1990-2006 by Gest at ional Age: States,1990-2006 Unit ed St at es, 1990-2006 United 37 and e in tant rise abor and 50 Percent of Change atically, from rise has been . 23 Data owed that uled of these weeks eriod 1990 17.5% of he distribuchanging ge over a 16 veries sharp een 36-38 25 0 -25 -50 <34 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 >42 Weeks of Gest at ion California Toolkit to Transform Maternity Care Source: CD C/N CH S, N ational V ital Statistics System. in deliveries between 37 and 39 weeks has been associated with an Netherlands: Timing of Elective Cesarean Deliveries 37 Weeks 38 Weeks 39 Weeks 40 Weeks Wilmink et al, Am J Obstet Gynecol, 2010 Increased Adverse Neonatal Outcomes at 370-386 Weeks of Gestation • • • • • • • Neonatal death NICU admission Newborn sepsis Respiratory distress syndrome Transient tachypnea of the newborn Treated hypoglycemia Hyperbilirubinemia Wilmink et al, Am J Obstet Gynecol , 2010 Tita et al, N Eng J Med, 2009 Neonatal Death Rates per 1000 Livebirths 0.7 0.6 0.66 0.5 0.4 0.42 0.3 0.33 0.34 0.2 0.1 0 37 Weeks 38 Weeks 39 Weeks 40 Weeks Zhang et al, J Pediatr, 2009 Percent Neonatal Complications: NICU Admission Rate 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 8.85 4.51 3.34 37 Weeks 38 Weeks 39 Weeks 3.62 40 Weeks Oshiro et al, Am J Obstet Gynecol, 2009 Neonatal Complications: Need for Ventilator 1.6 1.4 Percent 1.2 1.39 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.49 0.2 0.28 0.32 0 37 Weeks 38 Weeks 39 Weeks 40 Weeks Oshiro et al, Am J Obstet Gynecol, 2009 Netherlands: Adverse Neonatal Outcomes After Elective Cesarean Delivery 25 Percent 20 15 10 5 0 37 Weeks 38 Weeks 39 Weeks Wilmink et al, Am J Obstet Gynecol , 2010 Maternal Outcomes Associated with Labor Induction • Increased cesarean section rate for failure to progress in nulliparous women with unfavorable cervix • Increased cesarean section rate for fetal distress • Increased post-partum hemorrhage >500 mL • Prolonged maternal hospital stay Oshiro et al, Am J Obstet Gynecol, 2009 Baud et al, Am J Obstet Gynecol ,2011 Cognitive Development and Early Term Birth: Long-term Consequences Scotland: Increased risk for “special education need” Denmark: Increased reading and spelling difficulties at age 10 Belarus: Lower IQ test scores at age 6 United States: Lower standardized math and English/language arts scores in third grade University Hospital Obstetrical Service • 2010: 1440 deliveries – 897 by community physicians – 543 by UT Southwestern Medical Center employed physicians 12 Frequency of Births at 370- 386 Weeks 40 34.8 34.5 35 37.3 31.4 Percent of all deliveries 29.1 30 25 20 24.5 28.3 28.9 28.6 27.8 19.7 15 United States University Hospital 10 5 0 1990 2000 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 National Vital Statistics Report, 2010 % of Total Deliveries at 370386 weeks University Hospital Experience: Labor Induction Rate at 370-386 Weeks 40 35 34.6 30 25 20 25.6 27.9 28.6 29.1 21.5 15 10 5 0 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 (first half) Our Team Robyn Horsager MD* Chief OB/Gyn, University Hospital Patricia Santiago-Munoz MD* Maternal-Fetal Medicine Melissa Tarango RN Labor and Delivery Catherine VanBeek BSN, WHCNP Epic Analyst John Morris CS&E Facilitator * CS&E Course participant Aim Statement The aim of this project is to eliminate elective deliveries between 37 weeks 0 days and 38 weeks 6 days over the next 5 months. This project is important because delivery at this gestational age is associated with increased neonatal morbidity and healthcare costs and there is increasing public reporting of this measure by hospitals. 2009 Leapfrog Data: Dallas Area HOSPITAL ELECTIVE DELIVERIES AT 37-39 WEEKS Baylor 4.8% Medical City Dallas 29.8% Methodist Charlton 11.2% Methodist 5.3% Presbyterian Dallas 25% Doctors Hospital 13.5% Presbyterian Plano 4.7% Medical Center Plano 11.4% 17 CS&E Project Checklist Revise AIM statement (all) Write policy (RH &MT) Outside speaker with similar experience Speaker (RH) Room/breakfast (RH &PSM) CME (RH) CEU (MT) Create Clarity report (CV) Change scheduling log in L&D (MT) Mailing to physicians (RH&PSM) Find a “face” to the story (PSM) Obtain patient list Review charts Patient and nursing materials (all) Obtain Distribute Gather previous data (RH) 2005-2008 2009-2010 Create run chart (RH & PSM) Update OB/Gyn Best Practices Committee Policy Revision Scheduled induction of labor or cesarean delivery is not permitted before 39 weeks of gestation… Data Collection Communication Education Eliminating Elective Delivery < 39 Weeks Seton’s Experience Michael Nix , MD November 2, 2010 Our Results November 1, 2010- September 30, 2011 Elective Deliveries Between 37 and 39 Weeks of Gestation Elective Deliveries* Median UCL LCL 8 CS&E Project - Start Number of Deliveries 10 OB/Gyn Section Meeting 12 ACOG Practice Bulletin #107 Induction of Labor 14 6 4 2 0 * Jan 09 - Aug 09 data includes elective inductions only % total deliveries at 370-386 weeks University Hospital Experience: Elective Inductions* at 370-386 Weeks 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 30 13.5 7.4 2008 2009 2010 (first half) 2.4 11/2010-9/2011 * Project time period includes elective inductions and scheduled cesarean deliveries Decreased NICU Admissions with Intervention • Based on 2008 rate of elective delivery 4 fewer infants admitted to NICU • Based on 2009 rate of elective delivery 2-3 fewer infants admitted to NICU Dollars Cost per 100 Neonates for Treatment of Adverse Outcome 500,000 450,000 400,000 350,000 300,000 250,000 200,000 150,000 100,000 50,000 0 37 Weeks 38 Weeks 39 Weeks Robinson et al, Am J Obstet Gynecol, 2010 Potential Revenue Loss without Intervention • In 2009 there were 61 vaginal deliveries without medical necessity between 37-39 weeks • Would estimate approximately 30 scheduled repeat cesarean deliveries without medical necessity at same gestational age Professional Fees Hospital Stay • 61 vaginal deliveries @ $663 per patient= $40,443 • 30 cesarean sections @ $802 per patient= $24,060 • 61 vaginal deliveries @ $1742 per patient= $106,262 • 30 cesarean sections @ $2762 per patient= $82,860 Grand Total $253,625 Additional Savings • Reduced costs for other neonatal morbidities like treatment and readmission for hyperbilirubinemia • Reduced costs for maternal complications • What are costs for educational system long-term? What’s Next? • October 1, 2011 “hard stop” for scheduling cases with review by physicians • Determination of “medical necessity” for delivery before 39 weeks of gestation Thank you! References Baud D, Rouiller S, Hohlfeld P, Tolsa J et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2011;204:S328. Herson V, Feldman D, Borgida A, Fang YM et al. Full term NICU admission for respiratory morbidity: the role of gestational age. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2011;204:S85. Elimination of non-medically indicated (elective) deliveries before 39 weeks gestational age. A California Toolkit toTransform Maternity Care. Induction of labor. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 107. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Obstet Gynecol 2009;114:386-97. Kirkegaard MD, Obel C, Hedegaard M, et al. Gestational age and birth weight in relation to school performance of 10 year old children: a follow-up study of children born after 32 completed weeks. Pediatrics 2006; 118:1600-1606. Lipkind HS, Slopen ME, Pfeiffer MR, McVeigh KH. School-age outcomes of late preterm infants. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2011;204:S37. MacKay DF, Smith GCS, Dobbie R, et al. Gestational age at delivery and special educational need: retrospective cohort study of 407,503 schoolchildren. Plos Med 7 (6):e1000289. Martin JA, Hamilton BE, Sutton PD, Ventura SJ et al. Births: final data for 2008. National Vital Statistics Report 2010;59. References Oshiro BT, Henry E, Wilson J, Branch DW et al. Decreasing elective deliveries before 39 weeks of gestation in an integrated health care system. Obstet Gynecol 2009;113:804-811. Robinson CJ, Villers MS, Johnson DD, Sampson KN. Timing of elective repeat cesarean delivery at term and neonatal outcomes: a cost analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2010;202:632.e1-6. Tita A, Landon MB, Spong CY, Lai Y et al. Timing of Elective Repeat Cesarean Delivery at Term and Neonatal Outcomes. N Engl J Med 2009; 360:111-120. Wilmink FA, Chantal WP, Lunshof S, Mol BW et al. Neonatal outcome following elective cesarean section beyond 37 weeks of gestation: a 7-year retrospective analysis of a national registry. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2010;202:250.e1-8. Yang S, Platt RW, Kramer MS. Variation in Child Cognitive Ability by Week of Gestation Among Healthy Term Births. Am J Epidemiol 2010; 171:399-406. Zhang X, Kramer MS. Variation in mortality and morbidity by gestational age among infants born at term. J Pediatr 2009;154:358-362.