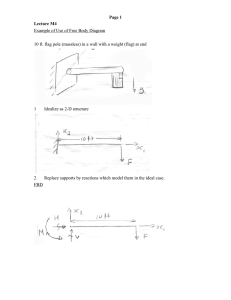
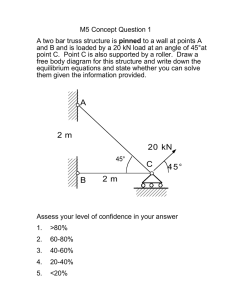
Old Lecture 22 sect ..
advertisement

ME 221 Statics Lecture #22 Sections 5.1 – 5.4 ME 221 Lecture 22 1 Homework #8 • Chapter 9 problems: – 42, 43, 50 & 55 • Chapter 5 problems: – 11, 13, 16, 20, 24 & 25 – See Blackboard for additional information • Due Wednesday, October 30 ME 221 Lecture 22 2 Quiz #5 • Friday, March 14 ME 221 Lecture 22 3 Chapter 5 Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies ME 221 Lecture 22 4 Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies • Equilibrium equations • Free body diagrams • Modeling supports • Problems ME 221 Lecture 22 5 Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies •Newton’s Second law states that if there is a net force acting on the body, then this will cause motion of the rigid body. •If there is no motion, then the object is said to be in equilibrium. ME 221 Lecture 22 6 Equilibrium Equations When the force system is replaced by a resultant force and moment that are zero, the rigid body is in equilibrium. F 0 ~ and M 0 ~ The moment equation is new and differentiates particle from rigid body equilibrium. F F F ME 221 x 0 y 0 z 0 M M M Lecture 22 x 0 y 0 z 0 7 Supports for Rigid Bodies If a rigid object is subjected to some set of forces but does not move, then its motion could be restrained by a normal force exerted by the ground, a wall or from fixing the object with some support. Examples of supports: • rollers • cables • smooth surfaces • links • rockers • fixed ME 221 Lecture 22 • clamps • slots • collars 8 Support Reactions • If the support prevents translation in a given direction, then a force is developed on the member in that direction. Likewise, if a rotation is prevented, then a couple moment is exerted on the member. • See Figures 5.1 and 5.2 (supports for rigid bodies subjected to 2-D and 3-D force systems) ME 221 Lecture 22 9 Free Body Diagram • Draw the body separate from all other bodies (including ground). • Draw the magnitudes and directions of all external forces acting on the body. – Include: applied loads, reactions due to supports, and the weight of the object. – No need to scale arrow size • Include necessary dimensions of the body – Dimensions are needed for summing moments • Draw the positive sense of the coordinate system used to write out equilibrium equations ME 221 Lecture 22 10 Importance of FBD • The FBD is at least half of an equilibrium problem. ME 221 Lecture 22 11 Chapter 5 Equilibrium Examples ME 221 Lecture 22 12