Lecture 21 sect 5.1.ppt
advertisement

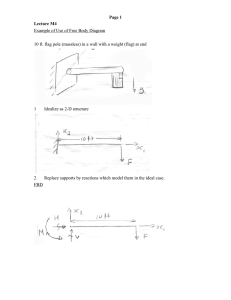
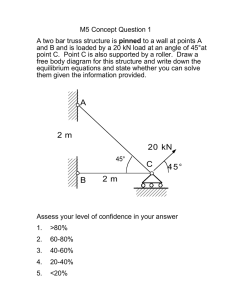
ME 221 Statics Lecture #21 Sections 5.1 – 5.4 ME 221 Lecture 21 1 Homework #8 • Chapter 9 problems: – 42, 43, 50 & 55 • Chapter 5 problems: – 11, 13, 16, 20, 24 & 25 – See Angel for additional information • Due Friday, October 24 ME 221 Lecture 21 2 Quiz #5 Friday, October 24 ME 221 Lecture 21 3 Note: No office hours on Tuesday, October 21 ME 221 Lecture 21 4 Chapter 5 Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies ME 221 Lecture 21 5 Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies • Equilibrium equations • Free body diagrams • Modeling supports • Example ME 221 Lecture 21 6 Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies • Newton’s Second law states that if there is a net force acting on a body, then this will cause motion of the rigid body. • If there is no motion, then the object is said to be in equilibrium. ME 221 Lecture 21 7 Equilibrium Equations When the force system is replaced by a resultant force and moment that are zero, the rigid body is in equilibrium. F 0 ~ and M 0 ~ The moment equation is new and differentiates particle from rigid body equilibrium. F F F ME 221 x 0 y 0 z 0 M M M Lecture 21 x 0 y 0 z 0 8 Supports for Rigid Bodies If a rigid object is subjected to some set of forces but does not move, then its motion could be restrained by a normal force exerted by the ground, a wall or from fixing the object with some support. Examples of supports: • rollers • cables • smooth surfaces • links • rockers • fixed ME 221 Lecture 21 • clamps • slots • collars 9 Support Reactions • If the support prevents translation in a given direction, then a force is developed on the member in that direction. Likewise, if a rotation is prevented, then a couple moment is exerted on the member. • See Figures 5.3, 5.9 and 5.10 (supports for rigid bodies subjected to 2-D and 3-D force systems) ME 221 Lecture 21 10 Free Body Diagram • Draw the body separate from all other bodies (including ground). • Draw the magnitudes and directions of all external forces acting on the body. – Include: applied loads, reactions due to supports, and the weight of the object. – No need to scale arrow size • Include necessary dimensions of the body – Dimensions are needed for summing moments • Draw the positive sense of the coordinate system used to write out equilibrium equations ME 221 Lecture 21 11 Importance of FBD • The FBD is at least half of an equilibrium problem. ME 221 Lecture 21 12 Chapter 5 Equilibrium Examples ME 221 Lecture 21 13