C18: Jovian Planets

Jovian Planets & Dwarf Planets
(Chapter 18)
Student Learning Objectives
•
Identify & describe each
Jovian planet
•
Compare and contrast the
Jovian planets
•
Characterize Pluto
Pluto & Charon
What are the basic qualities of Jovian planets?
Jovian planets are often called gas or ice giants.
Contain mostly low density materials
No solid surface
Several moons
Ring systems
Hydrogen rich atmospheres
Practice
What is the most likely method for Jovian planets to have acquired atmosphere? Explain.
a. Outgassing b. Volcanism c. Comets d. Capture
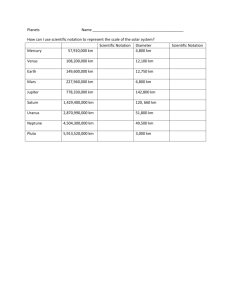
How are Jupiter and Saturn similar?
Deep layers contain liquid and metallic hydrogen
Alternating bands of belts and zones in atmosphere
Strong magnetic fields
Jupiter 20,000x Earth's
Saturn 8,000x Earth's
Jupiter
Rotation
Rotation Periods average 10 h
Non-solid objects have different rotation speeds at different latitudes.
Differential Rotation
Fluid Spinning Fast Oblate
The smaller the core, the more oblate the shape
Jupiter & Saturn
Jupiter Saturn
The Galilean Moons
•
Io (P = 1.769 days)
•
Europa (P = 3.551 days)
•
Ganymede (P = 7.154 days)
•
Callisto (P = 16.689 days)
The Great Red Spot on Jupiter is the longest lived weather disturbance in the solar system.
The Red Spot is Shrinking
May 15, 2014 NASA
Jupiter’s
Ring
Practice
1) Who was the first person to “see” the
Galilean moons? Why was observing these moons important?
2) Why is it difficult to observe Jupiter’s ring?
Saturn’s Rings
Saturn's ring system is divided into 7 major systems.
Each major system is comprised of several ringlets.
Saturn’s Moon Titan
Saturn's largest moon,
Titan , has an atmosphere and liquid methane lakes.
Practice
1) How did Saturn get it’s rings?
2) Why would scientists want to explore methane lakes on Titan?
How are Uranus and Neptune similar?
Uranus and Neptune both have methane rich atmospheres.
Uranus looks green-blue
Neptune looks very blue
Uranus & Neptune
Uranus
Neptune
Uranus and Neptune both have ring systems.
Uranus’s
Rings
Neptune’s
Rings
Uranus rotates on its side (90º Tilt), resulting in the most extreme seasons in our solar system.
Neptune’s Spot
Neptune has the strongest winds
(1,200 mph) ever recorded on any planet.
The Great Dark Spot on Neptune
Disappeared in 1994
APOD
May 8, 1996
Practice
1) Why do you think Neptune is more blue than
Uranus?
2) Write a general statement discussing how
Uranus and Neptune compare and contrast with Jupiter and Saturn.
What about Pluto?
Pluto is unlike either
Terrestrial or Jovian planets.
Orbit is inclined by 17º
Orbit is elliptical (e = 0.25)
Composition similar to comet
Pluto is characterized as a dwarf planet.
Pluto before New Horizons
Image Credit: NASA
Definition of a Planet
(2006, International Astronomical Union)
1. Is in orbit around the Sun
2. Has sufficient mass to assume a nearly round shape
3. Is not a satellite (moon)
4. Has cleared the neighborhood around its orbit
Dwarf Planets
Dwarf planets are defined as objects that are similar to planets but do not meet all planet criteria.
Ceres
Pluto
Eris
Practice
1) What criterion is Pluto missing to be classified as a planet?
2) How many moons does Pluto have?
Hubble Finds 'Tenth Planet' Slightly Larger
Than Pluto
04.11.06 NASA
Pluto’s Moons
NASA
Space.com