ISLO PRESENTATION_2-23-16.pptx
advertisement

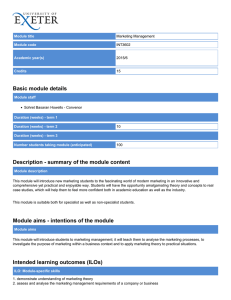
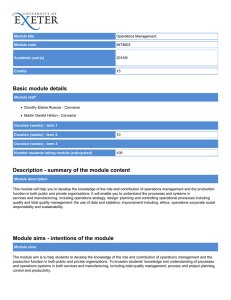
STRIVING FOR INSTRUCTIONAL AND INSTITUTIONAL EXCELLENCE What are ILOs? • Institutional Learning Outcomes encompass the whole student experience and include those things students should know, value, and be able to do upon completion of a degree, and perhaps even a certificate. • Importantly, they are meant to be achieved by the whole of a student's experience at College of the Canyons, not merely by completing coursework. Adapted from University of Hawaii, Manoa https://manoa.hawaii.edu/ovcaa/ilo/ Proposed Institution Learning Outcomes Institutional Degree, Certificate, Program Course Outcomes 1. Effective Communication 2. Critical Thinking 3. Collaboration 4. Information Literacy 5. Quantitative Literacy 6. Community Engagement & Global Responsibility 7. Creative & Innovative Thinking Overview of ILO Development ILOs Opening Day 14 ILOs Based on AA/AS + CTE + Basic Skills 2008 ILO Report & FLEX Feedback 2014-2015 2011-2012 2010 Development of Institutional Learning Outcomes (ILOs) Based on IGETC/CSUGE 2012-2013 ILO Assessment Move towards Adopting (or Adapting) AAC&U’s LEAP Outcomes 4 WHY Institution Student Learning Outcomes? • Working with a set of institutional learning objectives is an opportunity for the campus as a whole to understand student learning at the institutional level -- the comprehensive view of what students learn and what they should know upon leaving College of the Canyons. WHY Institution Student Learning Outcomes? • ILOs can provide a space within which the campus can think collectively about what we believe ought to be learned while at COC. • It can help frame the future directions in which we would like to see education move. • Faculty can use the ILOs as a guide to inform student learning activities and make the learning outcomes for COC students more visible and clear. It Takes More than a Major: Employer Priorities for College Learning and Student Success: Overview and Key Findings A 2013 National Survey of Business and Non Profit Leaders Methodology From January 9 to 13, 2013, Hart Research Associates conducted an online survey among 318 employers whose organizations have at least 25 employees and report that 25% or more of their new hires hold either an associate degree from a two-year college or a bachelor’s degree from a four-year college. Respondents are executives at private sector and nonprofit organizations, including owners, CEOs, presidents, C-suite level executives, and vice presidents. https://www.aacu.org/leap/presidentstrust/compact/2013SurveySummary “A collaboration between educators, students, policymakers, and business and community leaders.” Launched in 2005 Goal: Raise Quality of Education • Large-scale collaboration • Transformational change California State University system (2011) • Educational alignment • 12 LEAP States https://www.aacu.org/sites/default/files/files/LEAP/Introduction_to_LEAP.pdf The LEAP Initiative Promotes • Essential Learning Outcomes A Guiding Vision and National Benchmarks for College Learning and Liberal Education in the 21st Century • High Impact Practices Helping Students Achieve the Essential Learning Outcomes • Authentic Assessments of Student Learning Probing Whether Students Can APPLY Their Learning – to Complex Problems and Real-World Challenges • Seven Principles of Excellence, including Inclusiveness Diversity, Equity, Quality of Learning for All Groups of Students Essential Learning Outcomes Knowledge of Human Cultures and the Physical and Natural World Focused on engagement with big questions, enduring and contemporary Intellectual and Practical Skills Practiced extensively across the curriculum, in the context of progressively more challenging problems, projects, and standards for performance Personal and Social Responsibility Anchored through active involvement with diverse communities and real-world challenges Integrative and Applied Learning Demonstrated through the application of knowledge, skills, and responsibilities to new settings and complex problems COC Mission As an innovative institution of excellence, College of the Canyons offers an accessible, enriching education that provides students with essential academic skills and prepares students for transfer education, workforce-skills development, and the attainment of learning outcomes corresponding to their educational goals. To fulfill its mission, College of the Canyons embraces diversity, fosters technical competencies, supports the development of global responsibility, and engages students and the community in scholarly inquiry, creative partnerships, and the application of knowledge. According to ACCJC (Accreditor): “The Accreditation Standards expect institutions to focus on the learning of all students it serves. Institutions set goals and outcomes, including for student learning and student achievement, which can be tracked and evaluated to determine how the institution is meeting its mission.….” “The ILOs are, in essence, the institution’s promise to the community of the impact that the institution will have on individuals who come to the institution.” http://www.accjc.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/Standard_II_Q_and_A_July_2_2015.pdf • “These are the outcomes which other units of the institution (Student Services, ASG, TLC, etc.) also participate in and may report on in program reviews.” • “These stated ILOs tend to include the outcomes in Standard II.A.11, which apply to all programs. Institutions may include one or two additional areas in their ILOs.” • “The key is that these ILOs are articulated at a foundational level and then may be articulated at a higher level of competency as appropriate to completers of programs (shorter and longer certificates, 2-year degrees, and so forth).” http://www.accjc.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/Standard_II_Q_and_A_July_2_2015.pdf 1. Palomar College Four General Education/Institutional Learning Outcomes (based directly on the AAC&U Essential Learning Outcomes) Chaffey College Four Core Competencies Pasadena College Five General Education Outcomes Knowledge of Human Cultures and the Physical and Natural World 2. Intellectual and Practical Skills 3. Personal and Social Responsibility 4. Integrative and Applied Learning 1. Communication 2. Critical Thinking and Information Competency 3. Community/Global Awareness and Responsibility 4. Personal, Academic, and Career Development 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Communication Cognition Information Competency Social Responsibility Personal Development Salt Lake Community College Institutional Learning Outcomes 1. 2. 3. Students communicate effectively. Students develop quantitative literacies necessary for their chosen field of study. Students think critically and creatively. 4. Students develop the knowledge and skills to community engaged learners and scholars. 5. Students develop the knowledge and skills to work with others in a professional and constructive manner. 6. Students develop computer and information literacy. 7. Students develop the attitudes and skills for lifelong wellness. ACCJC Accreditation Standards (2014) II.A. 11. The institution includes in all of its programs, student learning outcomes, appropriate to the program level, in … • communication competency, • information competency, • quantitative competency, • analytic inquiry skills, • ethical reasoning, • the ability to engage diverse perspectives, • and other program-specific learning outcomes. http://www.accjc.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/07/Accreditation_Standards_Adopted_June_2014.pdf Outcomes Build Upon Each Other Proposed ILOs Institutional Degree, Certificate, Program Course Outcomes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Effective Communication Critical Thinking Collaboration Information Literacy Quantitative Literacy Community Engagement & Global Responsibility 7. Creative & Innovative Thinking 8. Lifelong Learning ILO Development Process • College-wide Collaboration – – – – – – – CASL, SENATE (since 2014) Faculty, Staff, Student, Administrators Committee work Surveys (Spring 15/Fall 16) Workshops (10+ including Opening Day 2015) CPT (Twice) ASG COC ILO Survey (Fall 15) Responses to the Fall 2015 ILO Survey Overall Adjunct Faculty Full-Time Faculty College Planning Team Division Deans Learning Resources Student Services Associated Student Government Responses Invited to Participate Response Rate 166 74 60 923 661 191 18% 11% 31% 11 9 32 14 34% 64% 5 4 6 6 83% 67% 3 13 23% Satisfaction with the Proposed ILOs Satisfied/ Very Satisfied Overall Adjunct Faculty Full-Time Faculty College Planning Team Division Deans Learning Resources Student Services Associated Student Government Dissatisfied/ Very Dissatisfied Neutral % 66% 77% 53% n 63 24 24 % 32% 23% 44% n 31 7 20 % 2% 0% 2% n 2 0 1 -- 6 -- 1 -- 1 -- 4 -- 2 -- 0 -- 2 -- 0 -- 0 -- 2 -- 0 -- 0 -- 1 -- 1 -- 0 Overall, two-thirds of the respondents are “satisfied” or “very satisfied” with the proposed ILOs. Please indicate your level of agreement that the proposed ILOs reflect College of the Canyons. Level of Agreement that the Proposed ILOs reflect College of the Canyons Disagree/ Agree/ Neutral Strongly Strongly Agree Disagree % n % n % n 75% 110 16% 23 9% 13 Adjunct Faculty 77% 49 16% 10 8% 5 Full-Time Faculty College Planning Team Division Deans 74% 40 19% 10 7% 4 -- 8 -- 0 -- 1 -- 5 -- 1 -- 2 Learning Resources -- 4 -- 1 -- 0 Student Services Associated Student Government -- 3 -- 0 -- 0 -- 1 -- 1 -- 1 Overall Summary • Overall, the majority of respondents “agree” or “strongly agree” that the proposed ILOs reflect College of the Canyons. • Less than 10 percent of respondents indicated that they “disagree” or “strongly disagree” that the proposed ILOs reflect College of the Canyons. Ranking (Fall 16 Survey) ILO #1 Critical Thinking - Students demonstrate the ability to think critically and analytically. Effective Communication- Students communicate effectively. ILO#3 Collaboration - Students develop the knowledge and skills to work with others in a professional and constructive manner. ILO#2 ILO#4 Creative & Innovative Thinking - Students think creatively and innovatively. Information Literacy - Students develop information literacy. ILO#5 Quantitative Literacy - Students develop quantitative literacies necessary for their chosen field of study. ILO#6 Community Engagement & Global Responsibility - Students develop the knowledge and skills to actively engage in the local, national and global community. ILO#8 Lifelong Learning - Students develop the knowledge and skills to be lifelong learners. ILO#7 What’s Next? • Senate Adoption/CPT Endorsement • More workshops/Days of Assessment – – – – Refining of ILOs Identifying Competencies for each area Rubric development for each ILO Collection and scoring of Signature Assignments mapped to each ILO – Expansion of use of ePortfolio • ISLO Workplan/”Business Plan” – Promotion – Implementation using courselevel assignments (Signature) https://manoa.hawaii.edu/ovcaa/ilo/ Signature Assignments What Are Signature Assignments? • An assignment that best displays the knowledge or skills essential to the learning outcomes of a course. Other coursework should build toward the completion of the course 'signature' assignment. • Signature assignments have the potential to help us know whether student learning reflects “the ways of thinking and doing of disciplinary experts.” • A generic task, problem, case, or project that can be tailored or contextualized in different disciplines or course contexts (can be collaboratively designed). Examples of Signature Assignments Salt Lake Community College (SLCC) • Political science class: students analyze campaign finance data and write papers about recent elections in Utah. • Quantitative reasoning class: students analyze arguments they’ve found on TV or the Internet for logical fallacies, making diagrams to help map the process. Characteristics of Signature Assignments • Course-embedded assessment • Well aligned with Learning Outcomes • Authentic in terms of process/content, “real world” application • Include student reflection component • Designed individually or collaboratively by faculty – Can follow a theme across curricular and cocurricular experiences Why Signature Assignments Rock! • They make learning more visible, both for students and instructors. • They encourage student ownership of course and program work. • They enhance student learning and foster an attitude of life-long learning. Why Signature Assignments Rock! • They chronicle the learning process and offer artifacts of rich qualitative data that help instructors measure their own effectiveness through more authentic assessment. • They can be easily developed from existing assignments, especially ones that already possess some characteristics of Signature Assignments. ePortfolios • An electronic platform where students can complete assignments using multi-media • An account on a platform (Digication or Pathbrite) • A tool to highlight student success • An excellent way for students to track their own progress Why ePortfolios? Student Centered (Batson) – Students are stewards of their own learning – They own the space, it is their information, and they control who can view it – “As the transcript and the diploma lose credibility with employers, the eportfolio gains credibility. It is a fuller and more palpable picture of what learners can do.” Why ePortfolios? Faculty Benefit – Diversity – Students becoming more creative – Deeper critical thinking – Creates a stronger connection between the students and the world around them How can you implement ePortfolios in your courses? • ePortfolios are a tool, but they must be used appropriately in order to be effective • Application in the classroom: – Class discussions – Grading – Class participation – Artifacts – Assignments Is a course redesign required? • This is up to you, it can happen on a large scale or a small scale • You can redesign your entire course or you can require students use the ePortfolio platform for a single assignment or project • Assign credit: 5% of grade? 30% of grade? The Future The Institutional Aspect of ePortfolios – We are excited about the implications this has for our student’s growth within our classes and throughout their experience at our college – This is an excellent tool for assessment – Signature Assignments: • The importance for each course and the importance on an institutional level