study guide exam 1.doc
advertisement

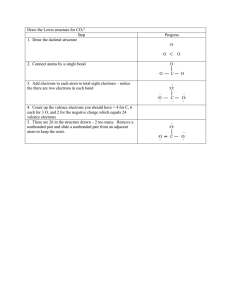
Exam #1 Objectives Remember this review is meant to serve as a guide and only a guide to ensure your notes are complete. You will need to be able to DO, show evidence of understanding and READ YOUR BOOK! Simply filling out this review sheet will not suffice to earn a good grade. • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Define “biology” Characteristics of living organisms Central Dogma Differences between Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Structure of atoms, three subatomic particles and their charges Nnumber of protons, and electrons of an element if given a periodic table of elements Define: ion, cation, anion What is the Importance of the electron Arrangement of electrons: Electron dot diagrams Bonds: ionic, covalent, polar covalent bonds and Hydrogen bonds Water, its structure (including its partial charges), its characteristics that make it so important to biological organisms Acids and bases pH and the concentration of hydrogen ions Organic molecules Macromolecules Structure and Functions of • carbohydrates • lipids • proteins • nucleic acids Dehydration synthesis Saturated, unsaturated and polyunsaturated structure/ function of nucleotides • difference between DNA and RNA • nucleotides in DNA, RNA or both--be able to recognize the structure • be able to give a complimentary sequence if given the sequence of one strand of DNA/RNA • organization of DNA (eukaryote vs. prokaryote) • • • • steps of transcription post-transcriptional modifications translation and protein structure Proteins functions and structure • structural levels of proteins • R group and protein folding Steps of translation Be able to use table 4.1 to generate a protein if given an mRNA sequence or DNA double strand. Four levels of protein folding Amino acid structure and peptide bonding Role of tRNA & Amino acyl tRNA synthase • • • • • Sample Practice problems: 1. Using your periodic table determine the numbers of each subatomic particle for Oxygen. Draw the electron dot diagram, which shell is the valence shell? How many valence electrons are there? What is the valence for Oxygen? What type of bond does oxygen make? Why? 2. If an atom has 7 valence electrons, what type of bond will it make? WHY? 3. If an atom has a valence of 5, what type of bond does it make? 4. If an atom has 17 electrons, 17 protons and 18 neutrons… what is its atomic mass? 5. Draw two molecules of water, indicating the type of bond that holds ONE water molecule together and the type of bond that holds MULTIPLE water molecules together by cohesion. 6. If [H+]= 10 -8, What is the PH? Is this acidic or basic? 7. If two solutions have a pH= 6 and ph =4. What is the difference in the hydrogen ion concentrations between the two solutions? 8. On the double stranded DNA helix below indicate where the promoter and termination sequences are in relation to the gene. Gene 9. If the DNA sequence is 5 ‘ ATCGTTACCGATTA 3” What is the complimentary strand of DNA? What is the sequence of the RNA strand that could be generated? Which was your template strand? Practice practice practice… self test… make sure you know ALL your notes !