Lecture - Political Geography
advertisement

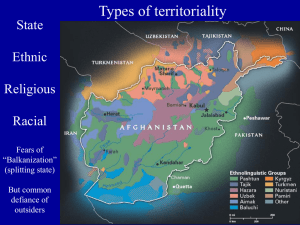
POLITICAL GEOGRAPHY Interaction of politics and place • A subfield within the human branch of geography. • The study of the interaction of geographical area and political process. • It is the formal study of territoriality. U.S.Canada boundary AlbertaMontana U.S.Mexico boundary Calexico, CaliforniaMexicali, Mexico Politics of Geography Effect of place on politics and effect of politics on place Example: Making political boundaries Politics on place Place on politics Political Geography • Economics supposedly eroding significance of national borders. • However, many ethnic minorities feel they deserve states of their own. • States under attack from above (global economics) and from below (ethnic communities). • Yet states are still powerful, and can respond. STATE • A politically organized territory • Administered by a sovereign government • Recognized by a significant portion of the international community. A state must also contain: – a permanent resident population – an organized economy NATION - STATE • A country whose population possesses a substantial degree of cultural homogeneity and unity. • Stems from European Renaissance idea (Rousseau) of the “social contract” as highest moral order. • Imposed on much of the world by the West. Classic Example of a Nation-State: Japan Multi-ethnic States Every U.S. citizen = American nationality Every American = belongs to a “race” (though this has no scientific meaning) Some Americans = identified with ethnicity Geographic Characteristics of States • SIZE – What role does size play in the economy of a state? In government services? In nationalism and patriotism? – Does shape have any effect? – What are the most powerful nations on earth today? – What were the most powerful nations on earth 200 years ago? Geographic Characteristics of States Shape • • Compact - smaller states, especially if they are simply shaped. Prorupt are nearly compact but possess one or sometimes two narrow extensions of territory. • • • Elongated – thin, narrow, long shapes. Fragmented – islands or other fragments. Perforated – “holes” cut into the state. On the next slide, match the term to the State. Shape • • • • • Compact Prorupt Elongated Fragmented Perforated African colonies Decolonization, 1940s-1990s Types of territoriality State Ethnic Religious Racial Fears of “Balkanization” (splitting state) But common defiance of outsiders Kurds – “Nation Without a State” Ethnic group in Turkey, Iraq, Iran, Syria. Many Kurds want to create a state of “Kurdistan” States pit Kurds against each other. Iraq Ethnic: Arabs vs. Kurds Religion: Sunnis vs. Shi’as Rulers were Sunni Arab Armenia-Azerbaijan War, 1988-94 ARMENIA (Christian) vs. AZERBAIJAN (Shi’a Muslim) Yet Shi’a Iran stayed neutral, fearing ethnic Azeris in NW Iran (Ethnic territoriality won) Armenian (above) and Azeri views Kashmir conflict KASHMIR (CHINA) PAKISTAN CHINA INDIA INDIA (Hindu) vs. PAKISTAN (Muslim) British India partitioned into two states, 1948. Kashmir had Muslim majority but Hindu ruler. Indian and Pakistani propaganda maps Wars split Kashmir between India, Pakistan, and China (all now have nukes) GEOPOLITICS - State’s power to control territory, shape international policy and other states’ foreign policy. Cold War propaganda map: “Red menace” Growth of Russian Empire Enlargement of Soviet bloc after World War II Berlin Wall, 1961-89 NATO and Warsaw Pact, 1945-89 View of Communist “Red Bloc” during Cold War Lumping failed to recognize differences among Communists, or local causes of conflict Terrorism, Al-Qaeda, and “The Axis of Evil” • President G.W. Bush used this phrase in 2002 to describe Iraq, Iran, and North Korea (formerly called “rogue states”) to suggest that post 9-11 geopolitics is best understood as capitalist democracies versus dictatorships and the terrorists they sponsor. • PBS NewsHour discussion of the speech. How Many Americans View the World Cartoon: Bush’s View of the World? Problem: some former allies later seen as “evil” United Nations Member States (191) Switzerland 2002 European Union Began as European Economic Community (EEC), 1957. Stronger in 1994 10 new members joined, 2004 Turkey, Greece, Romania, Bulgaria want to join. Levels of administrative regions ELECTORAL GEOGRAPHY Political Geography of Elections Variation of voting districts and voting patterns U.S. congressional delegation redistricting Reapportionment : allocating seats to a geographic area (after every census) “Gerrymandering” Redistricting for partisan purposes 1860 Presidential Vote Led to Southern secession, Civil War 1996 Presidential Vote Congressional reapportionment 2004 Presidential Vote 2004 Presidential Vote 2004 Presidential Vote Davis (D) Simon (R) Camejo (G) Copeland (L) 48% 42% 5% 2% I 205 229 1