Metric System Guide: Anatomy & Physiology
advertisement

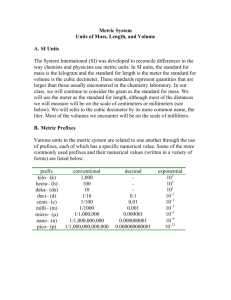
Anatomy & Physiology 34A The Metric System The metric system is a measurement method based on units of 10, rather than the arbitrary units of English measurements. The following is an introduction to the metric system. I. Basic Units of the Metric System A. Mass (weight) units are grams (g); 453.6 g = 1 lb. B. Volume units are liters (L); 1 L = 1.057 qt. C. Length units are meters (m); 1 m = 39.37 in. D. Temperature units are in degrees Celcius (°C); °C = 5/9 x (°F-32) E. Energy units are calories (c); one calorie is the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of one gram of water by 1 °C. One food Calorie (C) is actually a kilocalorie. II. Units of 10 A Prefixes for units greater than 1 base unit: 1. Mega (M) = 1,000,000 times the base unit (106) 2. Kilo (K) = 1,000 times the base unit (103) B. Prefixes for units less than 1 base unit: 1. Deci (d) = 1/10th of the base unit (10-1) 2. Centi (c) = 1/100th of the base unit (10-2) 3. Milli (m) = 1/1000th of the base unit (10-3) 4. Micro (µ)= 1/1,000,000th of the base unit (10-6) 5. Nano (n) = 1/1,000,000,000th of the base unit (10-9) C. Commonly used length measurement abbreviations 1. Kilometer = km (1 km = 0.62 mi., a little more than half a mile) 2. Meter = m (a little more than a yard stick) 2. Centimeter = cm (1 in. = 2.54 cm) 3. Millimeter = mm (about the width of a thin pencil line) 4. Micrometer = m (often used to measure microscopic cells) 5. Nanometer = nm (often used to measure light waves and subcellular objects) D. Commonly used mass (weight) abbreviations 1. Kilogram = kg (1 kg = 2.2 lbs); often used for a person’s weight 2. Gram = g (about the weight of two aspirins) 3. Milligram = mg (often used for solid medication measurements) 4. Microgram = µg (also used to measure doses of solid medications) E. Commonly used volume abbreviations 1. Liter = L (slightly more than a quart) 2. Deciliter = dl (100 ml) 3. Milliliter = ml (often used to measure doses of liquid medications; 1 ml = 1 cm3 = 1 cc) 4. Microliters = µl 2 III. Converting from one measurement unit to another A. Steps for conversions 1. Establish conversion units (e.g., 1 m = 100 cm = 1,000 mm = 1,000,000 um) 2. Set up equation to solve for the desired unit B. Examples of conversions 1. Convert 0.5 centimeter into millimeters. 0.5 cm x 1,000 mm = 5 mm 100 cm 2. Convert 2 inches into millimeters. 2 in. x 2.54 cm x 1,000 mm = 50.8 mm 1 in. 100 cm 3. Convert 500 ml to liters. 500 ml x 1 L__ = 5/10 L = ½ L = 0.5 L 1000 ml 4. Convert 1 ounce to grams (16 oz = 1 lb) 1 oz x 1 lb_ x 453.6 g = 28.35 g 16 oz 1 lb. 5. Convert 98.6 °F to degrees Celsius. °C = 5/9 x (98.6 °F – 32 °F) = 37 °C C. Additional Problems – practice by solving problems 1-19 on pp. xv-xix in the lab manual.