The Structure of DNA and Protein Synthesis
advertisement

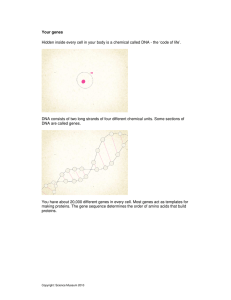
DNA and Protein Synthesis Nucleotide The Structure of DNA DNA’s Four Bases: Adenine Thymine Cytosine Guanine The Base Pairing Principle • Because of the number of hydrogen bonds between them (2 & 3), it is only possible for thymine to pair with adenine, and guanine with cytosine. Protein Synthesis • The DNA code serves as a blueprint for making specific proteins. • Examples of proteins: hormones, enzymes, neurotransmitters, receptors, components of tissue. • Proteins are composed of amino acids. • Codons are a sequence of three bases that code for a specific amino acid. Transcription Messenger RNA can leave the nucleus via a nuclear pore. Translation Transfer RNA Proteins and Genes • The tissues that constitute your body are complexes of proteins. For instance, skin is composed of the proteins collagen, keratin, and elastin. Since a number genes are involved in making this tissue, we say that the trait is polygenic. • Elastin is found in many of the bodies’ tissues. If something happens to this gene, the effects will be observed in all tissues where this protein occurs. The effect will be pleiotropic. Example: William’s syndrome is a disorder caused by the deletion of 26 genes from chromosome 7. Among the genes deleted is the ELN gene for making elastin. The result is both connective tissue and cardiovascular problems.