Chapter 9 Section 3 Notes
advertisement

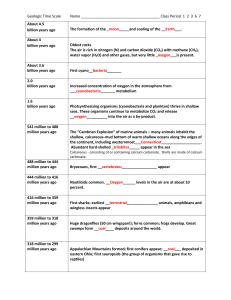
CHAPTER 9 A VIEW OF EARTH’S PAST III. THE MESOZOIC AND CENOZOIC ERAS - 90% of marine and 70% of land organisms died at the end of the Permian Period - mass extinction – an episode during which large numbers of species extinct - an abundance of new life forms appeared A. The Mesozoic Era 1. began 251 million years ago and ended 65 million years ago 2. “Age of Reptiles” 3. Sierra Nevada in California and the Andes in South America formed 4. conditions favored the survival of reptiles 5. The Triassic Period a. dinosaurs appeared b. dinosaurs ranged in size from squirrels to as large as 15 tons 30m long c. ammonites, a marine invertebrate, serve as an index fossil d. first mammals appeared 6. The Jurassic Period a. dinosaurs where dominant life form b. two major groups 1b. saurischians aa. “lizard-hipped” bb. contained herbivores and carnivores 1bb. Apatosaurs aaa. herbivore bbb. known as Brontosaurs ccc. weighed 50 tons and grew 25m long 2b. ornithischians aa. “bird-hipped” bb. stegosaurus 1bb. 9m long and 3m tall c. fossils of earliest birds appeared 7. the Cretaceous Period a. dinosaurs continued to dominate Earth b. Tyrannosaurus rex stood 6m tall and was 15m long c. earliest flowering plants (angiosperms) appeared 1c. magnolias 2c. willows 3c. maples 4c. oaks 5c. walnuts 8. The Cretaceous-Tertiary Mass Extinction a. the Cretaceous period ended with a mass extinction b. dinosaur fossils have never been found in rocks formed after Cretaceous period c. two beliefs to the mass extinction 1c. movement of continents and increased volcanic activity 2c. impact hypothesis aa. 65 million years ago a meteorite crashed into Earth bb. raised enough dust to block out sun’s rays cc. Earth’s climate became colder and plant and animal life began to die dd. dust formed a layer of iridium-laden rock 1dd. iridium is uncommon in rock on Earth 2dd. iridium is common in meteorites B. The Cenozoic Era 1. started 65 million years ago and includes the present period 2. continents moved to their current position 3. the Alps and Himalayas formed by the collisions of the plates 4. known as the Age of Mammals because mammals became the dominant life form 5. The Quaternary and Tertiary Periods a. the two periods of the Cenozoic Era b. Tertiary Period 1b. 65.5 million years to 1.8 million years ago 2b. includes time before the last ice age 3b. contains the Paleocene, Eocene, Oligocene, Miocene and Pliocene Epochs c. Quaternary Period 1c. 1.8 million years ago to present 2c. began with the last ice age and includes the present 3c. contains the Pleistocene and Holocene Epochs 6. The Paleocene and Eocene Epochs a. many new mammals evolved b. first primates evolved c. worldwide temperatures dropped by about 4°C at the end of the Eocene Epoch 7. The Oligocene and Miocene Epoch a. the Indian subcontinent began to collide with the Eurasian continent causing the uplifting of the Himalayas b. climate became significantly cooler and drier c. grasses, cone bearing trees and hardwood trees flourished d. many early mammals became extinct e. modern Antarctic icecap began to form f. largest known land mammals existed 8. The Pliocene Epoch a. predators evolved into modern forms 1a. bear 2a. dog 3a. cat b. herbivores flourished c. toward the end, continental ice sheets began to spread 9. The Pleistocene Epoch a. began 1.8 million years ago b. fossils of earliest modern humans were discovered c. ice sheets advanced and retreated several times 10. the Holocene Epoch a. began about 11 500 years ago and includes the present b. ice sheets melted, sea levels rose about 140m and coastlines took on their present shape c. modern humans developed agriculture and began to make and use tools made of bronze and iron