Sec. 2 Notes
advertisement

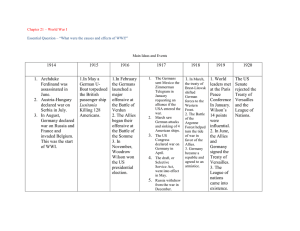
World War I A New Kind of War Chapter 26 section 2 1 Charlie Chaplin 2 3 4 Schlieffen Plan Germany’s plan to avoid a two front war First phase was to invade France through Neutral Belgium. Quickly Defeat France before Russia could mobilize 5 By violating the neutrality agreement signed between Belgium & Germany, England declared war on August 4th. This became known as the “Rape of Belgium” With Great Britain entering the war on the side of the Allies, Germany was now forced to fight the two front war they had been trying to avoid. The War becomes a stalemate 6 7 Nations take Sides By mid-August 1914, two sides at war throughout Europe Central Powers—Germany, Austria-Hungary (and other nations) Allies—Britain, France, Russia (and other nations) 8 9 Invasion of France The German army quickly advances towards the outskirts of Paris Early Sept., 600 Taxies are rushed back and forth to the front lines moving the troops 10 11 First Battle of the Marne September 5 – 12, 1914 12 French Soldiers during the battle German soldiers during the 1st Battle of the Marne 13 The French and the British troops are able to hold the Germans at the Marne River This battle ended Germany’s hope for a quick victory Both sides will begin to dig deep trenches in order to protect their armies Battle lines will barely change over the next four years 14 Western Front as of 1916 15 16 War in the Trenches Two systems of trenches stretched hundreds of miles, western Europe Millions of Allied and Central Powers soldiers in trenches of Western Front Battles result in many deaths, small land gains 17 18 19 20 Life in trenches is miserable, difficult, - Rain produced deep puddles, mud - Lice, rats, bad sanitation constant problems - Removing dead bodies often impossible 21 22 23 24 Over the Top Soldiers ordered out of trenches to attack enemy Sprinting across area known as “no-man’s-land” a deadly game Thousands on both sides died, cut down by enemy guns 25 26 27 28 New Weapons New technology led to greater numbers being killed more effectively Neither side able to make significant advances on enemy’s trenches Each side turned to new weapons like poison gas 29 http://www.history.com/videos/wwi-firsts#wwi-firsts Poison Gas First used by the Germans, but eventually used by all. There were different types of gas. Some caused blindness, severe blisters, or death by choking Value limited, must be careful of the wind both sides developed gas masks 30 31 32 Additional Weapons Rapid-fire machine guns in wide use Artillery and high-explosive shells, enormous destructive power 33 34 35 Artillery piece of the 320th. Artillery piece,"Cyclone ", and its escort on rail, registered ALPG.32. 9. P.3038. Hogstade. (Belgium September 5th, 1917). 36 37 Tanks Tanks pioneered by British and first used in 1916, in the Battle of the Somme Could cross rough battlefield terrain (no man lands) But Reliability was a problem 38 39 40 41 Aircraft Aircraft most useful At beginning of war, mostly for observation 1915 Zeppelins were used to bomb the coast of England Soon had machine guns, bombs attached Faster airplanes useful in attacking cities, battlefields 42 Zeppelins 43 44 Airplanes 45 46 47 Germany’s Red Barron: Manfred von Richthofen Is credit for 80 “kills” against the Allies pilots 48 US top ace, Eddie Rickenbacker, with 26 victories. He survived the war. 49 50 A Sopwith Camel rising from the flight deck of a lighter towed into the wind at top speed by a destroyer. This was the method used by Lt. S.D.Culley to take off when he shot down a Zeppelin off the borkum Riff lightship on 11th August 1918. 51 Submarines 52 AKA U-boats from the German word Unterseeboot First used by the Germans in 1914 Primary weapons were the torpedoes Allies ships were forced to travel in convoys to protect the merchant ships transporting supplies from the U.S. to Europe. 53 54 55 The Eastern Front Eastern battles were fought between the Russians and Serbs against the AH and Germans along the GermanRussian Border The line was more mobile than in the west, because trenches were used very little It was just as deadly, slaughter and stalemate were just as common. 56 Battle of Tannenberg First battle on the Eastern Front, August 26-30, 1914 The Russians are defeated after invading E. Prussia Out of 150,000 men only 10,000 escaped, 92,000 were taken Prisoner The Germans lost 20,000 men News of the defeat is kept out of the press. 57 58 59 60 Russia Struggles Russia’s war effort was suffering by 1916, many casualties, few supplies, due to slow industrialization Huge size of Russian army keeps it a formidable force Most importantly they prevent Germany from sending more troops to the Western Front 61 Southern Europe & Balkans In 1915, Bulgaria joined the Central Powers against rival Serbia Romania joined the Allies to gain land in Hungary Italy joined the Allies to gain land in Austria, by a secret treaty. 62 63 War around the World Japan joined the Allies as an excuse to capture German outpost in China and the Pacific Allies take control of remaining German holdings in Asia, Africa Britain and France use their colonial subjects to help in war effort 64 Ottoman Empire Because of its strategic location they were a desirable ally IF they had sided with the Allies, the Central Powers would have been completely encircled. Late October 1914, the Turks joined the Central powers 65 66 67 The Gallipoli Campaign 68 Cutting off crucial Allied supply line to Russia. Through the Dardanelles between the Mediterranean and Black Sea. Allies sent British, Indian, Australian and New Zealander troops to capture Ottoman Dardanelles strait in February 1915 They battled for 10 months, defeated, they are out in January 1916, after losing 200,000 + troops 69 70 Armenians Crisis A ethnic group living in the Caucasus Mountains, part of them lived in Russia the rest in the Ottoman Empire As Christians they were a minority, and did not have the same rights as Muslims Some Turkish Armenians joined the Russians. 71 The Ottomans used this as a reason to deport the entire population to Syria and Mesopotamia During this time period 600,000 to 1.5 million died Many were killed by planned massacres; others were starved by marching with no food (Genocide) Others immigrated to other countries, Leaving none in their native lands 72 73 74 75 76 77 3 Front for the Ottomans rd 1916, in the Middle East, Arab nationalist revolted, led by Husayn ibn Ali The raids are successful and the Ottomans lose territory and eventually Baghdad 78 Lawrence of Arabia British Colonel T.E. Lawrence sent to support the Arab revolt Lead guerrilla raids against the Turks 79