Ion Linac
advertisement

MEIC Ion Linac and Pre-Booster Design
Bela Erdelyi
Department of Physics, Northern Illinois University,
and Physics Division, Argonne National Laboratory
Review 09/2010
Page 1
Acknowledgements
• Joint Work of
• Bela Erdelyi (NIU/ANL)
• Shashikant Manikonda (ANL)
• Peter Ostroumov (ANL)
• Sumana Abeyratne (NIU student)
• With assistance from JLab staff (Y. Derbenev, Y. Zhang, G.
Krafft, etc.)
Review 09/2010
Page 2
ELIC Conceptual Layout
Three compact rings:
• 3 to 11 GeV electron
• Up to 12 GeV/c proton (warm)
• Up to 60 GeV/c proton (cold)
Review 09/2010
Page 3
Ion Linac for ELIC
• Pulsed linac
• Short Normal Conducting section: RFQ and IH
structure
• Followed by Superconducting section that contains
• Stripper for heavy ions at 12 MeV/u
Review 09/2010
Page 4
Basic Parameters of the Linac
• Linac layout
RFQ
IH
QWR
IS MEBT
Normal conducting
QWR
HWR
Stripper
Superconducting
Parameter
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
DSR
Ion species
Ion species for the reference design
Kinetic energy of lead ions
Maximum beam current averaged over the pulse
Pulse repetition rate
Pulse length
Maximum beam pulsed power
Fundamental frequency
Total length
Review 09/2010
Value
From Hydrogen to Lead
Pb
100 MeV/u
2 mA
10 Hz
0.25 msec
680 kW
80 MHz
115
150 m
208
Page 5
Superconducting Cavities
• Developed for the RIA/FRIB project
QWR
Review 09/2010
HWR
DSR
Page 6
4
4
3.5
3.5
3
3
2.5
Voltage (MV)
Voltage (MV)
Voltage Gain per Cavity for
Protons and Lead Ions
2
1.5
1
2.5
2
1.5
1
0.5
0.5
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
b
Review 09/2010
0.5
0.6
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
b
Page 7
0.4
0.5
QWR and HWR production at ANL
• QWR, f=109 MHz, b=0.15
• HWR, f=172 MHz, b=0.26
Review 09/2010
Page 8
Cryomodule assembly at ANL
beam
Review 09/2010
Page 9
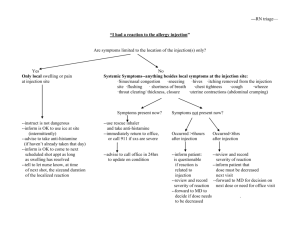
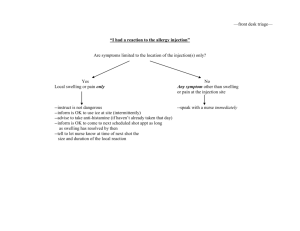
Accumulator/Pre-Booster Concept
•
•
Purpose:
• Inject from linac
• Accumulate ions
• Accelerate them
• Extract and send to large booster
Concepts:
• Figure-8 shape for ease of spin transport, manipulation and
preservation
• Modular design, with (quasi)independent module design
optimization
• FODO arcs for simplicity and ease of implementation of optics
correction schemes
• No dispersion suppressors
• Injection insertion
• Doublet/Triplet straights for long dispersion-less drifts
• Matching/tuning modules in between
Review 09/2010
Page 10
Constraints
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Figure-8 shaped; circumference ~250 m
Maximum bending field: 1.5 T
Maximum quadrupole gradient: 20 T/m
Momentum compaction smaller than 1/25
Maximum beta functions less than 35 m
Maximum full beam size less than 2.5 cm and 1 cm vertically in dipoles
5m m long dispersion-less sections for RF cavities, electron cooling
collimation and extraction
Sizable (normalized) dispersion for/at injection
Working point chosen such that tune footprint does not cross low
order resonances (tunability)
Review 09/2010
Page 11
Injection
• Protons (and light ions)
• Stripping injection
• Heavy ions
• Repeated multi-turn injection
• Transverse (horizontal and possibly also vertical)
and longitudinal painting
• Electron cooling for stacking/accumulation
Review 09/2010
Page 12
Heavy-Ion Injection
Review 09/2010
Page 13
Acceleration
• h=1
• RF swing necessary is [0.4,2] MHz
• 15 kV per cavity
• 50kV/turn => 3-4 cavities
• 56000 turns for 200MeV -> 3 GeV
• Less than 80 ms acceleration time
Review 09/2010
Page 14
Extraction
• Conventional fast extraction
Review 09/2010
Page 15
Layout
ARC 1
Injection Insertion
section
ARC 3
ARC 2
Beam from LINAC
RF cavity
Solenoid for Electron Cooling
Review 09/2010
Page 16
Review 09/2010
Page 17
Arc 2
Straight 2
Arc 3
Straight 1
Arc 1
Injection
Linear Optics
Optical modules
ARC1&2 FODO
STRAIGHT TRIPLET
Review 09/2010
ARC3 FODO
INJECTION INSERT
Page 18
Tunability
Review 09/2010
Page 19
Main Parameters
Units
Value
1
Circumference
m
302
2
Angle at crossing
deg
44
3
Number of dispersive FODO cells (Type I)
6
4
Number of dispersive FODO cells (Type II)
8
5
Number of triplet cells
18
6
Number of matching cells (2 types)
4
7
Minimum drift length between magnets
cm
50
8
Drift length in the injection insertion
m
5.0
9
Drift lengths between triplets (for RF, extraction, collimation and electron cooling)
m
5.3
10
Beta maximum in X
m
33
11
Beta maximum in Y
m
36
12
Maximum beam size
cm
2.3
12
Maximum vertical beam size in the dipole magnets
cm
0.6
13
Maximum dispersion (x|delta_KE)
m
3.3
14
Normalized dispersion value at injection insert
m½
2.1
15
Tune in X
7.92
16
Tune in Y
7.24
17
Gamma of particle
4.22
18
Gamma at transition energy
5.6
19
Momentum compaction
3.2E-2
Review 09/2010
Page 20
Magnets
Quantity
1
2
3
Quadrupole Magnets
Dipole Magnets (Type I)
Dipole Magnets (Type II)
Review 09/2010
Parameters
Units
Value
Length
cm
40
Half aperture
cm
5
Maximum pole tip field
T
1.5
Minimum pole tip field
T
0.15
Strength
T
1.41
Radius
m
9.0
Vertical aperture
cm
3.0
Angle
deg
11.6
Length
m
1.83
Strength
T
1.41
Radius
m
9.0
Vertical aperture
cm
3.0
Angle
deg
14.0
Length
m
2.19
113
16
18
Page 21
Summary and Work in Progress
• Presented a preliminary design of the linac and the
accumulator/pre-booster, which satisfy the constraints while
providing superior performance
•
•
•
•
Fine tuning first order optics
Space charge limits on current and emittance
Spin and spin-orbit resonance analysis
Dynamic aperture estimation
Review 09/2010
Page 22
BACKUP SLIDES
Review 09/2010
Page 23
Cavity subsystems
• 4 kW capacitive coupler
• Adjustable
• 1 cold/warm
windows
• Pneumatic slow tuner
• Piezoelectric tuner
(PZT)
• ~90 Hz window
• 35 m
displacement
LN in
beam
Ceramic disk
LN out
PZT has been tested with
excellent performance
Review 09/2010
Page 24
Proton beam
•
Setting 1:
•
•
•
•
Mass= 1, Charge= 1, Kinetic Energy = 3000 MeV
Electric rigidity (χe) = 3.71E+9 V
Magnetic Rigidity (χm) = 12.74 Tm
Proton beam Emittance in x and y = 16 π mm·mrad
• x=± 4mm y=± 4mm ,
• a=±4mrad b = ±4mrad
• Kinetic Energy Dispersion (δKE/KE )= 1E-4
•
Setting 2:
•
•
•
•
Mass= 1, Charge= 1, Kinetic Energy = 200 MeV
Electric rigidity (χe) = 3.68E+8 V
Magnetic Rigidity (χm) = 2.14 Tm
Proton beam Emittance in x and y = 140π mm·mrad
• x=± 4mm y=± 4mm ,
• a=±35mrad b = ±35mrad
• Kinetic Energy Dispersion (δKE/KE )= 1E-2
Review 09/2010
Page29-31
25July,2010
25
Main Parameters (1)
• Energy range
• Protons: from 200 MeV (β=0.57, γ=1.21) @ injection
to 3 GeV (β=0.97, γ=4.2) at extraction
• Lead ions: if fully stripped, from 80 MeV/u (β=0.39,
γ=1.08) @ injection to 1.18 GeV/u (β=0.9, γ=2.26)
@ extraction
• Circumference
• An integer multiple of it must be ~900-1000 m =>
~250-300 m
Review 09/2010
Page 26
Main parameters (2)
•
•
Revolution times/frequencies
• Protons @ injection:
• {0.883753 μs,1.13154 MHz} if C=150m
• {0.515181 μs,1.94107 MHz} if C=300m
• Protons @ extraction:
• {1.76751 μs,0.565769 MHz} if C=150m
• {1.03036 μs,0.970533 MHz} if C=300m
• Pb @ injection:
• {1.29609 μs,0.771552 MHz} if C=150m
• {0.557907 μs,1.79241 MHz} if C=300m
• Pb @ extraction:
• {2.59218 μs,0.385776 MHz} if C=150m
• {1.11581 μs,0.896207 MHz} if C=300m
If acceleration done with h=1
• RF swing necessary is [0.38,1.95] MHz
Review 09/2010
Page 27
Cooling times
•
Assuming:
• 3 m long cooling section
• 300 mA electron current
• 2.5 cm beam radius
• ± 5 mrad beam divergence
• ±0.004 momentum dispersion
• Cooling for 3 time constants
Transverse cooling time: ~ 130 ms
Longitudinal cooling time: ~ 67 ms
Cooling electron energies:
• @ injection: { 0.55394 MeV, γ=2.0840 }
• @ extraction: { 1.15511 MeV, γ=3.2605 }
Review 09/2010
Page 28
Lead Charge Distributions
• @ injection
• Q (0)
Q (1) Q (2)
•
0
4%
70%
• @ extraction
• Q (0)
Q (1)
•
83%
17%
Review 09/2010
Q (3)
22%
Q (4)
3%
Page 29
Intensities
• Protons
• If assuming 1A current, depending on circumference and
injection/extraction:
=> N_p ~ [ 3 , 11 ] x 1012
• Lead ions
• Under similar circumstances:
=> N_Pb ~ N_p / Q
Review 09/2010
Page 30
Pre-Booster Cycle Time
• Assuming 5x1010 lead ions need to be accumulated
• One linac pulse delivers ~2x108 ions (assumed @
~50% efficiency)
• 50 linac pulses, 250 μs each
• Total time = 50x 250 μs +50x130 ms+2x80 ms ≈ 7 s
Review 09/2010
Page 31
Shorter Version Layout
Review 09/2010
Page29-31
32July,2010
Shorter Version Lattice functions
Review 09/2010
Page29-31
33July,2010
Shorter Version Parameters
Units
Value
1
Total length
m
254
2
Angle at crossing
deg
60
3
Number of dispersive FODO cells (Type I)
6
4
Number of dispersive FODO cells (Type II)
8
5
Number of triplet cells
12
6
Number of matching cells
4
7
Minimum drift length between magnets
cm
50
8
Drift lengths in the insertion region
m
5.0
9
Drift lengths between triplets (for RF, collimation and electron cooling)
m
5.0
10
Beta maximum in X
m
32
11
Beta maximum in Y
m
32
12
Maximum beam size
cm
2.5
12
Maximum beam size in the dipole magnets
cm
0.6
13
Maximum Dispersion (x|delta_KE)
2.5
14
Normalized dispersion value at injection (x|δ_KE)/√β
1.41
15
Tune in X
7.24
16
Tune in Y
6.60
17
Gamma of particle
4.22
18
Gamma at Transition Energy
4.7
19
Momentum compaction factor
4.4E-2
Review 09/2010
Page29-31
34July,2010
Shorter Version Magnets
Quantity
1
2
3
4
Quadrupole Magnet
Dipole Magnet (Type I)
Dipole Magnet (Type II)
Dipole Magnet (Type III)
Review 09/2010
Parameters
Units
Value
Length
cm
40
Half aperture
cm
5
95
Maximum pole tip T
field
1.5
Minimum pole tip T
field
0.16
Strength
T
1.41
Radius
m
9
Vertical aperture
cm
3
Angle
deg
14
Length
m
2.19
Strength
T
1.41
Radius
m
9
Vertical aperture
cm
3
Angle
deg
12.9
Length
m
2.04
Strength
T
1.41
Radius
m
9
Vertical aperture
cm
3
Angle
deg
14.9
Length
m
2.35
12
18
18
Page 35
New Layout with 5 quads in each matching section
(302m)
Review 09/2010
Page 36