University of Hawaii Maui College Course Outline and CAR
advertisement

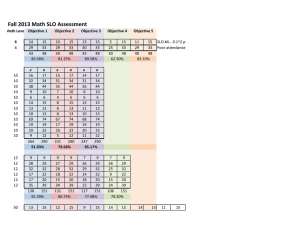
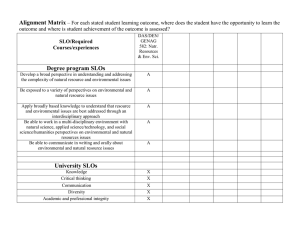
University of Hawaii Maui College Course Outline and CAR Author(s): Kathy Fletcher and Melissa Kirkendall, Ph.D. Department: Social Science Date submitted to Curriculum Committee: 3/31/11 Type of action: Addition: regular other; specify: Modification: alpha/number title credits description pre-requisite co-requisite recommended prep other; specify: Course: 1. Alpha: ANTH 2. Number: 225 3. Title: Medical Anthropology 4. Credits: 3 5. Contact Hours/Type: 3 lecture Existing course, if different from above: Alpha: Title: Credits: credits Number: Contact Hours/Type 6. Course Description: Surveys human health and disease and how it relates to cultural practices, belief systems, and environmental factors. Seeks to bridge the health sciences and anthropology by focusing on how social and environmental factors affect health. Explores alternative ways of understanding and treating disease. Includes ethnomedicine, the traditional healing and health practices of a selection of cultures, paleopathology, epidemiology, and human adaptation. 7. Pre-requisites: ENG 22 with grade C or better or placement at English 100 Pre-requisite may be waived by consent yes 8. Co-requisites: 9. Recommended Preparation: ANTH 200 or 215, or concurrent 10. Cross-list: no 11. Reason for this curriculum action: Medical Anthropology (ANTH 190V) has been taught for three sequential semesters with success. The course always fills prior to onset of the semester. The course is appropriate for individuals seeking work in the health care industry who will encounter individuals from various cultures in their practice, and allows for a more sensitive delivery of Western health care. It is also appropriate for individuals seeking a future degree in Anthropology. . Course is taught at another UH campus: no Explain why this course is proposed for UHMC: yes, specify college(s), course, alpha, and number where same or similar course is taught: University of Hawaii at Manoa, ANTH 425. This course is taught at the upper division level with a target population of Anthropology majors. 12. Proposed term of first offering: Spring 5-year Review Date 2018 semester of 2012 13. Grading: Standard (Letter, Cr/NCr, Audit) 14. Is this course repeatable for credit? unlimited. no year Explain, if not Standard grading: yes; maximum is credit or Many previous course outlines have SLOs and what are now called Competencies/Concepts/Issues/Skills combined in question number 6. In this form in number 15: SLOs are considered to be over arching “what the student will be able to do in the rest of life” type statements. In number 16: Competencies/Concepts/Issues/Skills are considered to be the more specific steps by which the SLOs are achieved. 15. Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs). List one to four inclusive SLOs. Use roman numerals (I., II., III.) to designate SLOs.. On successful completion of this course, students will be able to: I. Describe the wide range and variability of human culture in approaches to health and disease; II. Develop familiarity with the concept of culture, and culture as holistic and integrated system; III. Critically evaluate the medical transitions of other cultures and evaluate appropriate ethnographic research; IV. Describe insights into modern health through application of anthropological concepts and apply reasoning skills to resolution to various health issues. 16. Competencies/Concepts/Issues/Skills. Use lower case letters (a., b.…zz) to designate competencies/concepts/issues/skills.. On successful completion of this course, students will be able to: a. Demonstrate how definitions of disease and health are culture bound, and recognize that solutions must be culturally based as well; Explore the roots and history of Western medicine b. Compare and contrast how the environment, food, and population interact with health and disease, c.Identify how the ecology of a population influences the cultures in differing degrees at different times in history. d. Recognize that there is much to learn from all cultures as they solve problems of health and disease. 17. Suggested Course Content and Approximate Time Spent on Each Topic Linked to #15. Student Learning Outcomes and #16: Competencies/Concepts/Issues/Skills 1-2 weeks - operational definitions of health and disease and various cultures; (SLO I and Competency a.) 1-2 weeks - examine roots of Western medicine and the ecology of health and disease (SLO I and Competency a.) 3-4 weeks - examines health and human adaptation to varying environments from a holistic view of human populations; the role of evolution in human adaptation, disease, germ theory, and host and parasite interactions (SLO II, Competencies b and c) 2-3 weeks - examines paleopathology, change over time, (SLO III and Competencies c. and d.) 3-4 weeks diverse cultures and how their medical systems work within the construct of the culture (SLO III and Competencies c. and d.) 4-5 weeks - Non-Western medicine; healers and shaman with a focus on facilitating problem solving from a culturally relative perspective (SLO IV and Competency d.) 18. Suggested Course Requirements and Evaluation Linked to #15. Student Learning Outcomes and #16: Competencies/Concepts/Issues/Skills Specific course requirements are at the discretion of the instructor at the time the course is being offered. Suggested requirements might include, but are not limited to: - 1. Critical evaluation of at least one ethnography. Examples are "Dancing Skeletons: Life and Death in West Africa" by Katherine A. Dettwyler, and "The Spirit Catches You and You Fall Down" by Anne Fadiman (SLOs I, II and III, and Competencies a, b, c, and d) - 2. Critical Responses to various films shown during the semester that depict other cultures and their health systems or alternative methods of healing (SLOs I, II, and III, and Competencies a, b, c, and d). - 3. Participation in group exercises which provide opportunities for students to apply the skills/competencies that they are developing during the course of study (SLO IV, and Competencies c and d). - 4. Quizzes and Exams designed to assess student comprehension of the material (SLOs I, II and IV and Competencies a, b, and c). 19. College-wide academic student learner outcomes (CASLOs) this course supports: (mark all that apply) Written Communications Quantitative Reasoning Information Retrieval and Technology Oral Communication Critical Reasoning Creativity If this course supports one or more CASLO, then either complete the Assessment of Intended Student Learning Outcomes Standards (CCOWIQ) Grid (see Curriculum Committee website for grid form and submit it with this form) OR in the box following explain briefly how this course supports the particular CASLO or CASLOs: Students develop skills in written communication through the critical review of an appropriate ethnography, assigned film responses, and through the currently utilized essay examination format. Skills in oral communication are facilitated through the in class discussions, exam study groups and group exercises in problem resolution. Critical reasoning is also supported through the critical review, film responses, and group problem solving exercises. All three CASLOs are evaluated using a grading rubric. 20. Using the program student learning outcomes (PLOs) for the main program of which this course is a part, list only those PLOs this course supports: PLO: 1. The diversity of human conditions and cultures in local and global communities. PLO: PLO: PLO: PLO: PLO: PLO: 21. No question. Question 21 will be part of the process used in Curriculum Central. 22. Method(s) of delivery appropriate for this course: (mark all that apply) Traditional HITS/Interactive TV Cable TV Online Other, explain: Hybrid 23. Text and Materials, Reference Materials, and Auxiliary Materials Appropriate text(s) and materials will be chosen at the time the course is offered from those currently available in the field. Examples include: 2009. McElroy and Townsend, Medical Anthropology in Ecological Perspective (Fifth Edition); 1994. Dettwyler, Dancing Skeletons: Life and Death in West Africa Appropriate reference materials will be chosen at the time the course is offered from those currently available in the field. Examples include: Appropriate auxiliary materials will be chosen at the time the course is offered from those currently available in the field. Examples include: Films: Typhoid Mary, The Influenza Epidemic of 1918, Shamans of Siquojor: The Healers, Horse Boy, Juliette of the Herbs, Between Two Worlds. 24. Maximum enrollment: 35 Rationale, if less than 35: 25. Course is restricted to particular room type: projector, Elmo, etc. necessary 26. Special scheduling considerations: no no yes; explain: Computer, yes; explain: 27. Special instructional resources (personnel, supplies, etc.) required: no yes; explain: 28. Special student fees required: no yes; explain: 29. Function/Designation: Mark all that apply. AA* First Category CO - Human Understanding: Community Category, if appropriate Category Fulfills Hawaii Emphasis (HI) Graduation Requirement AS Any SS - Social Science AAS Any SS - Social Science BAS Any SS - Social Science Developmental/Remedial Second List Additional Programs and Category: List Additional Programs and Category: List Additional Programs and Category: Other/Additional: Explain: * Submit the appropriate form(s) to have the course placed in the requested category(ies) to both the Curriculum Committee and the Liberal Arts/AA Program Chair. If the course satisfies category I: Foundations/Skills: Foundations I or Ii, it needs to be submitted to the Foundations Board. If a course needs a diversity designation, it needs to be submitted to the Diversity Board. If a course needs a Hawaii/ Asia/ Pacific designation, it needs to be submitted to the HAPS board. See your Department Representative, the Curriculum Chair, or the Liberal Arts/AA Coordinator for information. 30. Course increases decreases makes no change to number of credits required for program(s) affected by this action. Explain, if necessary: 31. Course is: Not appropriate for articulation. Appropriate* for articulation as a general education course at: UHCC UH Manoa UH Hilo UHWO Previously articulated* as a general education course at: UHCC UH Manoa UH Hilo UHWO *Submit Course Articulation Form(available on the Curriculum Committee website) if course is already articulated, or is appropriate for articulation, as a general education (100-, 200-level) course. Check Curriculum Committee website under UH Courses for articulation sites. Standardized and/or appropriate for articulation by PCC or other UH system agreement at: UHCC UH Manoa UH Hilo UHWO Explain: Appropriate for articulation or has previously been articulated to a specific department or institution: UHCC UH Manoa UH Hilo UHWO Outside UH system Explain: This course outline is standardized and/or the result of a community college or system-wide agreement. Name of the responsible committee/group: 32. List catalog used and then degrees, certificates, prerequisites, and catalog sections and their page numbers affected by this proposal: 2010-2011 pages 16 and 93 33. Additional Information (add additional pages if needed): This course is a Diversification Social Science course. University of Hawaii Maui College Course Outline and CAR Signature Page ______________________________________________________________________ Proposed by: Author or Program Coordinator Date ______________________________________________________________________ Checked by Department Representative to Curriculum Committee Date ______________________________________________________________________ Requested by Department: Department Chair Date ______________________________________________________________________ Recommended by: Curriculum Chair Date ______________________________________________________________________ Approved by Academic Senate: Academic Senate Chair Date ______________________________________________________________________ Endorsed by: Chief Academic Officer Date ______________________________________________________________________ Course Approved by: Chancellor Date UNIVERSITY OF HAWAII MAUI COLLEGE ASSOCIATE IN ARTS DEGREE REVIEW OF COURSES FOR DIVERSIFICATION REQUIREMENTS Any UH course with a diversification or equivalent designation that transfers to another UH campus will be accepted with the sending campus’ designation. At each participating UH campus, the diversification designation is consistent with the hallmarks described below. Courses are approved through a campus level process and reviewed at least every five years to ensure that the course continues to meet the hallmarks. SUBJECT ALPHA: ____ANTH______ COURSE NUMBER: ___225_________ If the course is cross-listed, please provide the cross-listing: Subject _________ Course # _______ COURSE TITLE: ____Medical Anthropology___ ___________________________ UH MANOA DIVERSIFICATION CATEGORY: UHMC RECOMMENDED CATEGORY:___Social Sciences__________________ (Refer to attached Hallmarks) a) Use the terminology of theories, structures, or processes in the social or psychological sciences. b) Involve the concepts, models, practices, or issues of concern in the scientific studies of those theories, structures, or processes. Is the course outline, on file with the UHMC Curriculum Committee, consistent with the stated Hallmarks? __X ___ Yes _____ No If “No” and you wish to submit changes to correspond with the Hallmarks, attach a University of Hawaii Maui College Curriculum Action Request (CAR) (Form 4-93) with new course outline. OR Recommend course be changed to another sub-category: ____________________ OR Recommend course be used only as general elective ________________________________ Instructor’s Printed Name 2/2010 _______________________________ Instructor’s Signature Date HALLMARKS: To satisfy the Arts (DA) area requirement, at least two thirds of a course will Use the definitions, descriptions, and terminology of the visual arts, performing arts, and other creative arts. Emphasize the acquisition of practical and theoretical skills necessary to produce visual, performing, or other creative arts for primarily aesthetic purposes. Develop creative abilities in which artistic conventions are applied and originality is sought. To satisfy the Humanities (DH) area requirement, at least two thirds of a course will Use the terminology of historical, philosophical, language, or religious studies. Involve texts, artifacts, concepts, processes, theories, or issues of concern in these studies. Demonstrate inquiry that that involves the methods of study, reflection, evidence gathering, and argumentation that are employed in these studies. To satisfy the Literatures (DL) area requirement, at least two thirds of a course will Use the terminology of literary and/or cultural analysis. Involve the study of texts, concepts, forms, figures, styles, tonalities, processes, theories, or issues relating to literary and/or cultural analysis. Demonstrate inquiry that is guided by qualitative, argumentative, and/or quantitative methods employed in literary and/or cultural analysis. To satisfy the Biological Science (DB) area requirement, at least two thirds of a course will Use the terminology of the biological sciences. Involve knowledge and theories relating to processes in the biological sciences. Demonstrate inquiry that is guided by observation/experimentation and reasoning/mathematics. To satisfy the Physical Science (DP) area requirement, at least two thirds of a course will Use the terminology of the physical sciences. Involve knowledge and theories relating to processes in the physical sciences. Demonstrate inquiry that is guided by observation/experimentation and reasoning and mathematics. To satisfy the Laboratory (DY) area requirement, at least two thirds of a course will Use the laboratory methods of the biological or physical sciences. Involve processes and issues of design, testing, and measurement. Demonstrate the strengths and limitations of the scientific method. To satisfy the Social Sciences (DS) area requirement, at least two thirds of a course will Use the terminology of theories, structures, or processes in the social or psychological sciences. Involve the concepts, models, practices, or issues of concern in the scientific studies of those theories, structures, or processes. Demonstrate inquiry that is guided by quantitative and/or qualitative methods employed in the scientific study of structures or processes of these sciences. UNIVERSITY OF HAWAII MAUI COLLEGE ASSOCIATE IN ARTS DEGREE REVIEW OF COURSES FOR AA CATEGORY INCLUSION SUBJECT ALPHA: __ANTH_________ COURSE NUMBER: __225_________ If the course is cross-listed, please provide the cross-listing: Subject _________ Course # _______ COURSE TITLE: ___Medical Anthropology__________________________________ CATEGORY: II – BREADTH OF UNDERSTANDING AND EXPERIENCE SUB-CATEGORY: Human Understanding The Community RELATED PROGRAM LEARNING OUTCOME: Students will demonstrate knowledge of the diversity of human conditions and cultures in local and global communities. HALLMARKS: To satisfy the Human Understanding of the Community requirement, a course will: a) Develop students’ understanding of ideas, societies, artifacts, and cultures with an emphasis on the community. b) Practice various methods of inquiry such as reflection, analysis, observation, and/or argumentation. Is the course outline, on file with the UHMC Curriculum Committee, consistent with the Hallmarks stated above? __X___ Yes _____ No If “No” and you wish to submit changes to correspond with the Hallmarks, attach a University of Hawaii Maui College Curriculum Action Request (CAR) (Form 4-93) with new course outline. OR Recommend course be changed to another sub-category: ____________________ OR Recommend course be used only as general elective ________________________________ Instructor’s Printed Name _______________________________ Instructor’s Signature Date Assessment of Intended Student Learning Outcomes Standards – CCOWIQs with Ratings for ANTH 225 Key: 3 = Major Emphasis: The student is actively involved (uses, reinforces, applies, and evaluated) in the student learning outcomes. The learner outcome is the focus of the class. 2 = Moderate Emphasis: The student uses, reinforces, applies and is evaluated by this learner outcome, but it is not the focus of the class 1 = Minor Emphasis: The student is provided an opportunity to use, reinforce, and apply this learner outcome, but does not get evaluated on this learner outcome 0 = No Emphasis: The student does not address this learner outcome ANTH Standard 1: Written Communication 225 Write effectively to convey ideas that meet the needs of specific audiences and purposes. 1.1 Use writing to discover and articulate ideas 2 1.2 Identify and analyze the audience and purpose for any intended communication 3 1.3 Choose language, style and organization appropriate to particular purposes and audiences 3 1.4 Gather information and document sources appropriately 3 1.5 Express a main idea as a thesis, hypothesis, and other appropriate content 1 1.6 Develop a main idea clearly and concisely with appropriate content 3 1.7 Demonstrate mastery of the conventions of writing, including grammar, spelling, and mechanics 2 1.8 Demonstrate proficiency in revision and editing 1 1.9 Develop a personal voice in written communication 1 Standard 2: Quantitative Reasoning Synthesize and articulate information using appropriate mathematical methods to solve problems and logically address real-life situations. 2.1 Apply numeric, graphic and symbolic skills and other forms of quantitative reasoning, accurately and appropriately 0 2.2 Demonstrate mastery of mathematical concepts, skills, and applications, using technology when appropriate 0 2.3 Communicate clearly and concisely the methods and results of quantitative problem solving 0 2.4 Formulate and test hypotheses using numerical experimentation 0 2.5 Define quantitative issues and problems, gather relevant information, analyze that information, and present results 1 2.6 Assess the validity of statistical conclusions 1 Standard 3: Information Retrieval and Technology (Information Literacy) Access, evaluate, and utilize information effectively, ethically and responsibly. 3.1 Use print and electronic information technology ethically and responsibly 2 3.2 Demonstrate knowledge of basic vocabulary, concepts, and operations of information technology and retrieval 2 3.3 Recognize, identify, and define an information need 2 3.4 Access and retrieve information through print and electronic media, evaluating the accuracy and authenticity of that information 2 3.5 Create, manage, organize, and communicate information through electronic media 2 3.6 Recognize changing technologies and make informed choices about their appropriateness and use. 1 Standard 4: Oral Communication Practice ethical and responsible oral communications appropriate to a variety of audiences and purposes. 2 4.1 Identify and analyze the audience and purpose of any intended communication. 2 4.2 Gather, evaluate, select, and organize information for the communication. 2 4.3 Use language, techniques, and strategies appropriate to the audience and occasion. 3 4.4 Speak clearly and confidently, using the voice, volume, tone, and articulation appropriate to the audience and occasion 4.5 Summarize, analyze, and evaluate oral communications and ask coherent questions as needed. 2 4.6 Use competent oral expression to initiate and sustain discussion. 3 Standard 5: Critical Thinking Apply critical reasoning skills to effectively address the challenges and solve problems. 3 5.1 Identify and state problems, issues, arguments, and questions contained in a body of information. 2 5.2 Identify and analyze assumptions and underlying points of view relating to an issue or problem. 3 5.3 Formulate research questions that require descriptive and explanatory analyses. 2 5.4 Recognize and understand multiple modes of inquiry, including investigative methods based on observation and 2 analysis. 5.5 Evaluate a problem, distinguishing between relevant and irrelevant facts, opinions, assumptions, issues, values, and biases through the use of appropriate evidence. 5.6 Apply problem-solving techniques and skills, including the rules of logic and logical sequence. 5.7 Synthesize information from various sources, drawing appropriate conclusions. 5.8 Communicate clearly and concisely the methods and results of logical reasoning. 5.9 Reflect upon and evaluate their thought processes, value system, and world views in comparison to those of others. Standard 6: Creativity Able to express originality through a variety of forms. 6.1 Generates responses to problems and challenges through intuition and non-linear thinking. 6.2 Explores diverse approaches to solving a problem or addressing a challenge. 6.3 Sustains engagement in activities without a preconceived purpose. 6.4 Demonstrates the ability to trust and follow one’s instincts in the absence of external direction. 6.5 Applies creative principles to discover and express new ideas. 6.6 Builds upon or adapts the ideas of others to create novel expressions or new solutions. 3 2 3 2 3 0 0 2 0 0 0 2