Demonstrate knowledge of the construction and rigging requirements of trailer boats
advertisement

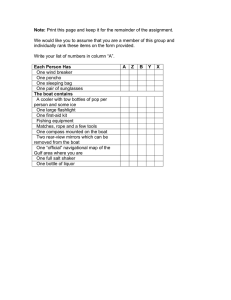
15451 version 3 Page 1 of 4 Demonstrate knowledge of the construction and rigging requirements of trailer boats Level 3 Credits 10 Purpose This theory-based unit standard is for people in the trailer boat repair industry. People credited with this unit standard are able to demonstrate knowledge of trailer boat construction and materials, and equipment rigging requirements for a trailer boat. Subfield Motor Industry Domain Trailer Boat Systems Status Registered Status date 21 September 2007 Date version published 21 September 2007 Planned review date 31 December 2012 Entry information Open. Accreditation Evaluation of documentation and visit by NZQA and industry. Standard setting body (SSB) NZ Motor Industry Training Organisation (Incorporated) Accreditation and Moderation Action Plan (AMAP) reference 0014 This AMAP can be accessed at http://www.nzqa.govt.nz/framework/search/index.do. Special notes 1 Legislation relevant to this unit standard includes but is not limited to – Health and Safety in Employment Act 1992. 2 Definitions Company requirements refer to instructions to staff on policy and procedures which are documented in memo or manual format and are available in the workplace. These requirements include but are not limited to – company specifications and procedures, work instructions, manufacturer specifications, product quality specifications, and legislative requirements. Gelcoat is a material used to provide a high quality finish on the visible surface of the glass reinforced plastic (GRP) material. The gelcoat is typically 0.5-0.8mm in thickness. New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 15451 version 3 Page 2 of 4 Rigging in the context of this unit standard refers to the fitting of engines and related accessories to a trailer boat. Service information may include but is not limited to – technical information of a vehicle, machine, or product detailing operation; installation and servicing procedures; manufacturer instructions and specifications; technical terms and descriptions; and detailed illustrations. This can be accessed in hard copy or electronic format and is normally sourced from the manufacturer. 3 Reference texts for this unit standard include but are not limited to: Mike Scanlan, Safety in small craft (Auckland: Coastguard Boating Education Service, Royal New Zealand Coastguard Federation, 2002). This book is available from local bookshops, the library lending service, or from Boat Books Limited, 22 Westhaven Drive, Auckland City, New Zealand; phone 09 358 5691; or website http://boatbooks.co.nz/seamanship_education.html#BM16303. Elements and performance criteria Element 1 Demonstrate knowledge of trailer boat construction and materials. Performance criteria 1.1 Nautical terms and terminology of boat components and materials are identified in accordance with boat manufacturer specifications and reference texts. 1.2 Trailer boat construction materials are identified in accordance with boat manufacturer specifications. Range 1.3 Building materials and their use are described in accordance with boat manufacturer specifications. Range 1.4 handtools, power tools. Types of damage to boat structures are described in accordance with boat repair manuals. Range 1.6 marine ply, treated timber, aluminium, GRP, steel alloys. Safe working practices when using woodworking tools are identified in accordance with legislative requirements. Range 1.5 aluminium, ply, GRP, fibreglass-over-ply, steel, polyethylene. rot in wooden boats, osmosis and delamination in GRP hulls, cosmetic damage. Types of gelcoat damage are identified in accordance with boat manufacturer instructions. Range stress, impact, scratching, abrasions. New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 15451 version 3 Page 3 of 4 1.7 Adhesives and sealants used in the manufacture and repair of boat structures are identified, and their handling and safety requirements are described in accordance with manufacturer instructions and legislative requirements. Range 1.8 polyester resin, epoxy resin. Procedures for cutting and sealing exposed holes are described in accordance with boat manufacturer instructions. Element 2 Demonstrate knowledge of equipment rigging requirements for a trailer boat. Performance criteria 2.1 Hull and boat plans and their specifications are interpreted to enable equipment layout requirements to be identified in accordance with company requirements. Range 2.2 Helm station design requirements are identified in accordance with boat manufacturer instructions. Range 2.3 includes but is not limited to – remote control steering, instruments and gauges, electrics and electronics, hardware. Procedure to locate a transom centre line and parallelism to water line is described in accordance with boat manufacturer instructions and marine engine service information. Range 2.4 boat specifications – profiles, body plan, half breadth; structural integrity; suitability of design to boat application. scribing arcs on transom and measuring angles. Procedure to measure transom angle is described in relation to power and transmission unit mounting. Range boat out of the water and supported. 2.5 Compatibility requirements of accessories and fittings with boats are identified in accordance with boat and accessory manufacturer instructions. 2.6 Factors to consider when rigging a hull are explained in accordance with boat manufacturer instructions. Range includes but is not limited to – customer requirements, equipment specifications, safety, security, compatibility, weight distribution, boat trim. New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 15451 version 3 Page 4 of 4 2.7 Equipment layout requirements are described in accordance with boat manufacturer instructions and engine service information. Range 2.8 includes but is not limited to – engine ventilation, space saving, ease of maintenance, location of essential monitoring and control systems, provision of protection from moving cables and linkages, wiring looms, exhaust system. Implications of re-powering outside of specifications are explained in accordance with boat manufacturer specifications. Range implications may include but are not limited to – buoyancy, flotation, safety, adhering to compliance plate. Please note Providers must be accredited by NZQA, or an inter-institutional body with delegated authority for quality assurance, before they can report credits from assessment against unit standards or deliver courses of study leading to that assessment. Industry Training Organisations must be accredited by NZQA before they can register credits from assessment against unit standards. Accredited providers and Industry Training Organisations assessing against unit standards must engage with the moderation system that applies to those standards. Accreditation requirements and an outline of the moderation system that applies to this standard are outlined in the Accreditation and Moderation Action Plan (AMAP). The AMAP also includes useful information about special requirements for organisations wishing to develop education and training programmes, such as minimum qualifications for tutors and assessors, and special resource requirements. Comments on this unit standard Please contact the NZ Motor Industry Training Organisation (Incorporated) janet.lane@mito.org.nz if you wish to suggest changes to the content of this unit standard. New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016