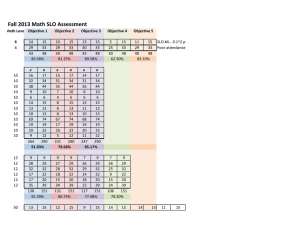
IAS 3063 Info Assurance Networking Fundamentals. Fall 2009
advertisement

Syllabus – IT3603 Fall 2009 -1IT3603 Human Computer Interface Development. Fall 2009 INSTRUCTOR: OFFICE PHONE: OFFICE HOURS: OFFICE: E-MAIL: PREREQUISITE: IT 2413. It would be helpful to have Visual Basic knowledge. REQUIRED TEXT: The Resonant Interface. Steven Heim. Addison Wesley. 978-0-321-37596-4 CATALOG COURSE DESCRIPTION: An exploration of Graphical User Interface development and human computer interaction using a current RAD tool. Issues of good and bad design of both Web and Application GUIs. Lecture 3 hours. Prerequisite: IT 2413 EXPANDED COURSE DESCRIPTION This course provides the foundations of human computer interfaces. Topics covered include, interaction paradigms, computing environments, interactions frameworks and styles, interaction design process, design principles, interface components, human factors. COURSE OBJECTIVES: Analyzing interaction paradigms. (BS – SLO 02) Understanding interaction frameworks and styles. (BS – SLO 02) Designing interaction. (BS – SlO 02) Analyzing and interpreting the discovery phase framework. (BS – SLO 01) Conceptualizing human computer interfaces. (BS – SLO 02) Comparing design principles. (BS – SLO 02) COURSE FORMAT: The strategy for this course calls on the student to be an active participant in the learning process. Students must prepare in advance each topic to be covered in class and as part of their preparation they must make home works which come directly from the class’ book. Usually students have to discuss topics with class mates. The instructor expands upon key concepts with comments and examples provided by the book and class slides. The course includes interactive instructor lecture, team discussions in class and students presentations. There will be time provided in class for working in projects. 1 Syllabus – IT3603 Fall 2009 -2ACTIVE vs. PASSIVE LEARNING 1: Studies indicate that students retain: 10% of what they read; 20% of what they hear; 30% of what they see; 50% of what they see and hear; 70 % of what they say; and 90% of what they say as they do. Adult learners learn better if they are ACTIVELY involved in the learning process! The following has been adapted from the West Virginia Department of Psychology Undergraduate Handbook (http://www.as.wvu.edu/psyc/Undergraduate/Handbook/StudentSuccess/actpass.htm ) Active: Come to lectures prepared, pay attention, take notes, participate in discussions, and asks questions. Active: Take your own notes. Active: Skim assignments first, make up a list of questions they want answered, and then read the assignment to answer the questions. Active: Study returned tests so they don’t make the same mistake again. Active: Volunteer to help others in class who are having trouble. Active: Participates in the learning environment, making choices, looking for answers outside of the class environment. Active learners want deep learning. Deep learning is insightful learning. Deep learners look for the meaning behind the learning. BLACKBOARD: Blackboard (http://blackboard.cameron.edu/ ) will be used throughout the course to provide a forum for disseminating information, group work, discussions, and for exams. The correct blackboard course in which to enroll is: Human Computer Interface Develop – Fall 09 IT3603. The Password for self-enrolling is IT3603 1 Kimberly Merrit. Sillabus MIS Spring 2007. Cameron University. Computing & Technology Department. 2 Syllabus – IT3603 Fall 2009 -3Appendix A…. INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY PROGRAM OUTCOMES AAS INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Upon completion of the program, the student must meet the following criteria (Cat Department, 2006). The student: SLO-01. must understand and demonstrate application of a high ethical standard SLO-02. must understand the impact that information technology has on society as a whole and must know the importance of continual learning SLO-03. must possess the ability to communicate in a variety of settings using oral, written, multimedia techniques to a variety of audiences and must interact with and understand diverse groups using a strong IT vocabulary SLO-04. must be able to choose from a variety of different problem solving methodologies to analytically formulate a solution using a high level programming language SLO-05. must understand the planning, performing, and evaluation process as it relates to information technology operations and must understand system phases, and the Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC) SLO-06. must understand basic computer networks infrastructure and demonstrate proficiency in assembling, configuring and administering networks BS INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Upon completion of the program, the student must meet the following criteria (Carroll, BS in IT Proposal, 2006). The student: SLO-01. must analyze, identify, and define the requirements that must be satisfied to address problems or opportunities faced by organizations or individuals applying current technical concepts and practices in the core information technologies; SLO-02. must design effective and usable IT-based solutions and integrate them into the user environment; SLO-03. must demonstrate an understanding of best practices and standards and their application in order to identify and evaluate current and emerging technologies and assess their applicability to address the users’ needs; SLO-04. must analyze the impact of technology on individuals, organizations, and society, including ethical, legal, and policy issues; SLO-05. must demonstrate independent critical thinking and problem solving skills; SLO-06. must communicate effectively and efficiently with clients, users, and peers both verbally and in writing, using appropriate terminology and must collaborate in teams to accomplish a common goal by integrating personal initiative and group cooperation 3