Simple Linear Regression - NFL Point Spreads and Actual Scores
advertisement

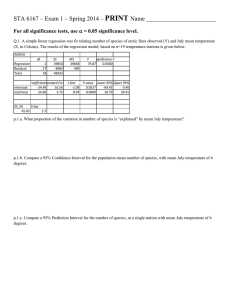
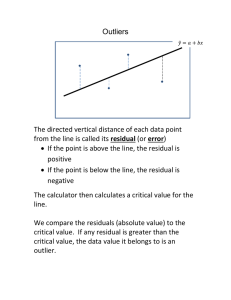
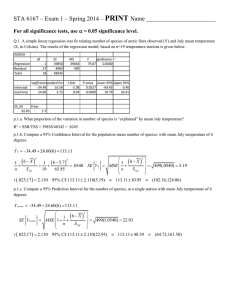
Simple Linear Regression NFL Point Spreads – 2007 Background • Las Vegas Bookmakers provide a point spread for each game • The spread reflects how many points the home team “gets” from the visiting team (negative values mean the home team “gives” points to visitor) • If bookmakers are accurate, on average the actual difference should equal prediction • Accurate ? How variable ? Statistical model Y 0 1 X where : Y Actual Difference (Away Team - Home Team) X Predicted Difference (Away Team - Home Team) 0 Mean Actual Difference when Predicted Difference 0 (" Pick ' em" ) 1 Change in mean Actual Difference per Unit Increase in Predicted ~ NID0, 2 (Assumptio n) If oddsmakers are accurate (on average), 0 0 and 1 1 Actual Difference (Y) vs Opening Spread (X) HomeAway 60 40 20 0 -20 -40 -60 -30 -25 -20 -15 -10 -5 0 5 10 15 20 25 Summary Statistics / Regression Equation Mean Std Dev Spread -2.72 6.23 Actual -1.69 15.37 df 1 254 255 SS 14008.25 46705.23 60713.48 Regression Statistics Multiple R 0.4803 R Square 0.2307 Adjusted R Square 0.2277 Standard Error 13.5602 Observations 256 ANOVA Regression Residual Total Coefficients Standard Error Intercept -0.2023 0.9008 Open Spread (HT) 1.0778 0.1235 MS 14008.25 183.88 t Stat -0.2245 8.7282 F 76.18 P-value 0.0000 P-value Lower 95%Upper 95% 0.8225 -1.9763 1.5718 0.0000 0.8346 1.3209 Actual vs Spread - With Fitted Equation 60 55 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 Actual (AT-HT) 15 10 5 0 -5 -10 -15 -20 -25 -30 -35 -40 -45 -50 -55 -60 -35 -25 -15 -5 Vegas Spread (AT-HT) 5 15 25 OLS Residuals vs Fitted Values 50 40 30 Residuals 20 10 0 -10 -20 -30 -40 -30 -25 -20 -15 -10 -5 Fitted Values 0 5 10 15 20 Histogram of Residuals 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 -30 -25 -20 -15 -10 -5 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 Residuals versus Normal Scores = Z((Rank0.375)/(n+0.25)) 50 40 30 20 10 0 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 -10 -20 -30 -40 -50 1 2 3 4 Testing normality of errors (I) Shapiro - Francia Method (n 5) (see Royston, 1993) Order Errors : e(1) e( 2 ) ... e( n 1) e( n ) i 0.375 Obtain Normal scores for each observatio n : m i 1 n 0.25 ~ ~ Obtain " c"-Weights : ci mi n ~ 2 m and u 1 n j j 1 Obtain approximat e " a"-Weights : ~ a n cn 0.221157u 0.147981u 2 2.071190u 3 4.434685u 4 2.706056u 5 ~ a n 1 cn 1 0.042981u 0.293762u 2 1.752461u 3 5.682633u 4 3.582633u 5 ~ 2 n m i ~ 2 ~ 2 2 m n 2 m n 1 i 1 ~2 ~2 1 2 a n 2 a n 1 ~ ~ ~ mi a1 a n ~ ~ a 2 a n 1 ~ ai i 3,..., n 2 Testing normality of errors (Ii) H 0 : Errors are normally distribute d H A : Errors are not normally distribute d 2 a i e(i ) Test Statistic : W ' ni 1 2 e(i ) e n ~ i 1 Converted to a Z - statistic, where : Z ' g (W ' ) where : g (W ' ) ln( 1 W ' ), 1.2725 1.0521ln(ln( n)) ln( n) , 2 1.0308 0.26758 ln(ln( n)) ln( n) P - value PZ Z ' Example – NFL Spread errors H 0 : Errors are normally distribute d H A : Errors are not normally distribute d 2 a i e(i ) 46568.34 0.997069 Test Statistic : W ' ni 1 2 46705.23 e(i ) e n ~ i 1 Converted to a Z - statistic, where : Z ' g (W ' ) -1.10938 where : g (W ' ) ln( 1 W ' ) -5.83241, 1.2725 1.0521ln(ln( n)) ln( n) -5.30441, 2 0.475945 1.0308 0.26758 ln(ln( n)) ln( n) P - value PZ Z ' 0.866367 Testing accuracy in mean H0: 0 0, 1 1 HA: 0 ≠ 0 and/or 1 ≠ 1 Fit Model UnDer H0: Y*=X Obtain error sum of squares under Y* • Compare with error sum of squares from full model (HA). • • • • Testing for Accuracy ^ F Full Model (H A ) : Y i -0.2023 1.0778 X i ^ R Reduced Model (H A ) : Y i X i Test Statistic : Fobs SSE ( F ) Yi Y i i 1 n ^ F 2 46705.23 2 ^ R SSE ( R) Yi Y i 46818 i 1 n SSE ( R) SSE ( F ) 2 (46818 46705.23) 2 56.385 0.307 SSE ( F ) (n 2) 46705.23 254 183.879 P - value : PF2, 254 0.307 0.7359 Do not reject the null hypothesis that 0 0, 1 1