Genetics Test 2 Review
advertisement

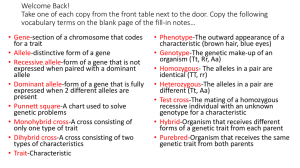
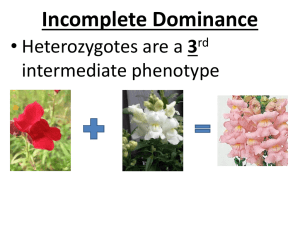
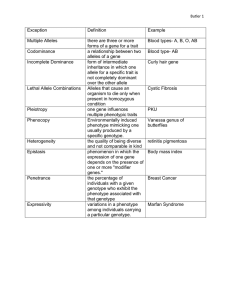
Genetics Test #2 Review (Multiple alleles/X-linked/Pedigrees/Polygenic traits) *To receive credit, answer the questions on a separate sheet of paper* Multiple Alleles 1. What is an allele? 2. How many alleles make up a person’s genotype in a simple dominance type of inheritance pattern? 3. What does the term “multiple alleles” mean? 4. Human blood type is an example of ____________ inheritance pattern. 5. How many different alleles exist in the population to determine blood types? 6. How many blood types exist in the population? 7. List all blood types (phenotypes) along with possible genotype combinations. 8. Alleles A and B are _____________________________. Alleles A and B are ___________ over allele O. 9. What is an antigen? What is an antibody? 10. How is each blood type different in regards to antigens and antibodies? 11. How are blood types matched for a safe transfusion? List all correct matches for donors and recipients. (CHART!) 12. Can a man who has type AB blood and a woman who has type O blood have a child with type O blood? (Show work) 13. If a woman heterozygous for type B blood and a man homozygous for type A blood have a child, what will be the genotypic/phenotypic ratios for the expected blood type? Show your work. 14. Can a woman who is type AB have a child that is type O? Explain your answer. X-linked Inheritance 15. What sex chromosomes do males have? Females? 16. What does “X-linked” gene mean? 17. What does “X-linked recessive inheritance” mean? 18. Name some human conditions that follow X-linked recessive inheritance pattern. 19. Suppose a woman is a carrier for muscular dystrophy and she mates with a man who is normal. --What are the chances that their baby will have muscular dystrophy? Will it be a boy or a girl? (Show your work) 20. Can a woman who is normal for colorblindness and a color blind man have a color blind daughter? (Show work) 21. Why are X-linked recessive disorders more common in males than females? Pedigrees 1. How do we show a female who has the trait being studied? 2. How do we show marriage? 3. How can we show a carrier for a trait? 4. Use the pedigree to answer the questions…. How many people have the trait being studied? a. How many females are in the pedigree? b. Could the trait be sex-linked recessive? If not, why not? If so, what is the genotype of II6? c. Could the trait be sex-linked dominant? If not, why not? If so, what is the genotype of II6? d. Could the trait be autosomal dominant? If not, why not? If so, what is the genotype of II6? e. Could the trait be autosomal recessive? If not, why not? If so, what is the genotype of II6? Polygenics 1. What does the word polygenics mean? 2. What does it mean to say that a trait is controlled by a single gene? 3. Are traits like height and skin color single gene or polygenic traits? 4. Sketch a graph to represent: a. Single gene trait in a population b. Polygenic trait in a population