I. The respiratory and circulatory systems
advertisement
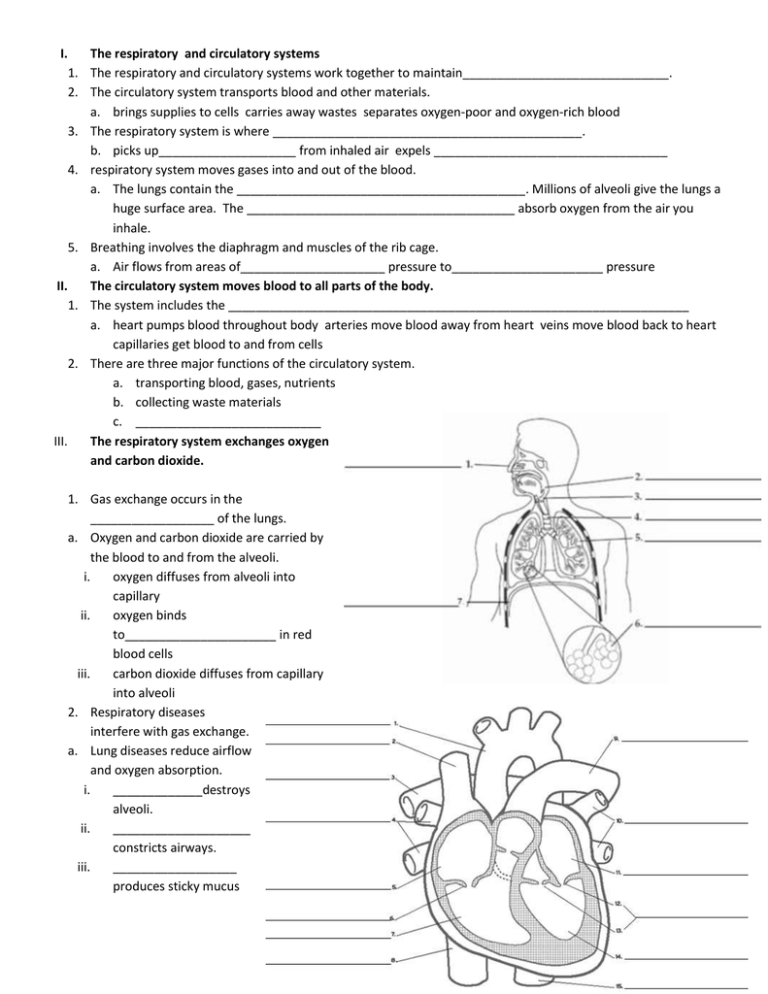
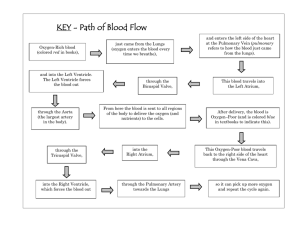
I. The respiratory and circulatory systems 1. The respiratory and circulatory systems work together to maintain______________________________. 2. The circulatory system transports blood and other materials. a. brings supplies to cells carries away wastes separates oxygen-poor and oxygen-rich blood 3. The respiratory system is where _____________________________________________. b. picks up____________________ from inhaled air expels __________________________________ 4. respiratory system moves gases into and out of the blood. a. The lungs contain the __________________________________________. Millions of alveoli give the lungs a huge surface area. The _______________________________________ absorb oxygen from the air you inhale. 5. Breathing involves the diaphragm and muscles of the rib cage. a. Air flows from areas of_____________________ pressure to______________________ pressure II. The circulatory system moves blood to all parts of the body. 1. The system includes the ___________________________________________________________________ a. heart pumps blood throughout body arteries move blood away from heart veins move blood back to heart capillaries get blood to and from cells 2. There are three major functions of the circulatory system. a. transporting blood, gases, nutrients b. collecting waste materials c. ___________________________ III. The respiratory system exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide. 1. Gas exchange occurs in the __________________ of the lungs. a. Oxygen and carbon dioxide are carried by the blood to and from the alveoli. i. oxygen diffuses from alveoli into capillary ii. oxygen binds to______________________ in red blood cells iii. carbon dioxide diffuses from capillary into alveoli 2. Respiratory diseases interfere with gas exchange. a. Lung diseases reduce airflow and oxygen absorption. i. _____________destroys alveoli. ii. ____________________ constricts airways. iii. __________________ produces sticky mucus IV. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The heart is a muscular pump that moves the blood through two pathways Cardiac muscle tissue works continuously without tiring. The heart has four chambers: two atria, two ventricles. _______________________________ in each chamber prevent backflow of blood Muscles squeeze the chambers in a powerful pumping action. The heartbeat consists of two contractions a. ______________________________, or pacemaker, stimulates atria to contract b. ______________________________ stimulates ventricles to contract 6. Blood flows through the heart in a specific pathway. a. _____________________________ b. oxygen-rich blood from lungs enters left atrium, then left ventricle c. _____________________________ d. oxygen-poor blood enters right atrium, then right ventricle 7. The heart pumps blood through two main pathways. a. ________________________________ occurs between the heart and the lungs. i. oxygen-poor blood enters lungs excess carbon dioxide and water expelled blood picks up oxygen oxygen-rich blood returns to heart b. ___________________________ occurs between the heart and the rest of the body. i. oxygen-rich blood goes to organs, extremities ,oxygen-poor blood returns to heart 8. Arteries, veins, and capillaries transport blood to all parts of the body. a. _________________ carry blood away from the heart. i. blood under great pressure ii. thicker, more muscular walls b. __________________ carry blood back to the heart. – blood under less pressure – thinner walls, larger diameter – valves prevent backflow c. Capillaries move blood between veins, arteries, and cells. 9. Blood pressure is a measure of the force of blood pushing against artery walls. a. ____________________________: left ventricle contracts b. ____________________________: left ventricle relaxes A. ___________________________ lack of oxygen to the heart B. ___________________ lack of oxygen to the brain C. Tissue damage due to lack of oxygen Blood is a complex tissue that transports materials. 1. Blood is composed mainly of cells, cell fragments, and plasma. 2. Whole blood is made up of different materials. a. ________________________ b. ________________________ 3. 4. a. b. c. d. V. 1. 2. c. _________________________________ d. _________________________________ Plasma is a key factor in maintaining homeostasis. a. molecules diffuse into and out of plasma b. contains proteins that stabilize blood volume c. contains clotting factors d. contains immune proteins Platelets and different types of blood cells have different functions. The _________________________________ manufactures most of the blood components. Red blood cells make up 40-45 % of all blood cells. i. transport oxygen to cells and carry away carbon dioxide ii. have no nuclei and contain hemoglobin White blood cells fight pathogens and destroy foreign matter. _____________________________ help form clots that control bleeding. The ____________________________________________ provides another type of circulation in the body. The lymphatic system is a major part of the immune system. a) tonsils filter bacteria and viruses b) thymus develops white blood cells c) spleen filters lymph, contains immune cells ____________________________________ help destroy pathogens, parasites, and foreign matter. 3. White blood cells attack infections inside the body. a. Phagocytes engulf and destroy pathogens. b. ______________________ destroy infected cells. c. ______________________ produce antibodies. 4. Functions of the Immune System a. ________________________________________________ b. ________________________________________________ ____________________________ any non-self substance capable of triggering an immune response An antigen can be a whole non-self cell, a bacterium, or a virus. Even allergens and cancerous cells _____________________________: Protein that recognize and bind to pathogens. Once the body has been exposed to a pathogen, the body creates memory B cells, reducing the chance of being infected again! ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM 1. immune cells develop in the _______________________________ 2. immune responses occur in the secondary organs __________________: filters and removes old and damaged red blood cells removes infectious agents and uses them to activate cells called lymphocytes ____________________: tissue insides bones that produces blood cells B cells and T cells are types of white blood cells ____________________: T cells mature here (learn their job) ____________________ small organs that filter out dead cells, antigens, and other “stuff” to present to lymphocytes ____________________ collects fluid (lymph) “leaked” from blood into the tissues and returns it to circulation ______________________________ 3 pairs masses of lymphoid tissue- helps protect against bacteria around the throat ______________________________: “safe house” for the beneficial bacteria living in the human gut The Immune Response Nonspecific Defense Mechanisms Specific Defense Mechanisms (Immune Response) First Line of Defense Goal: Second Line of Defense Goal: Details: Details: Third Line of Defense Two types of cells are involved: B cells: provide immunity against antigens and pathogens in the body fluids by making antibodies This is called _____________________________________________ Vaccines cause _______________________________ to produce _____________________________________ T cells: provide defense against abnormal cells and pathogens inside living cells In___________ diseases, white blood cells attack the body’s healthy cells.