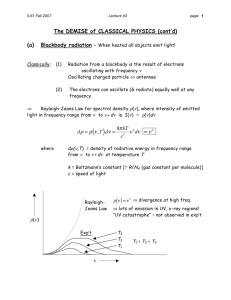
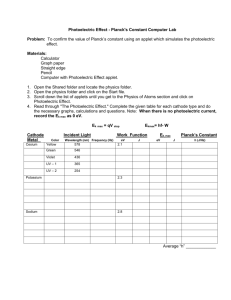
2.1-2.3
advertisement

Physics 222 D.S. Durfee The Physics Revolution of the 20th Century Relativity – physics of the fast Quantum Mechanics – law of the small – – – – – – Atoms: clocks, discharge lamps, lasers Molecules: chemistry Nuclei: fission, fusion Solid State: semiconductors Degenerate Matter: superconductors Coherence & Superposition: quantum computing Puzzles at the Beginning of the Twentieth Century Null result of the Michelson-Morley Experiment Ultraviolet Catastrophe Photoelectric Effect Maxwell’s Equations Spell the Demise of Atoms! Discrete atomic emission lines Blackbody Radiation Maybe better called “Thermal Radiation” Sun, hot burner plate, incandescent lights P eAT 4 u( )d Energy radiated per unit frequency i.e. the amount of light radiated which has a frequency between and dv. Cosmic Microwave Background from http://aether.lbl.gov/www/projects/cobe/CMB_intensity.gif COBE Map of Microwave Background from http://aether.lbl.gov/www/projects/cobe/COBE_Home/cmb_fluctuations_big.gif Blackbody Radiation Max Planck, Planck’s constant Found an empirical formula which fit the measured blackbody curve Looked for way to derive this empirical formula Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck Photo from http://www-groups.dcs.st-and.ac.uk/~history/PictDisplay/Planck.html Planck’s Law 8X u ( ) X / kT e 1 5 Max Planck, Planck’s constant E n fh Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck Photo from http://www-groups.dcs.st-and.ac.uk/~history/PictDisplay/Planck.html Are you pondering what I’m pondering? Why do we only have problems with the short wavelength (high frequency) part of the blackbody spectrum? Is the energy in a light mode quantized because light can only exist that way, or because the atoms that emit it can only emit quantized amounts of light? Hints of Quantum Mechanics Quantization of Matter – Very early idea, not really proven until ~1900 – Nature of mater not understood until much later (Rutherford, etc.) Quantization of Electric Charge – – – – Faraday’s law of electrolysis (1833) Zeeman, q/m J.J. Thompson discovers the electron Millikan’s oil drop Strange or Common Sense? Does it bother you that mass is quantized? Does it bother you that charge is quantized? What are some differences in the way that mass and charge are quantized? Pay Attention... You need to know this to do the homework! Statistics... What does u( )d really represent? It represents the electro-magnetic energy in a box per unit volume per unit frequency... How much electro-magnetic energy is there inside my oven? Quick Writing Assignment In one minute, write a short, clear, and concise paragraph which explains how Max Planck came to the conclusion that light was quantized. What did Einstein Win his Nobel Prize for? photo from http://www.th.physik.uni-frankfurt.de/~jr/gif/phys/einst_7.jpg Puzzles at the Beginning of the Twentieth Century Null result of the Michelson-Morley Experiment Ultraviolet Catastrophe Photoelectric Effect Maxwell’s Equations Spell the Demise of Atoms! Discrete atomic emission lines The Photoelectric Effect The Photoelectric Effect Photoelectric Effect Intuition What would a plot of current vs. light intensity look like? What would a plot of current vs. voltage look like? What would a plot of threshold voltage vs. light frequency look like? Wave Theory of Light and the Photoelectric Effect Existence of a threshold voltage Current increases with intensity Threshold is a function of light frequency No intensity threshold No time delay Fairly monochromatic electron energies Einstein’s Explanation... Planck was right! photo from http://www.th.physik.uni-frankfurt.de/~jr/gif/phys/einst_7.jpg What is the velocity of the electrons coming off the metal? 1 2 mv h 2 Quick Writing Assignment In one minute, write a short, clear, and concise paragraph which explains why the existence of a “threshold” voltage in the photoelectric effect suggests that light is quantized. Hmmm… Does Planck’s work on blackbody radiation prove that light is quantized? Does the photoelectric effect prove that light is quantized? But don’t we already have proof that light is a wave? Double Slit Interference Single Photon Interference X Rays Discovered in 1895 by Roentgen Generated when electrons hit target Materials transparent to them Not deflected by magnetic field Roentgen saw no interference and little diffraction! Bragg diffraction – explained in 1912 X rays are EM waves with wavelengths from 0.01 to 0.10 nm X-Ray Tube + Tungsten Target Anode - Filament Cathode Bragg Diffraction θin=θout θ d Bragg Diffraction 2d sin(θ) = m λ θ d Bragg Diffraction What do X-Rays Have to Do with Quantum Mechanics? Compton Effect Compton noticed that x-rays were “softer” after they had passed through a substance. Compton showed that this could be explained by treating scattering as “collision” between a photon of light and a particle of matter Compton Scattering of a “Photon” Before After ee- Are you pondering what I’m pondering? Yes, but how will we ever get that many rubber bands? No you buffoon! Why do you need x-rays to see this? Quick Writing Assignment In one minute, write a short, clear, and concise paragraph which explains why the Compton effect suggests that light is quantized. Puzzles at the Beginning of the Twentieth Century Null result of the Michelson-Morley Experiment Ultraviolet Catastrophe Photoelectric Effect Maxwell’s Equations Spell the Demise of Atoms! Discrete atomic emission lines Radiating Atoms