Lectures/notes/lecture 34 Gaussian beams, Fourier optics.pptx
advertisement
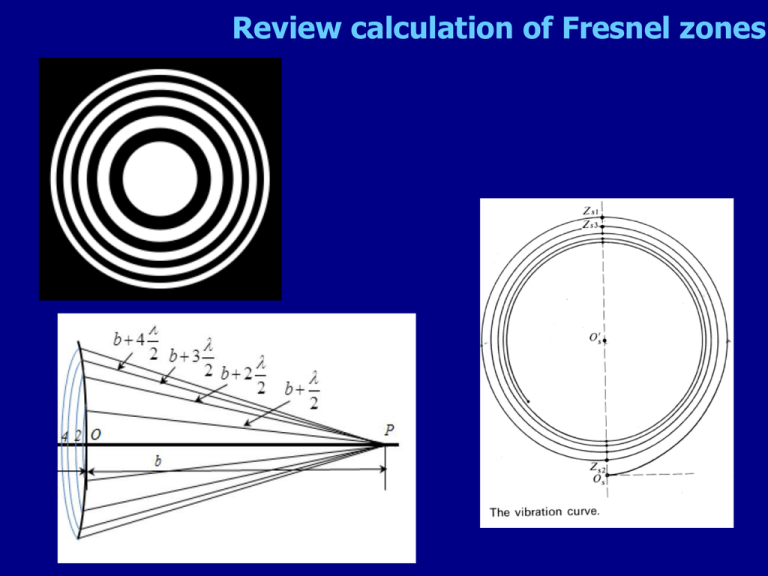
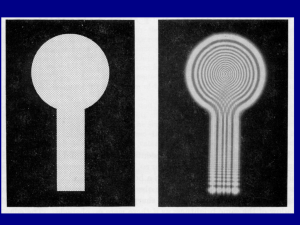
Review calculation of Fresnel zones For off-center points on screen, Fresnel zones on aperture are displaced …harder to “integrate” mentally. When white and black areas are equal, light at P’ is _____ a) dimmest b) brightest P’ Fresnel zone plates as “lenses” f is the distance used to calculate the zones. Will change with l Spatial resolution of image is r ,width of narrowest zone 1.22r min D Fresnel zone plates as “lenses” Thinnest zone included: r=25 nm. Used to image cell structures with soft xrays Fresnel zones are widely used in antenna-receiver tech L+l L+l/2 L No aperture: The zones here have to do with the phase of reflections from other objects How high to raise an antenna from the ground? If the ground reflects zone 2, you may do better lowering the antenna How tightly can we focus light? Ray picture Wave picture Diffraction from the focus of a gaussian beam Every finite-width beam is constantly diffracting. Must be always either diverging or converging! Self-divergence is largest for narrowest beams or tightest focus Fresnel method works well E x, y, z i ikz e e i k 2 2 x y 2z lz dxdy Eoe x 2 y 2 2 wo w2 z E , z Eo e e w z wo2 e i k x 2 y 2 2z e i k xx yy z k2 z ikz i i tan1 2 R z zo kwo2 zo: Rayleigh range. When z > zo, we are far enough zo 2 from focus to go back to rays (Fraunhofer regime). w z wo 1 z 2 zo2 beam width in terms of beam waist Wavefronts on gaussian beams Wavefronts are flat only at z=0, and have radius R for z > zo R z z zo2 z w z wo 1 z 2 zo2 (radius) kwo2 zo 2 D Given the ray geometry of focusing, find wo in terms of f,D f 2fl wo D Laser cavities: rays vs waves Laser cavity : besides finding the waist size, need also to find where focus (origin) is. R z z zo2 z It’s simple algebra: R must match mirrors, measured from the unknown focus. Fourier optical manipulation The “transform plane” is f after the lens. Suppose the aperture were removed. How would the plane wave look in the transform plane? With a different angle? In this FT of the letter E, sketch what you would see in the image plane if you blocked most of the dots arranged in the horizontal direction. a) I got it mostly right b) I got it mostly wrong. Where do you block the high spatial frequencies?. K-space Undersampling Jorge Jimenez Fully sampled k-space Low frequencies High Frequencies Vertical Image resolution Horizontal Image resolution