Announcements 9/2/11
advertisement

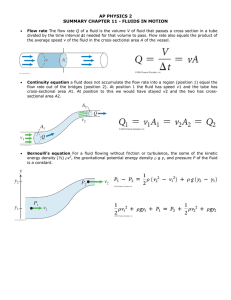
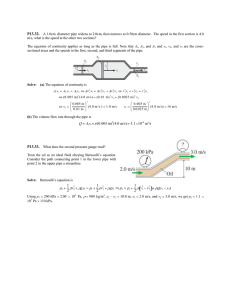
Announcements 9/2/11 Prayer Signup sheet, final time Any new people? Please see me after class. Don’t forget to come to office hours for help on HW a. Colton: MWF 2-3 pm (in underground lab) b. Chris: MW 5 - 6:30 pm, F 3:30 - 5 pm (UGL) Worked Problem An upside-down pyramid (side length s, height h) is placed in a fluid. rpyramid < rfluid, so it floats. In terms of the given quantities and fundamental constants, how far into the fluid does the pyramid settle? (It doesn’t tip.) s water level Answer: y 3 r p r f h h y=? Reading question (graded): Which of the following is NOT one of the four assumptions we make when we model “ideal fluids?” a. The fluid is incompressible b. The fluid is massless c. The fluid is nonviscous d. The flow is irrotational e. The flow is laminar The power of viscosity (watch on your own): http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W3YZ5veN_Bg Reading quiz (graded): Water flows from a pipe with large diameter into a pipe with smaller diameter. The speed of the water in the small tube will be _________ the speed in the large tube. a. greater than b. less than c. equal to The pressure of the water in the small tube will be _________ the pressure in the large tube. a. greater than b. less than c. equal to The Bernoulli Effect When a constantly flowing fluid has regions of different speed in its flow, the pressure of the fluid will be lowest in regions where the speed is fastest. What this doesn’t mean… Why would the fluid change speed? The “garden hose equation”, aka Eqn of C_____ Terminology: “volume flow rate” VFR A1v1 A2v2 Demos Bernoulli red fluid Floating ball Chimney effect Ball in funnel Cards & wooden block Piece of Paper Quick writing In the reading assignment for today, Ralph noticed two different equations both labeled "Bernoulli's Equation". One said, P1 + ½ rv12 + rgh1 = P2 + ½ rv22 + rgh2 whereas the other said, P + ½ rv2 + rgh = constant He asks you how they can both be the same equation when they look so different? And what it’s the value of the constant in the second equation, anyway? What should you tell him? Why does this happen? View #1: you’re a molecule right there in what direction is the net force? View #2: energy & work, per volume (yields “Bernoulli Equation”) Thought questions (ungraded): Water flows from right to left, from the little pipe into the big pipe. Ignore any friction or height change. The volume flow rate on the right will be ______ on the left a. greater than b. the same as c. less than The speed on the right will be ____ times the speed on the left. a. 1/9 b. 1/3 c. 1 d. 3 e. 9 Airplane Wings Principle 1: deflection Principle 2: Bernoulli “airfoils” http://www.av8n.com/how/htm/airfoils.html Curve balls Ball moving to the right (i.e. air moving to the left), with topspin Ping pong demo! Worked Problem: faucet r2 Pmain 3m r1 The faucet of radius r2 = 2 cm puts water out at 15 liters/minute. The pressure at the opening of the faucet is about 1 atm. The water main (r1 = 6 cm) is 3 m below the faucet. a. What is the speed of the water in the narrow pipe? b. What is the pressure in the main? Answers: 0.199 m/s; 1.307E5 Pa = 1.290 atm