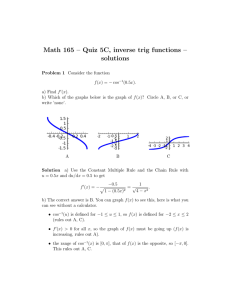
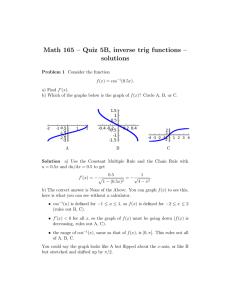
lecture 21 - beats, uncertainty
advertisement

Announcements 10/18/10 Prayer Found: Physics phor Phynatics book, still unclaimed Term project proposals due on Saturday night! Email to me: proposal in body of email, 650 word max. See website for guidelines, grading, ideas, and examples of past projects. Resonator boxes and the Beatles Flame standing wave video from website http://www.physics.byu.edu/faculty/colton/courses/phy123-fall10/ Colton “Fourier series summary” handout Demo: PVC pipe vs. “Spectrum Lab” Beats Demo: Tuning forks; Spectrum lab software “beat period” “beat frequency”: fbeat = |f1 – f2| (or wbeat = |w1 – w2| ) Beats, cont. Video: http://stokes.byu.edu/beats_script_flash.html Beats: Quick Math a b a b cos a cos b 2cos cos 2 2 Can be proved with trig identities cos(30t ) cos(31t ) 2cos 30.5t cos 0.5t carrier “envelope” (beat) Wait… is beat frequency 0.5 rad/s or is it 1 rad/s? (class poll) Review: Wave packets Adding cosines together with Mathematica, “sum of cosines.nb” http://www.physics.byu.edu/faculty/colton/courses/phy123fall10/lectures/lecture%2017%20-%20sum%20of%20cosines.nb What did we learn? a. To localize a wave in space, you need lots of frequencies b. To remove neighboring localized waves, you need those frequencies to spaced close to each other. (infinitely close, really) Review: How did I create this? Still mesmerizing… if someone wants a few extra credit points you could post it to Wikipedia’s group and/or phase velocity articles as an example of group & phase velocities being in opposite directions. Cos 1.23457 t 0.9 x Cos 1.20758 t 0.91 x Cos 1.18147 t 0.92 x Cos 1.13173 t 0.94 x Cos 1.10803 t 0.95 x Cos 1.08507 t Cos 1.06281 t 0.97 x Cos 1.04123 t 0.98 x Cos 1.0203 t Cos 1.1562 t 0.96 x 0.99 x Cos 1. t Cos 0.980296 t 1.01 x Cos 0.961169 t 1.02 x Cos 0.942596 t 1.03 x Cos 0.924556 t 1.04 x Cos 0.907029 t 1.05 x Cos 0.889996 t 1.06 x Cos 0.873439 t 1.07 x Cos 0.857339 t 1.08 x Cos 0.84168 t 1.09 x 10 1500 1000 500 500 10 20 1000 1. x Cos 0.826446 t 20 What I didn’t show you: (zoomed out) 0.93 x 1500 1.1 x Sine Wave What is its wavelength? What is its frequency? What is its location? When does it occur? Animations courtesy of Dr. Durfee Beats in Time What is its wavelength? What is its frequency? What is its location? When does it occur? Localization in Position/Wavenumber What is its wavelength? What is its frequency? What is its location? When does it occur? Beats in Both... Pure Sine Wave y=sin(5 x) Power Spectrum “Shuttered” Sine Wave y=sin(5 x)*shutter(x) Uncertainty in x = ______ In general: Power Spectrum Uncertainty in k = ______ 1 xk 2 (and technically, = std dev) Uncertainty Relationships Position & k-vector 1 xk 2 Time & w 1 t w 2 Quantum Mechanics: momentum p = k xp “” = “h bar” = Plank’s constant /(2p) energy E = w Et 2 2 What’s a “transform”? A one-to-one correspondence between one function and another (or between a function and a set of numbers). a. If you know one, you can find the other. b. Why? One representation might give you more insight into the function than the other. Example: ex = 1 + x + x2/2! + x3/3! + x4/4! + … a. If you know the function (ex), you can find the Taylor’s series coefficients. b. If you have the Taylor’s series coefficients (1, 1, 1/2!, 1/3!, 1/4!, …), you can re-create the function. The first number tells you how much of the x0 term there is, the second tells you how much of the x1 term there is, and so forth. c. Why use a Taylor’s series? Sometimes it’s useful. “Fourier” transform The coefficients of the transform give information about what frequencies are present Example: a. my car stereo b. my computer’s music player Fourier Transform 20 10 600 400 200 200 400 Do the transform (or have a computer do it) 600 10 Cos 0.9 x 20 Cos 0.91 x Cos 0.92 x Cos 0.93 x Cos 0.94 x Cos 0.95 x Cos 0.96 x Cos 0.97 x Cos 0.98 x Cos 0.99 x Cos 1. x Cos 1.03 x Cos 1.04 x Cos 1.05 x Cos 1.06 x Cos 1.07 x Cos 1.08 x Cos 1.09 x Cos 1.1 x Cos 1.01 x Cos 1.02 x Answer from computer: “There are several components at different values of k; all are multiples of k=0.01. k = 0.01: amplitude = 0 k = 0.02: amplitude = 0 … … k = 0.90: amplitude = 1 k = 0.91: amplitude = 1 k = 0.92: amplitude = 1 …”