lecture 19 - doppler, superposition
advertisement

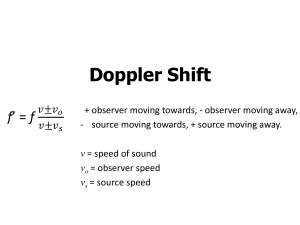
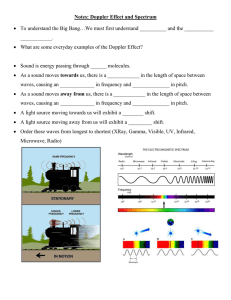
Announcements 10/13/10 Prayer Change to reading assignment: a. For Friday: 18.2 – 18.6 b. For Monday: 18.7 and PpP 4.1 Exams graded, returned to boxes. See email. Tutorial Lab will be a bit understaffed this Friday and Saturday because many TAs will be at a conference. A student asked me if you could ever have a situation where the group velocity and phase velocity were in different directions. I found out you can very easily create animated gifs with Mathematica, so here is his answer: http://www.physics.byu.edu/faculty/colton/courses/phy123-fall10/weirdwave.gif Thought question: You have a 1 volt amplitude sine wave. You want to go up 3 dB in power. How many volts do you need? (Recall: Power ~ amplitude2; true for voltages as well as waves on a string) a. 1 V b. 2 V c. 3 V d. 2 V e. 3 V Plane Waves Spherical Waves Doppler Effect What happens if the source is moving? What happens if the observer is moving? Key point: Frequency is _______________when the source and observer approach each other, ______________ when they go away from each other Demo: Doppler Speaker Stokes Come, Come, Ye Saints recording a. http://stokes.byu.edu/bells.wav The Pie Factory vbelt Spacing between pies = ? a. = v/f vs source speed f = vnew/old f = vold/new vo observer speed v speed of sound (vbelt) If observer moves toward source (pie maker), she wavelength but the pies are would measure the same ___________ speed coming at her at a faster ________ wavelength If source moves toward observer, the __________ speed doesn’t change shrinks, but the pie _______ Doppler, cont. Stokes Flash video a. http://stokes.byu.edu/doppler_script_flash.html Combine both effects: v vo f f v vs What does mean? Thought Question v vo f f v vs On a particularly windy day the wind is blowing at half the speed of sound. If I am standing still and a cow is flying towards me at the same velocity as the wind, by what factor will I hear his mooing shifted in frequency? a. f’ = (1/2) f b. f’ = (2/3) f c. f’ = (3/2) f d. f’ = 2 f e. None of the above. Thought Question v vo f f v vs If I am standing still and a cow is also standing still, by what factor will I hear the frequency his mooing shifted by if the wind is blowing at half the speed of sound in the direction from the cow to me. a. f’ = (1/3) f b. f’ = (2/3) f c. f’ = f d. f’ = 3 f e. None of the above. Light source (galaxy) traveling toward you: frequency will _____, wavelength will _____. See HW 19.4 for equation Astronomy How far away is a galaxy? Hard question Edwin Hubble, 1929: Distance away proportional to speed a. Distance measured through supernovae observations b. How did he measure speed? – Doppler shift of spectral lines! That’s now a standard technique for today’s astronomers when they want to measure distances… just measure Doppler shift. Hubble’s Law and the Big Bang a. (Yes, it’s OK for LDS to believe in the Big Bang…) Sonic Boom http://stokes.byu.edu/boom_flash.html http://stokes.byu.edu/boomray_script_flash.html Happens with all types of waves whenever the sources is traveling faster than the speed of the wave… …so, what is “sonic boom” of water waves? Sonic Boom Sonic boom manifested by condensation of water in air θ sinq = vsound/vsource = 1/“Mach number” Sonic Boom Sonic boom of bullet in flight (holographic interferometry?) How fast is the bullet traveling? a. Mach # = 1/sinq Reading Quiz Which term did not appear in the discussion of wave interference for today’s reading assignment? a. antinode b. constructive c. destructive d. path length e. superposition Interference Path length a. Constructive b. Destructive Video: Two outdoor speakers Demo: Moire pattern transparencies Demo: Hearing test Demo: 2-speaker interference a. Speed of sound = ? Ripple Tank image: wikipedia