East Hoke Middle School 2015-2016 Unit Lesson Plan
Unit Description: Geologic Time: Dating of Rocks
Timeframe: 1 week
Common Core State Standard (s):
East Hoke Middle School
2015-2016
Unit Lesson Plan
Grade: 8
All Units Must Include Rubrics, descriptive feedback for students, and an opportunity for students to redo the task based on the feedback.
Products must afford students the opportunity to cite from primary and secondary text.
Essential Question( s):
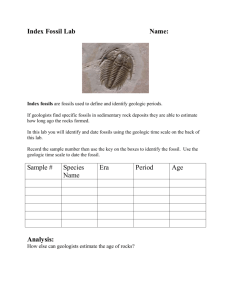
8.E.2- Understanding the history of Earth and its life forms based on the evidence of change recorded in fossil records and landforms.
8E2.1- TLW infer the age of Earth and relative age of rocks and fossils from index fossils and ordering of rock layers (relative dating and radioactive dating).
Literacy Common Core State Standard (s):
Information and Technology Standard (s):
College and Career Readiness Standard (s) : (What connection does this unit have to college and career readiness?)
Learning Target(s): (What will students know & be able to do as a result of this lesson?)
1.
How have geologists used the following to help to determine and understand the Geologic time scale: the Law of Superposition, the Law of Crosscuts, index fossils, igneous intrusions, faulting of rock layers, and radiometric dating?
Focus Question (s): (Questions students can answer at the end of a lesson)
DOK1:
●
What does the Law of Superposition state?
●
What are the most common index fossils and where do they occur in the
DOK2:
Geologic time scale?
●
How can the relative age of rock layers be determined by using index fossils (by using an example)?
●
How does a geologist deconstruct rock layers, intrusions, faults, and index fossils to determine how landforms developed over time?
●
How do geologists determine the number of half-lives which have occurred?
Relevance/Rationale: (Why are the outcomes of this lesson important in the real world? Why are these outcomes essential for future learning?)
Define radioactive decay, half-life, absolute age, Law of
Superposition, index fossil, nonconformity, and relative age.
To determine conditions of the geologic past helps one understand current changes and relationships between landforms and environments/organisms.
Determine the relative age of rocks by using superposition, crosscuts, and index fossils.
Understanding how geologists have determined the age of Earth will relate to overall geologic timescale.
Determine the absolute age of rocks by using radiometric dating
(calculating half-life of rock sample).
Essential Vocabulary: radioactive decay, half-life, absolute age, Law of Superposition, index fossil, nonconformity, and relative age
How will this Unit address reading, speaking, listening, writing, and technology?
S.I.O.P strategy:
Pre-Assessment & Prior Knowledge Activities
Anticipation Guide Y/N on foundational facts of Earth’s geologic timescale.
Quick Review of processes that change the Earth’s surface: rock cycle, earthquakes, volcanoes, mountain formation, and Theory of
Plate Tectonics.
Pacing
Day 2
Teacher Input (Modeling)
(Whole Group Instruction)
Practice using scale in timelines through example of school career.
Day 1 Introduce new vocabulary using www.quizlet.com
activities.
Whole-group reading activity with graphic organizer. “History of the Earth”
Categorizing Organizer.
Instructional Strategies
(Include Guided and Independent Practice)
Scaled model of major geologic time events using 46-m rope and activity “pins.” Students will use information from text, reading selection to place events where they think they should be in the model.
Prewriting activity for paragraph on the reading selection.
Students will pair up and use strips of cash register paper to develop their own
Closure
(Formative Assessment)
What evidence from the reading selection supports the current geologic timescale? Cite specific examples in a 5-7 sentence paragraph.
Day 3-
5
Overview of how to use Alice program, where to access the file, demonstration of a few science related Alice worlds to allow students to see what they can do.
Guide students to open Alice on PCs.
Students will individually run through Alice World,
“Determining Geologic Time Scale, Part 1: Relative Age.”
Answering the questions in the world activity.
Unit Closure/ Summative Assessment
“Determining Geologic Time Scale, Part 2: Absolute Age.”
Answering the questions in the world activity.
Criteria for Success: (How will Modifications/Accommodations you & your students know if they have successfully met the outcomes?
What specific criteria will be met in a successful product/process ? What does success on this lesson’s outcomes look like?)
Common assessment
Completion of Alice activities with evidence of complete note outline, and quiz questions.
STEM Connection
Description of Activity
Preview of Alice world examples Engagement The activities in this section capture the participants’ attention, stimulate their thinking, and help them access prior knowledge
Exploration In this section, participants are given time to think, plan, investigate, and organize collected information
Complete Alice interactive worlds. manipulating through different scenes and questions.
Explanation
Participants are now involved in an analysis
After Alice world completed, students will
STEM STANDARD
of their exploration. Their understanding is clarified and modified because of reflective activities. Students must cite from the text.
Extension This section gives participants the opportunity to expand and solidify their understanding of the concept and/or apply it to a real world situation.
Evaluation
Evaluation occurs throughout the lesson.
Scoring tools developed by teachers and participants target what participants must know and do. Consistent use of scoring tools improves learning.
Resources and materials used
Reflection complete follow-up activity of “radioactive
M&Ms” and relative 3d clay model
Students after a tutorial on adding objects, dropping billboards, and adding dialog will make an alice world on a Geologic Time period.
Students will add one question to the world.
Students will share their Alice world on
GoogleClass and present their world to the class.
Alice world will be scored using a rubric.