school of history
advertisement

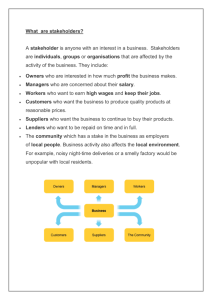
What determines history? Not great men Not pivotal moments Social class Economic realities HISTORY FROM BELOW Marxist interpretations: Telelogical Everything moves towards a certain end, a final result The final result: a classless human society What is ‘Historical materialism’? • In order to understand human society and historical development you have to study how humans produce and reproduce the material requirements of life • To successfully produce these material requirements people have to enter into ‘production relations’ – the relationship between those who do the work and those who own the ‘means of production’ The stages of historical materialism Marxists identified several historical stages of this relationship: Tribal (primitive communism) Ancient (slaves and slave owners) Feudalism (serfs and landowners) Capitalism (owners and workers) Society (politics, culture, laws etc) is shaped by these relationships How does society change? The dominant class is overthrown by a new emerging class Why was this interpretation different? Introduced the idea of ‘coherence’ into human history Suggests that historical change is as a result of the struggle between different classes Examined ‘history from below’ Criticisms