PERANCANGAN SKEMATIS
advertisement

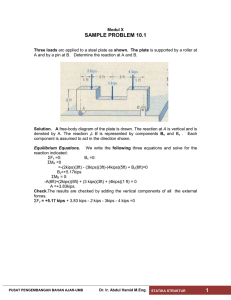
8 PERANCANGAN SKEMATIS 1. Merancang /Designing 1. Traditional methods 1. Crafmant do not / often can not, draw their works & neither can they give adequate reasons for the decisions they take. 2. The form of a craft product is modified by covaless failures and successes in a process of trial & error over many century 3. The weakness of changing only one-thing at a time, and relying on precedent when what seems to be called for is a complete reorganization of the form as a whole 4. The form o fthe product it self, which is not changed except to correct error or to meet new demands 5. Designing to day, - the shape of the product is a whole - the reason for the shape – experiment with the product it self 2. Design by Drawing 1. Spesifying dimentions in advance of manufacture make it possible to split up the production work in to separate pieces with can be by different people 2. Drawing before making made possible the planning 3. The division of labour made possible by scale drawings can be used not only to increase the size of the product but also to increase their rate. 3. The need for now methods 1. How do traditional designers cope with the complexity ? – Long period for ‘ incubation’ – A change of set – Enemy originallity – mental rigidity & wishfull thingking 2. In what ways are modern design problems more compliated than traditional ones ? PUSAT PENGEMBANGAN BAHAN AJAR-UMB Ir.Joni Hardi MT. PERC. ARSITEKTUR 5 1 Performance systems Cimplexity of systems New Methods Problem Designers as black box Input Output Black box Brainstarming Synectics Analogies Designer as magicians - Output is governed by input Output canbe speeded up, but more random Output is relevant to the problem is dependent open within himse Depend on inteligent control over the form / problem structure Designers as glass box Output 1 max Output 1 Reseach Action Design Action-2 Output 2 Characterisics : Designers as computer PUSAT PENGEMBANGAN BAHAN AJAR-UMB - objectives, variables and criteria are fixed in advance analysis is completed, or at least attempted, before solution are sought evaluation is largerly linguistic and logical (as opposed experimental) Ir.Joni Hardi MT. PERC. ARSITEKTUR 5 2 Designers as self-organizing system Design Effect : 1. That which carries out the search for suitable design 2. That which control and evualuates the pattern of search (strategy control). Designing as a three stage process 1. Divergence ; characteristic : - The objective are unstable & tentative - The Problem boundary are unstable & tentative - Evaluation is deferred 2. Transformation ; - a pattern - Problem boundary fixed, critical variabled are identified - Split up into subploblem - Succesful transformation : the freedom to change sub goals 3. Converge ; persistence and rigidity of mind and methods is a virtue : flexibility & raegueness are to be stunned. input D C T Design Strategy - Linear strategy Stage 2 Stage 1 - Stage 3 Cyslic strategy Stage 1 Stage 2 brief PUSAT PENGEMBANGAN BAHAN AJAR-UMB Proceedor return Stage 3 Ir.Joni Hardi MT. Proceedor return Stage 4 PERC. ARSITEKTUR 5 3 - Branctring Strategy Stage 2a Stage 4 Stage 2b Stage 1 Select 4 or 5 Stage 3 Stage 6 Stage 5 Stage 2c selection stage Parallel stage - alternative stage in oremental strategy Adjust existing solution to accommodate modification Re-assess an existing solution outcome Explore a few minor modification Example 1. Brief : To design a car that is very easy to park 1. Brief 4.1 Brainstorming 3.2 Literature searding 2. design situation 2. 5.8 classification 3. problem structure 1.4 man machine system designing 6. Final design PUSAT PENGEMBANGAN BAHAN AJAR-UMB Ir.Joni Hardi MT. PERC. ARSITEKTUR 5 4 Contoh Perancangan Skematis, Denah & Tampak-Potongan BLOCK PLAN PUSAT PENGEMBANGAN BAHAN AJAR-UMB Ir.Joni Hardi MT. PERC. ARSITEKTUR 5 5 PUSAT PENGEMBANGAN BAHAN AJAR-UMB Ir.Joni Hardi MT. PERC. ARSITEKTUR 5 6 PUSAT PENGEMBANGAN BAHAN AJAR-UMB Ir.Joni Hardi MT. PERC. ARSITEKTUR 5 7 PUSAT PENGEMBANGAN BAHAN AJAR-UMB Ir.Joni Hardi MT. PERC. ARSITEKTUR 5 8