Introduction to Computing
advertisement

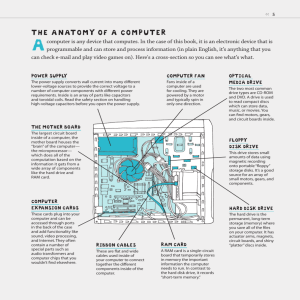
Introduction to Computers Essential Understanding of Computers and Computer Operations Topics The term “computer” Four basic computer operations Data and information Principal components of computer Data storage devices and usage Software The Internet & WWW What is a Computer? A programmable machine that inputs, processes, and outputs information An electronic device for storing and processing data Composed of hardware and software Can exist in a variety of sizes and configurations Examples What Do Computers Do? Input, Process, Output, & Store data Input Process Store Data Output Input, Processing, Storage, and Output Devices What is Data? The raw material of information Contain facts w/o interpretations The information entered into, and stored within a computer or file Used by applications to accomplish tasks Unprocessed information E.g. text, numbers, images, audio, & video What is Information? Contains meaning, knowledge, instruction, communication, & representation of data Result of processing, manipulating and organizing data in a way that adds to the knowledge of the person receiving it The output of information systems Flow of Computing Data Processing Information Example Pat Brown 1001 Jump Street Shoreline, WA 98123 $25 per hour 40 hours Retrieve data Calculate weekly wage: $25 X 40 hours = $1000 Send information to output device Principal Components of Computer Input devices System units Storage (memory) devices Importance of Saving Output devices Input Devices Keyboard, mouse, scanner, & etc System Units CPU (Central Processing Unit) Random Access Memory (RAM) Secondary Storage Devices Central Processing Unit (CPU) Main processor of a computer that makes everything work Interprets & carries out the basic instructions Performs all the instruction, logic, & mathematical processing Storage (memory) Devices Two types: Primary: Temporary memory for dynamic access by the processor (CPU) RAM (Random Access Memory) Secondary: Primary & Secondary For large data storage, e.g. hard disk drive RAM is much faster than disk drives for dynamically interacting with the processor Random Access Memory (RAM) – the Primary Memory Temporarily stores instructions and data waiting to be processed by the processor Memory units are measured in kilobytes, megabytes, or gigabytes 1 kilobytes = 1,000 bytes = 1,000 memory locations ≈ 1,000 characters 1 megabyte (MB) = 1 million memory locations 1 gigabyte (GB) = 1 billion memory locations E.g. 512 MB = 512 million characters 1 MB can hold approx. 500 pages of text Secondary Memory (Semipermanent) Magnetic Disks Optical Disks Hard disks, floppy disks, zip disks CD-ROM, CD-R (Recordable), CD-RW, DVD Flash Memory Cards USB flash drive: Small, lightweight, & large storage capacity Importance of Saving and Saving Often When using an application, data is stored in RAM temporarily When the file, application, or computer closes, the data in the RAM is erased Where do I save the files? At the Lab: Removable disks such as floppy, zip, or USB. At home: Hard drive (C:\) or any removable disk. Never remove a disk while the light flashes Saving on an existing file replaces the old data with new (Save vs. Save As) Importance of Data Backup All secondary storage devices such as floppy and hard drive disks eventually fail, and you lose the data Make backup files weekly, if not daily If you have a computer, use the hard drive or a removable disk as your backup Otherwise, use the second removable disk Output Devices Printers Monitors and more Personal Computers PC, Mac, and other microcomputers Desktop, Laptop, PDA Windows, Mac OS, Linux, etc. Increasingly more capable, portable, affordable, and mobile System Software Manages computer operations Instructs computer how to perform functions of loading, storing, and executing an application software and how to transfer data Examples: Windows, Mac OS, Linux, & etc. Application Software Programs that tell a computer how to perform tasks and produce information Categories: Word processing Spreadsheet Database Presentation graphics Web and Internet access Desktop publishing / image editing / multimedia editing The Internet and WWW The Internet is the world’s largest network Uses: Send messages (e-mail) Access a wealth of information Electronic commerce Online meeting Access entertainment and multimedia WWW (World Wide Web) The more popular component of the Internet Web page: A document containing text, hyperlinks, images, & other multimedia contents Web site: A collection of Web pages Communications Devices Modem Network card Router Wireless modem, network card, & router