Karen Chan
advertisement
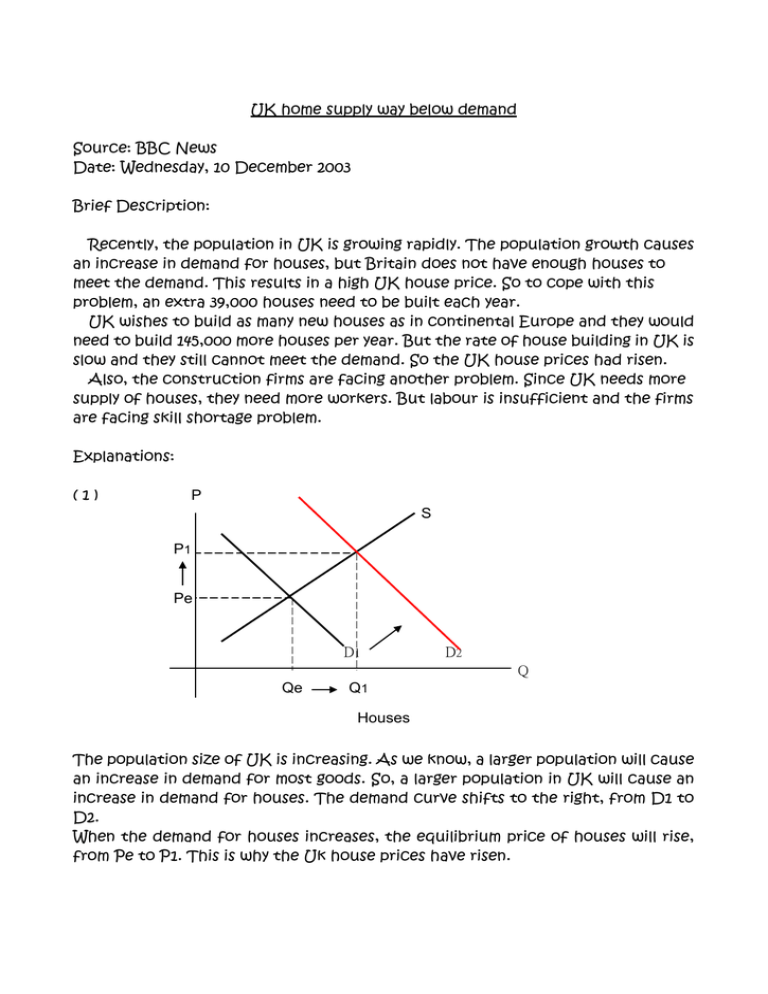
UK home supply way below demand Source: BBC News Date: Wednesday, 10 December 2003 Brief Description: Recently, the population in UK is growing rapidly. The population growth causes an increase in demand for houses, but Britain does not have enough houses to meet the demand. This results in a high UK house price. So to cope with this problem, an extra 39,000 houses need to be built each year. UK wishes to build as many new houses as in continental Europe and they would need to build 145,000 more houses per year. But the rate of house building in UK is slow and they still cannot meet the demand. So the UK house prices had risen. Also, the construction firms are facing another problem. Since UK needs more supply of houses, they need more workers. But labour is insufficient and the firms are facing skill shortage problem. Explanations: (1) P S P1 Pe D1 D2 Q Qe Q1 Houses The population size of UK is increasing. As we know, a larger population will cause an increase in demand for most goods. So, a larger population in UK will cause an increase in demand for houses. The demand curve shifts to the right, from D1 to D2. When the demand for houses increases, the equilibrium price of houses will rise, from Pe to P1. This is why the Uk house prices have risen. (2) P S1 S2 P1 Excess demand 2 Pe Excess demand D2 D1 Q Qe Q1 Houses We know that the quantity demanded for houses is larger than the quantity supplied of it, there is an excess demand as shown in the graph. To minimize the problem, the UK builds more new houses and there is increase in supply. The supply curve shifts to the right, from S1 to S2. The size of excess demand drops to excess demand 2. It is because of the low rate of house building, so the supply of houses still cannot meet the demand. There will be a tendency for price to increase, therefore the UK house prices had risen. At the higher price, producers will increase their quantity supplied, but consumers will buy less. The size of excess demand will drop. (3) P S Pe P1 Excess demand D Qs < Qd Labour For building more new houses, more labour is needed. But the number of labour is insufficient. The quantity demanded for labour is larger than the quantity supplied of labour (Qd > Qs), and this is an excess demand. (4) P S P2 P1 D2 D1 Q Q1 Q2 Cement Cement is a factor for production. People have a demand for it because it helps build houses. The demand for cement is a derived demand. When the demand for houses increase, people will need more cement. The demand for cement will also increase, from D1 to D2. The equilibrium price of cement will rise, from P1 to P2. The equilibrium quantity transacted will rise, from Q1 to Q2. Karen Chan ( 1 ), Candy Cheung ( 5 )



