2005 Report
advertisement

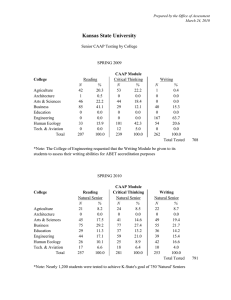
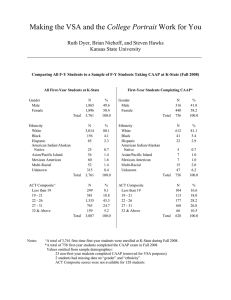
RESEARCH BRIEF COLLEGIATE ASSESSMENT OF ACADEMIC PROFICIENCY (CAAP) CRITICAL THINKING RESULTS Introduction The Assessment Committee (Committee) wished to track “critical thinking” skills of a test cohort of students from each academic division to pilot the CAAP test, which has a 40-80 score range. In no way were students who took the test selected to be representative of the overall student population or even the student population within the division. Consequently, the results of this brief are qualified and should not be generalized to the entire student population, not used for decision-making beyond the small sample of students taking the test. This report is part of the pilot process to gauge the types and variety of data available through the CAAP test. Participating Divisions Average Score by Division 44 50 40 30 20 10 0 25 14 6 Business Community Services Health Professions Social Sciences Average CAAP Score Number of Test Takers Test Takers by Division 65 64 64 63 63 62 62 61 61 60 59 Business Division Community Services Health Professions Social Sciences Division Eighty-eight Volunteers were selected from each division representing four distinct majors. Scores in each division were relatively close to the cohort average of 62. While Community Services and Social Services recorded the lowest and highest average scores by division, respectively, they also contributed the lowest amount of test takers. Test Effort Average CAAP Score by Effort 63 50 41 40 30 22 17 20 8 10 0 Tried My Best Gave Moderate Effort Effort Gave Little Effort No Response Average Score Number of Test Takers Reported Effort on CAAP Test 61.9 62.5 62.4 62 61 59.8 60 59 58 Tried My Best Gave Moderate Effort Gave Little Effort Reported Effort No Response The CAAP test asks volunteers to report the level of effort they put into the assessment, since the test has no bearing on GPA or graduation. Nearly 72% of test takers reported at least a moderate effort. In fact, those reporting a moderate effort achieved a higher average score than those reporting their best effort. Not surprisingly, those reporting little effort reported the lowest scores – although only 3.3% less than those trying hardest. What do the results reflect on a macro-scale? NCSC Frequency Distributions CAAP Scores, Critical Thinking The chart on the left is scoring frequency. There is definitely a mid-level scoring frequency of 61. While the distribution doesn't reflect the classic bell curve pattern, the scores are clustered together pretty tightly to the average. In fact, the mean (average) and median (middle number in series) are both 62. 14 12 Frequency 10 8 6 4 2 0 -2 0 20 40 60 80 100 CAAP Score NCSC Critical Thinking Cumulative Percentage National Critical Thinking Cumulative Percentage 100 80 Cumulative Percentage Cumulative Percentage 120 60 40 20 0 0 20 40 60 Scaled Score 80 100 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 0 20 40 60 Scaled Score The two above charts reflect display both NCSC and national cumulative percentages for the critical thinking test. A cumulative percentage is defined as the percentage of scores falling at or below a given score. The CAAP score range is 40-80 for each objective. The national figure is based on CAAP-tested sophomores at 2-year institutions. The comparison indicates a mean NCSC score of 62.0, compared to a national mean of 60.5. Further, the standard deviation for NCSC students is 4.5, compared to 5.4 for national. This means the NCSC scores are much more tightly clustered around the mean than the national scores, resulting in a steeper curve on the scatterplot chart. In other words, NSCS scores better on the mean, but tends to have fewer "outlier" scores on either end than the national students. 80 What do the results reflect when considering certain attributes of cohort? The test breaks out results according to various demographic and academic attributes. For the sake of brevity, this brief will present charts only on areas deemed in potential need of further review. Results by ethnicity were inconclusive since 97% of test takers responded being white. There was less than 2% difference in male/female scores and full-time/part-time scores were exactly the same. Average CAAP Scores by Age CAAP Scores 33 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 18 15 13 9 19-20 21-25 26-30 31-39 65 64 63 62 64 63 63 61 61 60 59 58 60 > 40 19-20 21-25 26-30 Age Range 31-39 > 40 Age The test takers spanned a wide variety of ages, with 35 percent reporting they were 31 and older. While the 26-30 age range reported the highest average score, it also was the smallest sample size. One issue that could be investigated further is the lower scores achieved by those 40 and older. Average CAAP Score Average CAAP Score by GPA 66 64 62 60 58 56 64 61 61 2.5-3.0 3.0-3.5 59 2.0-2.5 > 3.5 Cum ulative GPA The test takers also spanned a wide variety of GPAs, although 69% ranked 3.0 or higher. Those with the highest GPAs scored 3.2% above the average, while those with the lowest GPAs scored 4.8% below the average although it is a small sample. Those in the two middle ranges each scored 61. Again, this demonstrates there is not an extremely wide variance from the average. Educational Plans by Average CAAP Score Respondents on Educational Plans 80 62 60 40 20 11 13 Return to NCSC Transfer 0 65 CAAP Score Number Taking Test Number Taking Test Age Range of Test Takers 64 64 63 62 62 Transfer Other 62 61 Intentions Other Return to NCSC Intentions Finally, test takers were asked to list their immediate intentions for educational plans – 12.5% responded they would return, 14.8 percent responded transfer and 70.4 percent listed other (not specified). Those noting an intention to return scored 3.2 percent higher than the other groups. Future Issues to Consider During this brief analysis, two issues arose which the Committee should consider for future CAAP tests: Is it possible to obtain a clarification or further breakout of “other” for future educational plans? The CAAP test asked respondents to list education level by freshmen – senior. Many students marked junior and senior, although NCSC is only a two-year college. Is it possible to clarify this question with CAAP or when administering the test?