Notes: present change and future climate
advertisement

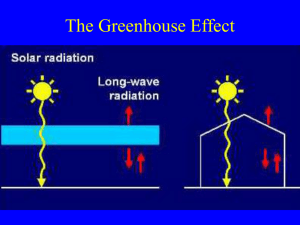
Welcome! Please get out homework for a stamp: Two questions on RCP’s, bracket map, 10 terms Please read the board. Kahoot practice! What do these have in common? Climate and civilization Human civilizations change when climate changes 20,000 ybp (years before present) ice age: Bering strait freezes, people migrate to the Americas 8,000-7,000 ybp – warming period Mesopotamia flourishing, Jericho established suddenly 950 CE (common era – used to be called AD) Leif Erikson – 950 CE sails to Greenland from China Little Ice age – 1550-1850 Irish Potato Famine Dust Bowl – 1930’s Mild but persistent La Nina conditions coupled with changes of sea surface temperatures + poor farming practices SPM 1: Current observations What details need to be added? Correlation/causation pg 5 CO levels currently 2 Mauna Loa Observatory - Hawaii CO2 at beginning of Industrial revolution: 280 ppm Current CO2 levels: 398ppm (watch the movie – when is CO2 highest? Where??? Why???) Figure 4 – Current observable effects Circle most certain effects What are the implications? Examples from the news? Which is of greatest concern to Houston/US/you? SPM figure 5 What are the predictions? How do they get from CO2 to change in temperature? Predicting future climate How do they do that anyway? Global Circulation model Global Climate Models: GCM’s Computer model divides atmosphere into chunks. Current conditions programmed into each chunk: temp, wind, [GHGs], etc Computer can generate current and future global temperature averages based on [GHGs] Limitations of GCMs Complexity Feedback loops (not included in GCMs) (+)Melting tundra permafrost and lower geologic formations– 500 billion tons CH4 (+)Loss of albedo effect with ice (-)Increasing albedo effect with clouds (+) Increasing greenhouse effect with evaporating water Role of ocean and CO2 absorption Lesson from the Ozone Hole: 1930’s – CFCs invented 1970’s – mechanism of O3 destruction understood; models of possible effects suggest general thinning of O3 layer 1985 – Ozone hole documented as complete surprise – models were wrong. 1987 – Montreal Protocol ratified Predictions: If CO2 goes to 450ppm by 2050, +2oC (3.6oF) CO2 to 550ppm by 2050, +3oC (5.4oF) In 50 yrs, expect 4oC warming (2012 World Bank Report) CO2 of 350ppm is considered sustainable by climatologists Tipping point is probably at 2oC (the point at which change due to human activity brings about sufficient new processes in nature to make any human reversal of the change impossible. ) Homework tonight Read SPM 2.1 and 2.2 add details to your bracket map. Studystack.com to review terms: search IPCC terms WHS or carolynklein Chasing Ice – ice core graphs, effects, glaciers Big seven effects Change in precipitation patterns More severe weather events (droughts, floods, extreme hot/cold) Rising sea levels (glaciers melting) Changing seasons – earlier spring and shift of biomes away from equator Increased insect-borne disease Decreased availability of fresh water Acidification of ocean and bleaching of coral reefs (H2CO3) Sea level rise .7 m by 2100 Melting glaciers add water volume to ocean (Greenland ice sheet stores enough water to raise sea level by 5-7 meters) Thermal expansion creates most of the increase Where will the environmental refuges go? 50% of global population lives within 100 miles of a coastline. Shift of biomes away from equator Trees can shift 5mi/10years through seed dispersal Shift of habitat to higher latitudes and elevations Potential large loss of biodiversity Fig. 11–9 © Brooks/Cole Publishing Company / ITP Don’t forget!