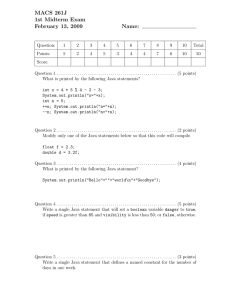
Variables and Assignment
advertisement

Lecture 1:
Comments, Variables, Assignment
Definitions
• The formal (human-readable) instructions that
we give to the computer is called source code
• The compiler translates our source code into a
format that the computer can understand
Comments
• Comments are places in your source code where you write
stuff intended only for humans to read
• The compiler always totally ignores comments, as if they
weren't even there
• There are two types of comments in Java
• Single-line comments
–
–
–
–
Everything including the ``//'' and after on that line is ignored.
System.out.println("Hello World!"); //Greet the user
//This is a comment, too.
``Commenting-out'' code is a quick way to make a line of code
do nothing temporarily.
• // System.out.println("Hello World!");
• Multi-line comments
– Start with ``/*'' and end with ``*/''
– /* They can be just one line, too */
• Here is a Java program that illustrates different
ways to use comments:
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
ALL STUDENTS COMPLETE THESE SECTIONS
// Title:
HelloWorld2
//
// Author:
Michael Kowalczyk
// CS Login:
mkowalcz
// Lecturer's Name:
// Lab Section:
//
public class HelloWorld2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//This is a single line comment
/* This
is a multi-line
comment
*/
//Note that the following System.out.println statement is
//commented out, so it won't do anything.
//System.out.println("Hello, World!");
System.out.println("Hi!"); //Prints a greeting to the user.
}
}
Identifiers
• Identifiers are the names that we give to different
things (variables, methods, classes) in Java.
– Rules for making identifiers:
•
•
•
•
Identifiers can be made up of a-z, A-Z, 0-9, as well as _ and $
Identifiers cannot start with a number
Can't be a ``reserved word'' (public, void, class, int, etc.)
Don't try to memorize all the reserved words; just remember that
they are words with special meaning in Java
• Case sensitive, so myIdentifier is different than
MyIdentifier or MYIDENTIFIER.
• Identifiers in this code fragment have been underlined.
• Some examples of good/bad identifiers?
Data Types
• There are precisely two categories of data
types in Java: primitives and classes.
• There are only 8 primitive types and they are
all listed here
– The most important ones in this course are int,
double, boolean, and char
• A ton of classes are already given in the Java
libraries, and we can make new ones, too.
Variables
• Every variable has a name, type, and contents
– The name must be an identifier
– The type is fixed, and is either one of the 8 primitives or some class
– The contents must match the type, and can be changed over time (unlike
typical variables in math)
• In general, you can declare (that is, define) a variable by using a statement
of one of the following 2 forms:
– type identifier;
– type identifier = value;
• You have to declare a variable before using it and you can only declare it
once.
• If you want to change the contents of a variable once declared, you just
use an assignment statement, of this form:
– identifier = value;
• Let's write up an example to make this all clear
•
/*
* This application class demonstrates how to declare, assign, and use
* variables with primitive types.
*/
public class Primitives {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Declare a variable called letter that can hold a char
char letter;
//Declare a variable called myInteger that can hold an int, and make it 3
int myInteger = 3;
//Store the character "a" in the variable called letter
letter = 'a';
System.out.println(letter); //prints out the letter a
//Declare j (which can hold an int) and make it equal 5
int j = 5;
j = j - myInteger; //evaluates 5-3 and stores the result in j
System.out.println(j); //prints 2
double d = 3.7;
//myInteger = d; //causes compile-time error (can't convert)
d = myInteger; //But this conversion is ok.
}
}
System.out.println(myInteger); //prints 3
System.out.println(d); //prints 3.0
We'll now start our first lab
• Mind-Reading Number Trick
1) Think of a number, any positive integer (but
keep it small so you can do computations in your
head).
2) Square it.
3) Add the result to your original number.
4) Divide by your original number.
5) Add, oh I don't know, say 17.
6) Subtract your original number.
7) Divide by 6.
8) The number you are thinking of now is 3!