Document 15071703
advertisement

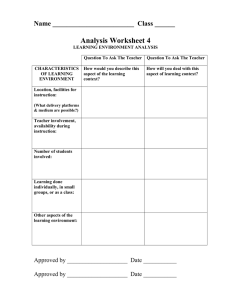
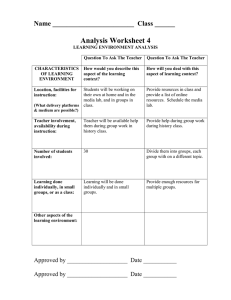
Matakuliah Tahun : S0902 – Manajemen Infrastruktur : 2010 Topic 5 Sustainability Infrastructure Session 10-13 Learning outcomes Mahasiswa dapat mengevaluasi kondisi infrastruktur manajemen dari berbagai negara dengan berbagai kasus-kasus yang ada, berdasarkan aspek-aspek yang sudah dipelajari sebelumnya , dalam upaya menciptakan infrastruktur manajemen yang baik dan berkelanjutan. Bina Nusantara University 3 Mind Map ( Topic 5 ) Bina Nusantara University 4 Contents • • • • • Public Involvement Environmental & Social Aspect Legal & Institutional Aspect Financial & Economic Aspect Case Study Bina Nusantara University 5 Sustainability "The design of new infrastructure, and the re-design, rehabilitation, re-use or optimization of existing infrastructure, which is consistent with the principles of urban sustainability and global sustainable development“ [file://localhost/F:/D1935/as%20Lecturer/TEACHING/Infrastructure%20man agement/topik%205/SUSTAINABLE%20INFRASTRUCTURE.mht] Sustainability sustainability development "Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of the future generations to meet their own needs." [ World Commission on Environment and Development, 1987 ] Sustainability Sustainable urban development A sustainable city is "one in which its people and businesses continuously endeavour to improve their natural, built, and cultural environments at neighbourhood and regional levels, whilst working in ways which always support the goal of global sustainable development." [ Haughton & Hunter, 1994 ] Sustainability Sustainable urban development Sustainable urban development is... "a process of change in the built environment which fosters economic development while conserving resources and promoting the health of the individual, the community and the ecosystem." [Richardson, 1989 ] Sustainability 1. 2. 3. 4. Principles minimizing the use of non-renewable resources minimizing impacts on the natural environment protecting biodiversity using renewable resources in a sustainable manner Sustainability This definition encompasses: • infrastructure renewal • long-term economic analysis of infrastructure, e.g. lifecycle analysis, ecological footprinting • modeling of land use and transportation for assessment of policies on emissions, energy use and reduced infrastructure costs. • the protection of existing infrastructure from environmental degradation, e.g. preservation of historical masonry buildings Sustainability This definition encompasses: • material selection for sustainability - quality, durability and energy conservation • making better use of so-called "waste" water and materials • the redesign of infrastructure in light of global climate change • the remediation of environmentally damaged soils and water Sustainability Public Involvement Public involvement is a process by which interested an affected individuals, organizations, agencies, and government entities are consulted and included in the decision making process of a planning effort …. ( Yoe and Orth 1960) Public Involvement Benefits of public participation : 1. Identify legal requirement, funding limitations or other constrains and ensure the plan is compatible with them 2. Take advantage of technical expertise that may be available in the various publics involved 3. Identify and clarify positions of different groups and individuals affected by the plan Public Involvement Benefits of public participation : 4. Identify sensitive issues and ways of preventing or reducing adverse impacts 5. Overcome conflicts and reach a consensus when there are different points of view with respect to plan components, particularly when multiple objectives are involved 6. Gain support for the project or project implementation Public Involvement The successful of Public participation depend on :: 1. Pre planning 2. Agency policy 3. Resources 4. Outreach 5. Effective communication 6. Techniques 7. Responsiveness 8. Monitoring and evaluation Public Involvement Typology how people participate in planning 1. Passive participation 2. Participation in information giving 3. Participation by consulting 4. Participation by material incentives 5. Functional Participation 6. Interactive Participation 7. Self mobilization Environmental & Social Aspect Environmental action during project cycle :: 1. Identification : Pre feasibility studies : Environmental screening, identification of issues scoping phase 2. Preparation : Feasibilities study : examine alternatives, asses impacts and possible mitigation measures, preparation of EA ( environmental assessment ) reports, economic analyses, policy decisions Environmental & Social Aspect Environmental action during project cycle :: 3. Detailed Design : Incorporated improvements and mitigation measures 4. Appraisal : Review EA procedure and findings, review institutional arrangements 5. Negotiation : Clearance by regional env. dev. ; incorporate environmental covenants into agreement 6. Loan Approval : Conditions of disbursement Environmental & Social Aspect Environmental action during project cycle :: 7. Implementation 8. Supervision : Monitoring and reporting on compliance with environmental conditions and effectiveness of mitigation measures; remediation of foreseen effect; evaluation of treatment of anticipated /unanticipated env. Impacts; preparation of project completion report 9. Completion : Post audit by operations Evaluation Department •World Bank paper 139-1991 ; •[ Goodman Infrastructure Planning Handbook p.11.4 ] Environmental & Social Aspect 1. Different types of Environmental Assessments – – – – Policies Plans Programs Projects 2. Perception of Environmental & Social impacts – – – – – – Natural disaster Increasing population Population Movement Economic factor Technologies application Missteps of government [ Goodman Infrastructure Planning Handbook Chapter 11] Environmental & Social Aspect 1. Different types of Environmental Assessments – – – – Policies Plans Programs Projects 2. Perception of Environmental & Social impacts – – – – – – Natural disaster Increasing population Population Movement Economic factor Technologies application Missteps of government [ Goodman Infrastructure Planning Handbook Chapter 11] Environmental & Social Aspect 3. Multidimensional Nature of Environmental assessment – – – – – – – – – – Physical and socio economics Direct and indirect Short run and long run Local and strategic Adverse and beneficial Reversible and irreversible Quantitative and qualitative Relating to distribution by group Actual and perceived Relative and other developement [ Goodman Infrastructure Planning Handbook Chapter 11] Environmental & Social Aspect 4. Identifying and assessing the quality and /or Quality of environmental attributes 5. Interdisciplinary Nature of Environmental Assessment 6. Economic costs of Environmental Impacts ( to protect, conserve, and enhance env.and nature resources ) – The difficulty of estimating the base line values of environmental resources and estimating the change in values attributable to projects – issues of present VS future values [ Goodman Infrastructure Planning Handbook Chapter 11] Environmental & Social Aspect 7. Direct and indirect Environmental & social Impacts 8. Stakeholder involved in Planning Process and decisions 9. Sustainability and Environmental & social Impacts [ Goodman Infrastructure Planning Handbook Chapter 11] Environmental & Social Aspect [ Goodman Infrastructure Planning Handbook Chapter 11] Legal & Institutional Aspect Enforcement of law is through permits, prohibitions and penalities Legal & Institutional Aspect Conflict management and resolution :: 1. Conflict over data 2.Conflict due to incompatible interest 3.Conflict due to value differences 4.Conflict over relationship issue Financial & Economic Aspect There are 4 main sources through which infrastructure development can be financed : 1. User charges that are invested 2. International Capital market 3. Public financing through government budgetary resources 4. Domestic capital market Case Study [ WB, Indonesia Averting an infrastructure crisis ] Case Study • Infrastructure was significant for Indonesia’s gain in poverty reduction and economic development [ WB, Indonesia Averting an infrastructure crisis ] Case Study • Infrastructure was significant for Indonesia’s gain in poverty reduction and economic development [ WB, Indonesia Averting an infrastructure crisis ] Case Study [ WB, Indonesia Averting an infrastructure crisis ] Case Study [ WB, Indonesia Averting an infrastructure crisis ] Case Study [ WB, Indonesia Averting an infrastructure crisis ] Case Study Case Study – P. Jawa Case Study – P. Sumatera Case Study – P. Kalimantan Case Study – P. Sulawesi Case Study – P. Irian Case Study – Kep. Maluku Case Study – Kep. NusaTenggara