Harald Fritzsch,17/11 [PPT 12.27MB]
advertisement
![Harald Fritzsch,17/11 [PPT 12.27MB]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/015070540_1-7432e3ae8f5bce29b11abdd14e8c1ceb-768x994.png)
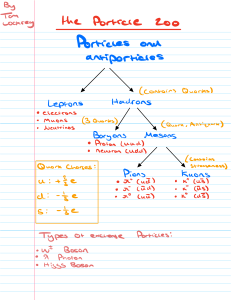
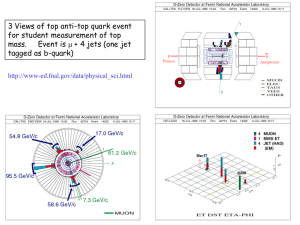
first fundamental constant m1 m2 force G 2 r G 6.674 10 11 3 m 2 kg s first basic constant Discovery of electron m(electron ) 0.511 MeV second basic constant atoms atoms => quantum electrodynamics Arnold Sommerfeld, 1916 3.constant e 2 / hc 2 2 e 1 4 137 h, c 1 Sommerfeld Einstein 1/ 137 1958 Pauli Nr 137 Kanton-spital Zürich Richard Feynman alpha one of the biggest secrets in physics - a magic number, written by the hand of God 2 e hc e A Gauge group i ( x ) U (1) e one gauge boson => photon me 4 gauge bosons 1 1 2 1 mass of weak boson mass of “Higgs” boson coupling constants Electron mass proton u u d d Fritzsch / Gell-Mann proton mass field energy (gluons and quarks) E( gluons ) E(quarks) M p c 2 M const. c 860 _ MeV c fundamental constant c M p c cu mu cd md cs ms celm u c t ... ... d s b 7 fundamental constants in strong interactions ____ c ___ mu mc mt md ms mb III 3 families of leptons and quarks. II I Johannes Paul II Newtons constant G fine structure constant coupling constant of strong interaction coupling constant of weak interaction mass of W boson mass of Higgs boson masses of 6 quarks and 6 leptons flavor mixing of quarks flavor mixing of leptons 1 1 1 1 1 1 12 4 6 md ms mb me m d u 2 mu Mw s sun atm GN m w MH 3 l mc chooz m2 m3 mt m1 md ms mb me m d u 2 mu Mw s sun atm GN m w MH 3 l mc chooz m2 m3 mt m1 Mw GN w MH s Higgs boson ? weak bosons quarks leptons 1.8 billion years ( Gabon, Africa ) Natural Reactor 3.7% U 235 (today 0.72 %) Moderator: water from river Oklo (Oklo) ( now) 7 10 Change of alpha: / 10 16 / year (if no other parameters change) ??? Observation : fine - structure of atomic levels Quasars 5-7 billion years back Quasar absorption spectra Light Fine structure of Fe, Ni, Mg, Sn, A Quasars, back to 11 bn years in time / ( 0.54 0.12)10 / 1.2 10 15 / year 5 / ( 0.54 0.12)10 / 1.2 10 15 / year Oklo reactor ? 5 ? grand unification grand unfication Grand unification 8 s GUT const . 2 2 3 s GUT Calmet, Fritzsch Langacker, Segre (2002) 8 s GUT const . 2 2 3 s GUT 8 s 2 2 3 s 38.8 change of magnetic moments of atomic nuclei (per year) 3,9 10 14 Change of unification scale 31 change of change of ~ 10 15 ~ 10 14 / year / year Time =>Cesium clocks Hyperfine transition magnetic moment of cesium nucleus Difference: 3 CS oscillations per day MPQ-Experiment 486 nm dye laser in hydrogen spectrometer Reference: cesium clock Pharao LPTF Paris Hydrogen: 1s - 2s transition 2 466 061 413 187 127 (18) Hz : magnetic moment / / d / dt : (2.4 6.8) 10 15 yr 1 d / dt : (2.4 6.8) 10 d / dt : 2 10 14 15 yr 1 d / dt : (2.4 6.8) 10 d / dt : 2 10 14 15 yr 1 Simultaneous change: unification coupling constant unification scale Partial Cancellation? (Superstrings) E. Witten 8 s GUT const . 2 2 3 s GUT 15 3 1 10 / year Reinhold et al. PRL 96 (2006) 2 quasars - 12 billion years mp me / ( 2 0.6) 10 5 / 3 10 / 3 1015 / year 15 / year ===>MPQ Grand Unification QFD QCD time variation alpha time variation QCD scale 15 3 10 / year / 3 1015 / year fundamental „constants“ functions of time? Murray Gell-Mann Fundamental Constants Cosmic Accidents ? Gn me s