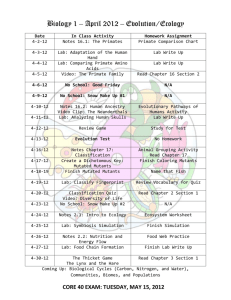
Pseudomonas fluorescens Characterization of non-fluorescent mutants of A506

Characterization of non-fluorescent mutants of
Pseudomonas fluorescens
A506
Student researcher:
Kevin Hockett
Mentor:
Dr. Virginia Stockwell
USDA ARS
Loper Lab
Why is the bacterium A506 important?
•Commercial biocontrol agent for fire blight
•Fire blight is a bacterial disease of pear and apple trees caused by Erwinia amylovora
• $68,000,000 in damage in Oregon and Washington due to fire blight in 1998
Background information
•A506 produces an antibiotic toxic to containing excess iron
E. amylovora only in media
•In several experiments in orchards, adding iron to A506 improved control of fire blight
•Received two mutants of A506 always make the antibiotic in culture
(iron is no longer required). These mutants are non-fluorescent .
Background information
•A graduate student in the lab created a collection of twenty-three mini-Tn fluorescent
5 km mutants of A506 that are nonparental strain
A506
Tn 5 non-fluorescent mutant number 8
A506 Genome mini-Tn5 mini-Tn5
A506 Genome
A506 Genome
Fluorescence of Pseudomonas fluorescens
•Fluorescence under UV is caused by a pyoverdine
•Pyoverdines are a class of siderophores (chelating compounds produced by organisms)
•Siderophores are produced in iron-deficient environments, such as aerial plant surfaces
O receptor
NH
2
A506
Fe II
O
H
N
N
O
N
H
N
H
2
N
N
H O
OH
OH
Fe III O
H O
H
3
C
H
N
OH
H O
O
N
H
O
N
H
O
NH
NH
CH
3
O
O
O
CH
3
A link between pyoverdine and antibiosis?
•Two non-fluorescent mutants of A506 do not require iron to make the antibiotic in culture (from California)
•Of 23 non-fluorescent, mini-Tn 5 mutants:
11 no longer required iron for antibiosis
12 still required iron for antibiosis
A subset of 8 mutants chosen for further evaluation based on phenotype
•Is there a relationship between antibiosis and pyoverdine production in A506?
•Which gene(s) were affected by Tn 5 insertion?
•Do all mutants of the same phenotype have similar mutations or are all different?
•Single, double or triple insertion?
Hypothesis: At least one mutant that does not require iron for antibiosis contains a single insertion in a regulatory gene
Investigating phenotypes of non-fluorescent mutants of
A506
Cross-feeding assay : Determine if the non-fluorescent mutants can utilize the iron bound to the pyoverdine of A506 in iron-limited media
Siderophore-mediated Iron Uptake by
A506
EDDHA
FeEDDHA
Pyoverdine+Fe
Pyoverdine
Receptor
A506
Pyoverdine
EDDHA
Fe III
Utilization of a Pyoverdine by Non-fluorescent Mutants
A506
Pvd
Pvd -
A506
Mutant 8 Four non-fluorescent mutants
Conclusions
•No receptor/uptake mutants
•Mutant 8 produced a compound that cross-feed other mutants, though not a pyoverdine
8 was a mutant that produced the antibiotic irrespective of iron
Next step
•Investigate the gene that has been disrupted
Putative regulatory gene disrupted by mini-Tn5 insertion
X mini-Tn5 +
Mutant A506 Genome
Antibiotic
Pyoverdine
How to achieve?
Southern Analysis: Used to estimate the number of insertions and the uniqueness of their location
Steps
First: digest genomic DNA of mutants with various restriction enzymes
A506 Mutants :
NcoI,SphI, BglI-Single cut
XbaI,MluI,SpeI-No cuts
Second: separate digested
DNA on gel based on size mini-Tn5
NcoI SphI
*Not good representation
Digested Genomic DNA
Third: Blot the gel (transfer DNA from gel to a nylon membrane)
Southern analysis continued:
Hybridization
After probe is applied, membrane is washed in a visualization solution
7 6 5 4 3 2 1
Mutant #
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
SphI-digest
8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
NcoI-digest membrane
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Flipped compared to the gel gel
Southern analysis continued:
Mutant Size of Bands
3 <23130
4 15000
5 <23130
6 7200
7 6900, 4300
8 -
3 4 5 6 7 8
Size markers
23,130 bp
9,416 bp
6,557 bp
4,361 bp
2,322 bp
2,027 bp
Interpretation from Southern Blotting
Of the 8 mutants:
7 single insertions, 1 double insertion
All band patterns were unique- no insertions were in the exact same spot with in the genome
Number Representative Enzymes
Mutant: of insertions NcoI SphI PstI
8 1 4150, 9144 2690, 6400 810, 1720, 4512
7 2 1200, 5500 1768, 6860,
9039, 11094
6 1 <564, 8800 5084, 7136
Inverse PCR
Inverse PCR: a method to amplify DNA adjacent to mini-Tn 5 for sequencing
Steps: i. Cut genomic DNA with restriction enzyme mini ii.
Ligate digested genomic DNA into circular DNA mini mini iii. Run PCR rxn.
Why is it called inverse-PCR?
Inverse PCR continued:
Forward Primer
Normal PCR:
Reverse Primer
End Primer
Inverse PCR: mini
Rev. Primer
Run amplified DNA on a gel, extract, and send DNA for sequencing.
Perform a BLAST search on sequence with GenBank to help determine identity of the disrupted gene.
Progress in inverse PCR for non-fluorescent mutants
Found
•NcoI, PstI, and SphI are good restriction enzymes for inverse PCR for these mutants
•Primers have been developed and obtained for inverse PCR from the mini-Tn5
Conclusions:
1. 22 of 23 non-fluorescent mutants of A506 were unable to grow on media amended with EDDHA
2. One mutant grew on EDDHA and cross-fed all other mutants
3. All non-fluorescent mutants could be cross-fed on iron-depleted media by the parental strain A506.
4. Of eight mutants evaluated with Southern analysis, seven had a single insertion of Tn5
5. Of 8 mutants evaluated with Southern analysis, each yielded a distinct band pattern with several restriction enzymes. Each mutant may have an unique insertion.
•Next step is to amplify fragments containing insert so flanking DNA can be sequenced
Acknowledgements
Howard Hughes Medical Institute Summer Fellowship Program
Dr. Kevin Ahern
USDA-Western Regional Integrated Pest Management Program
OSU Dept. of Botany and Plant Pathology
Dr. Virginia Stockwell
USDA/ARS Horticulture Crops Research Laboratory
Dr. Joyce Loper
Todd Temple
Brenda Schaffer
Marcella Henkels
Meg Roche Larsen
Amy Davis
Andy Mumford