DNA
advertisement
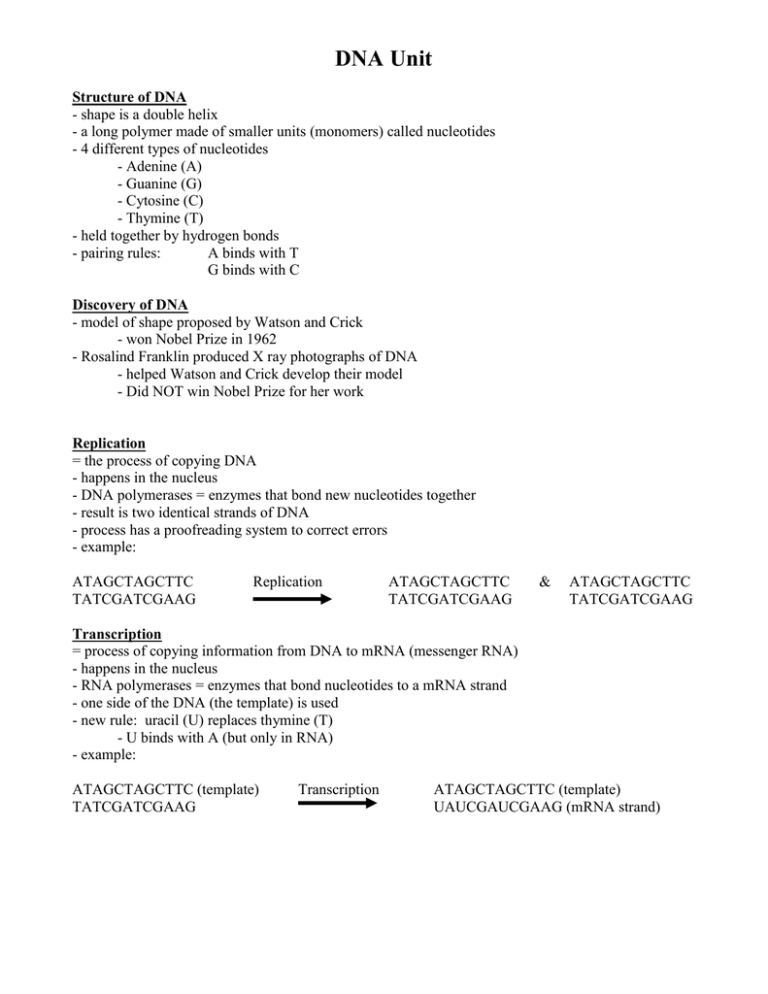
DNA Unit Structure of DNA - shape is a double helix - a long polymer made of smaller units (monomers) called nucleotides - 4 different types of nucleotides - Adenine (A) - Guanine (G) - Cytosine (C) - Thymine (T) - held together by hydrogen bonds - pairing rules: A binds with T G binds with C Discovery of DNA - model of shape proposed by Watson and Crick - won Nobel Prize in 1962 - Rosalind Franklin produced X ray photographs of DNA - helped Watson and Crick develop their model - Did NOT win Nobel Prize for her work Replication = the process of copying DNA - happens in the nucleus - DNA polymerases = enzymes that bond new nucleotides together - result is two identical strands of DNA - process has a proofreading system to correct errors - example: ATAGCTAGCTTC TATCGATCGAAG Replication ATAGCTAGCTTC TATCGATCGAAG & ATAGCTAGCTTC TATCGATCGAAG Transcription = process of copying information from DNA to mRNA (messenger RNA) - happens in the nucleus - RNA polymerases = enzymes that bond nucleotides to a mRNA strand - one side of the DNA (the template) is used - new rule: uracil (U) replaces thymine (T) - U binds with A (but only in RNA) - example: ATAGCTAGCTTC (template) TATCGATCGAAG Transcription ATAGCTAGCTTC (template) UAUCGAUCGAAG (mRNA strand) Translation = the process that converts info in mRNA into proteins - done by ribosomes in the cytoplasm - codon = 3 nucleotides together - each represents an amino acid - example: mRNA strand broken into codons UAUCGAUCGAAG (mRNA strand) Translation UAU Tyrosine CGA Arginine UCG Serine Amino Acid Sequence = a protein Central Dogma = the flow of information from DNA to RNA to proteins - involves the three main processes: replication, transcription, translation Mutations = a change in an organism’s DNA - they can be neutral (do nothing), harmful, or beneficial - substitution mutations = one nucleotide is switched with another - insertion mutations = added nucleotide to a sequence - deletion mutations = one nucleotide is deleted from sequence - mutations in body cells affect only the organism itself and are not passed to offspring mutations in sex cells (egg and sperm) may be passed to offspring - most of the time this is bad, but not always - another source of genetic variation in organisms - mutagens = agents in the environment that can cause a change in DNA AAG Lysine





