Pertemuan 07 Metode Pengembangan SIG Matakuliah : T0234 / Sistem Informasi Geografis
advertisement

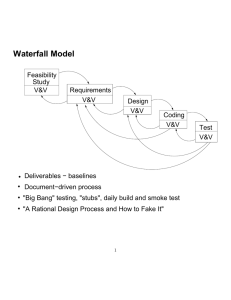
Matakuliah Tahun Versi : T0234 / Sistem Informasi Geografis : 2005 : 01/revisi 1 Pertemuan 07 Metode Pengembangan SIG 1 Learning Outcomes Pada akhir pertemuan ini, diharapkan mahasiswa akan mampu : • memilih metode pengembangan SIG yang sesuai dengan kebutuhan yang ada (C4, TIK07) 2 Outline Materi • Materi 1 : Waterfall/ SDLC Model • Materi 2 : Prototyping Model 3 Waterfall Model (1) Waterfall Model/SDLC (Skidmore & Wroe, 1988): Feasibility Study System Investigation System Analysis System Design Implementation Review & Maintenance 4 Waterfall Model (2) • House hunting case study : 1. Feasibility Study (FS) : Asking the real estate agents & home buyer questions about whether they would make use of the system being proposed for development & what the costs & benefits of developing a GIS would be. If the FS is positive then the project moves to the second phase. 2. System Investigation & System Analysis Designer would try to establish the current way in which home buyers & real estate agents interact to identify houses for sale in appropriate neighborhoods. This would include identifying the data & analysis requirements as well as the preferred output types. A soft systems approach could be 5 used to help with this phase. Waterfall Model (3) • House hunting case study : 3. System Design The GIS data model is constructed using information collected in the previous phase. In this example, cartographic modeling techniques might be used to help structure the analysis requirements of the GIS. 4. Implementation, Review & Maintenance Now the house-hunting GIS is built & provided to users. This may be the first opportunity for users to comment on, or interact with, the system since their involvement in the FS. Users’ experiences inevitably require changes to the system : addition of new data layers, new analysis techniques or new ways of visualizing the output. 6 Waterfall Model (4) • Advantages : Provides a very structured framework for the management. Extremely important when good time management is an essential aspect of the project. Often easier to budget for the resources required, because requirements of the system established at an early stage. • Problems : Often fail to address the context of the business. The timescale & linear nature of process do not allow for change in the scope & character of the problem. Does not put the user at the center of the system design. Offers a very technocentric view of the system development. (Because, often considered to favour hierarchical & centralized systems of information provision) 7 Prototyping Model (1) The user first defines the basic requirements of the system. USER ANALYST Basic Requirements System to meet user needs Experiment Refine 8 Prototyping Model (2) The user first defines the basic requirements of the system. This could be achieved by using the rich picture & root definition techniques. The system designer takes these basic ideas to construct a prototype system to meet the needs identified by the user. In GIS Projects such systems are often described as demonstrators. The users who identified the original requirements for the system then experiment with the demonstration system to see if it is what they expected. Other potential users the final system may be brought in at this stage to see if the system is of wider value. The system designer uses their recommendations 9 to improve the system Prototyping Model (3) Advantages : User have a more direct & regular involvement in the design. Easier to adapt the system in the face of changing circumstances which were not identified at the outset of project. The system can be abandoned altogether after the first prototype if it fails to meet the needs of users. Reduces the cost of developing full systems If money & time are available a number of prototypes can be built until the user is satisfied. Problems : Prototyping can be difficult to manage. There may be large numbers of users with large numbers of ideas & opinions. The resource implications may change following the development of the first prototype Knowing when to stop development can also be a problem. Some GIS designers argue that this is a positive aspect. 10 Penutup • Mahasiswa diharapkan telah mampu memilih metode pengembangan SIG yang sesuai dengan kebutuhan yang ada. 11