WhyDetailsMatterinTechnicalW.ppt
advertisement

Why Details Matter in
Technical Writing
Little things that make a big difference
© M. Reber
6/27/2016
Why Do I Insist Details Matter?
I’m Anal Retentive?
I’m Too Picky?
It’s My Personal Opinion?
I’m a Hard Teacher?
I Want to Make You Miserable?
I’m Just Making up Stuff?
2
The Answer Is…
NONE OF THE ABOVE!!!
3
Details Matter Everywhere!
Programming JavaScript
Updating Financial Reports
Baking a Cake
Jumping a Dead Car Battery
Preventing Computer Viruses
4
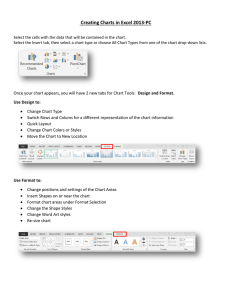
Programming JavaScript
If you leave a “}” or a “=“ out of a script…
<script language="javascript" type="text/javascript">
<!—
function popitup(url) {
newwindow=window.open(url,'name','height=200,width=150');
if (window.focus) {newwindow.focus()}
return false;
}
var newwindow = '';
function popitup(url) {
// -->
</script>
5
Programming JavaScript (cont.)
You might see this…
6
Programming JavaScript (cont.)
Instead of this:
7
Updating Financial Reports
If you place decimals incorrectly…
12.11
1.211
121.1
-------------
8
Updating Financial Reports (cont.)
You might see this…
12.11
1.211
121.1
------------134.421
9
Updating Financial Reports (cont.)
Instead of this:
12.11
12.11
12.11
------------36.33
10
Baking a Cake
If you add 1t of baking powder
instead of 1T in a recipe…
Amaretto Sponge Cake
Ingredients:
3 tablespoons butter or margarine
1T baking powder
1 large egg
1/4 cup all-purpose flour
3 (8-ounce) packages cream cheese
3/4 cup granulated sugar
3 tablespoons all-purpose flour
3 large eggs
1/4 cup amaretto liqueur
11
Baking a Cake (cont.)
You might get this…
12
Baking a Cake (cont.)
Instead of this:
13
Jumping a Dead Car Battery
If you clamp the red (+) cable onto the
black (-) post...
14
Jumping a Dead Car Battery (cont.)
You might get this…
15
Jumping a Dead Car Battery (cont.)
Instead of this:
16
Preventing Computer Problems
If you forget to protect your hard drive…
Scan for viruses
Turn your firewall off
Give out your password
Open suspicious e-mails
Let dust build up in the vents
17
Preventing Computer Problems (cont.)
You might get this…
18
Preventing Computer Problems (cont.)
Instead of this:
19
So What Did We Learn?
Every discipline has rules!!!
20
What Kinds of Detail Matter in
Technical Writing?
Accuracy of Information
Consistency
Formatting
Styles
Graphics
21
Accuracy of Information
Ensure the steps or procedures in a process
are in an exact order.
Ensure the system you describe works the
way you say it does.
Ensure the information you share is well
researched.
22
Consistency
Consistency is a critical concept in writing,
especially technical writing.
Consistency of naming conventions
Consistency of formatting & style
Inconsistency can confuse your reader.
23
Consistency (cont.)
Examples of inconsistent naming
conventions:
an item
A 2nd item
A third item.
item 4
Item #5
Print dialog box
Print Screen
PrtScrn
Thumbnail
Icon
email
E-mail
Email
Internet
net
Web site
website
24
Consistency (cont.)
Examples of consistent and inconsistent
formatting & styles:
Consistent
Heading 1
Heading 2
Inconsistent
Body text
Heading 1
Heading 1
Heading 2
Heading 2
Body text
Body text
Heading 4
Body text
Heading 3
Body text
Heading 3
25
Formatting
Formatting creates:
Distinct styles for each element of your document.
Formatting keeps:
Style elements consistent throughout a document.
Formatting establishes:
A relationship between subject.
26
Formatting (cont.)
Formatting elements include:
Headings (H1) and Subheadings (H2)
Body Text
Bulleted Lists
Tables
Headers and Footers
White Space
“Note!”, “Caution!” or “Warning!” Boxes
27
Styles: Personal Style
Style: noun [stahyl]:
Style is a particular, distinctive, or
characteristic mode of action, appearance or
manner of acting.
28
Styles: Personal Style (cont.)
Compare this style…
29
Styles: Personal Style (cont.)
…to this style.
30
Styles: Personal Style (cont.)
Just as physical attributes and mode of dress
give a person a different look, feel or image…
31
Styles: Text and Typeface
…dressing up your text gives it a different look, feel or
image.
Bold it
Italicize it
Give it some …….. space
Give it some COLOR
Differentiate your text levels:
Headline Level 1
Headline Level 2
Headline Level 3
Body Text
Use Microsoft Word to help you define common text
styles that create your distinctive design.
32
Styles: Microsoft Word Styles
Are a set of stored formatting commands you can use
repeatedly throughout a document
For example, you can define a style for headings that is
left-justified, bold, blue, 18 pt. font, with a 1.5 border
With a mouse click, you can apply formatting characteristics to
selected text all at once instead of one at a time
Used to “tag” or identify parts of a document
You can create unique styles for each type of text in a document
(headings, body text, captions, etc.)
You can easily revise a style and automatically update all
occurrences of that style throughout a document
Allow you to customize the look/layout of a document
33
Styles: Writing Style
Your unique writing style is defined by:
The way you use metaphorical expression, words,
grammar and punctuation, etc.
But in the corporate environment, your writing
style must mesh with others by:
Modifying your personal style to match your
company’s style guide conventions and corporate
image.
Writing in the corporate voice using standard
abbreviations, verbiage, and term usage.
34
Graphics
Just as text and writing styles make your document
unique, graphics alter its mood and appearance.
Graphics can:
Give a specific, consistent look to your document
Break up the monotony of straight text
Emphasize important information
Appeal to right-brained users
Convey quantitative relationships (percentile rankings,
trends, etc.)
Communicate internationally
35
Graphics (cont.)
Use graphics to:
Show how something looks or is constructed
Show how to do something
Explain how a process works
Show how something is organized
Help the reader find specific facts
Show relationships
Make a persuasive point
36
Not to beat a dead horse but...
37
Details…
DO MATTER!!!
38