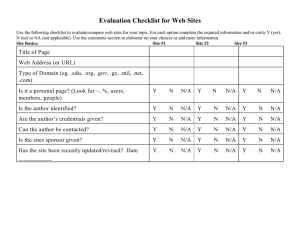
Bertin.ppt

Graphics and
Graphic Information Processing
J. Bertin
Presented by Fusun Yaman
Overview
Introduction
Description of the paper
My favorite sentence
Contributions
Notes on the references
Critique
What happened to this topic
Introduction
Section from Graphics and Graphic
Information Processing
(1977/1981)
Problem addressed in section B
Collection of objects that are described by n characteristics
How to graphically represent this information when usually n > 3
Terminology
Information is in Data Table
Objects correspond to cases (A, B, C, D)
Characteristics correspond to variables
(income,education, experience)
A B C D
Income
Education
Experience
Terminology (continued)
Objects can be
Ordered (0) , like months
Reorderable (
), like individuals
Topographic (T), like cities
Characteristics can be
Nominal, like movie titles
Ordinal, like movie ratings
Quantitative, like length of the movie
“Impassable barrier”
Image has only 3 dimensions
This barrier is impassable
Le n be number of variables (rows)
n
3 : Use scatter plots
n > 3 : Other solutions needed
Solutions for n > 3
Constructing several scatter plots
Sacrificing overall relationship
Constructing a matrix
Overall relationship is discovered by permutations
Synoptic
Classifies graphic constructions according to two properties of Data Table
If n is number of characteristics
n > 3 and n
3
Nature of objects
Ordered , reorderable, topographic
Graphics for n
3
Matrix construction when objects are reorderable
Graphics for n
3
Arrays of curves when objects are ordered
Graphics for n
3
Scatter plots for both reorderable and ordered cases
Third row is represented by the size of the marker (9)
Graphics for n
3
In topographies bi- or tri-chromatic superimposition reveals the overall relation ships
Graphics for n > 3
Objects and characteristics are reorderable (
)
Reorderable matrix
Objects are ordered, characteristics are reorderable
Image file (2)
Array of curves when slops are meaningful (3)
Ordered objects and characteristics
Collection of tables or maps (4,5)
Use super imposition to discover similar groups
Reorderable Matrix
Objects and characteristics are reorderable (
)
Permutable in x and y
Overall relationship is discovered by permutations
What if characteristics are not nominal?
Special Cases for
(
)
Weighted matrix
Areas become meaningful
Applicable to a data table in which row and column totals are meaningful
Limited in dimension
Matrix-file
When one of the dimensions is too large
Constructed similar to image files
Use sorting to discover correlations
Image File
Used for ordered objects and reorderable characteristics
One card for each characteristic
Values greater than the mean of that row are darkened
Matrix-File
Special case for permutable matrix; one of the dimensions is too big.
Large number of objects across a small number of characteristics.
Constructed similar to image files
Use sorting to discover correlations
Matrix-File Example
Ordered by salary, origin, age
Higher salaries are paid to men, who are married, older and who have more childeren then others
Graphics for Networks
A network portrays the relationships that exists among the elements of a single component .
can also be represented in matrix form
If this component is
Reorderable: network is transformable on a plane (19)
Ordered: network is transformable on one dimension (20)
Topography: non-transformable; ordered network (21)
Utilization of Synoptic
Using synoptic choose the appropriate graphic construction for your data
Deviating from suggested construction leads to loss of information and requires justification
Size limitations
My favorite Sentence
“A problem involving n rows does not correspond to n problems involving one row.”
“[
Graphics ] is a strict and simple system of signs, which anyone can learn to use and which leads to better understanding.”
Contributions
Synoptic
Classification scheme for 2D graphical presentation
Permutation Matrix
General solution for more than 3 variables
(In the book) Identifies seven visual variables
Position,size, value, orientation, color, texture and shape
Texture
Position
Color
Size
Orientation
Value
Shape
References
The book has no reference section!
Semiology of graphics: Diagrams, networks, maps, J. Bertin, 1967
Identifies basic elements of diagrams
Describes a framework for their design
Critique
Strength of the paper
One image summerizes his all theory on graphic construction selection
Weakness of the paper
No 3D discussion
Not easy to follow, lack of examples (in the given section)
Outdated implementation techniques
What happened to this topic?
Formed a basis for research in Information
Visualization
Graphical constructions and ideas presented in this section are implemented in information visualization tools
Tablelens (matrix file)
Spotfire (scatter plots using seven visual variables)
What happened to this topic?
Classification enabled auotomation studies
Automating the design of graphical presentations of relational information, Mackinlay
1987 NSF report, DeFanti (uses the term visualization)
Extension to 3D graphics
Information Animation Applications in the capital markets, Wright
1987 NSF report, DeFanti



![VII. FOOD SYSTEMS GRAPHICS [F-14 - F-18]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/014124523_1-6d60a6b2913aa206f2f840646ca22e51-300x300.png)
