FDA Human Factors of Medical Devices Ensuring a safe,
advertisement

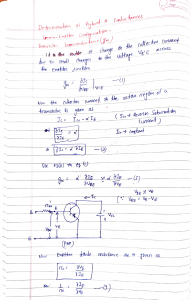
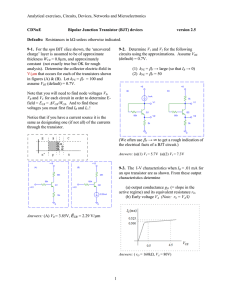
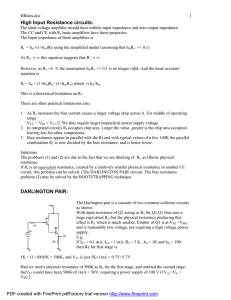
FDA Human Factors of Medical Devices Ensuring a safe, user friendly device-user interface Medical Errors in U.S. each Year Result In: • Up to 98,000 deaths • 5th leading case of death: exceeds auto accidents, breast cancer and AIDS • $29 Billion added cost FDA Medical Device Incident Reports: • 100,000 reports per year • More than 1/3 involve use error • Tip of the Iceberg FDA Recall Study • 44% of medical device recalls due to design problems. • Use error often linked to design. More user friendly Design • Operations - don’t exceed user capabilities • Information - Sufficient, legible and intelligible • Procedures - logical and intuitive • Operations - consistent with conventions • Dangerous error - designed out • Conditions of use - considered and addressed Key safety concepts in design • • • • • • • make things visible simplify the operation avoid reliance on memory avoid reliance on vigilance use natural mappings use forcing functions make it easy to reverse an error FDA’s authority • Quality Systems Regulation/ CGMP - Design Controls (1996) Design Controls • Regulatory Language: – “… design requirements … intended use … needs of the user and patient.” – “… testing production units under actual or simulated use conditions.” – “… conduct risk analysis.” Design Controls • Preamble Language: – “… conduct appropriate human factors studies, analyses, and tests …” – “… human interface includes both the hardware and software characteristics…” Design Controls - Human Factors Engineering (HFE) Process • HFE applied from concept stage to final design • Early Involvement of typical users is critical • The process is iterative Human Factors Engineering Process Concept Design Phase Input Perform * Develop Studies & RequireAnalyses ments Design Output Develop Specs. Verification Test Output Against Input Validation Test Against Patient & User Needs HF Elements Literature Safety Drawings Analyses Complaints Environment Mockups Observation Users Performance Computer Prototypes Expert Evaluation Interviews Rapid Prototyping *Design and Development Planning Important Here Production Units Full Usability Test Risk Assessment Human Factors Engineering Summary of Methodology • Study the user population and use conditions • Analyze function, tasks, and hazards • Incorporate findings in requirements Human Factors Engineering Summary of Methodology • Test and analyze prototypes against requirements • Test production models in simulated environment • Conduct a risk assessment HFE Standards • ANSI/AAMI HE74:2001 Human factors design process for medical devices • IEC 60601-1-6, Ed1, Usability ANSI/AAMI HE74:2001 • Overview of the HFE process • Planning the HFE process • HFE process: a systems approach • Methods and techniques • Risk & cost benefit analysis ANSI/AAMI HE74:2001 • Need for user input • Scaling the HFE work • Documenting the HFE activities • Design evaluation: verification & validation ANSI/AAMI HE74:2001 • Relevant FDA regulations • Practical tips • Bibliography - General HFE references - Human error - Human computer interface - Usability testing FDA Web Site • http://www. fda.gov/cdrh/humanfactors.html fda.gov/cdrh/usererror.html