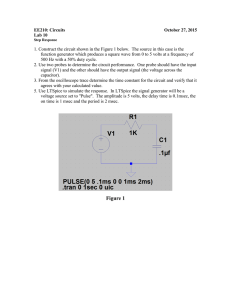
Time - Delay Circuit Using a 555 Integrated Circuit
advertisement

UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS DARTMOUTH DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 201 CIRCUIT THEORY I INTRODUCTION TO THE 555 INTEGRATED CIRCUIT TIMER BACKGROUND The 555 integrated circuit timer is a device used to generate accurate time delays or oscillations. It is packaged in an 8-pin MINI-DIP with the pin connections shown in Figure 1. Figure 1. Package and pin outline for the 555 IC timer “Under the hood” of the 555 timer are more than 20 transistors, 15 resistors, and 2 diodes. However, at this point, it is not necessary to understand how any of these individual devices operate in order to make simple use of the 555 timer! It turns out that we can think of the 555 as a SPDT switch that provides an output which is either a DC voltage (VCC) or 0 volts (GROUND). The position of the switch is determined by the voltage at pin #6 (THRESHOLD). This is illustrated in Figure 2. Figure 2. A simplified representation of the 555 timer If the voltage at pin #6 is 2/3VCC, the switch is connected to GROUND, and the OUTPUT at pin #3 is 0 volts (LOW). If the voltage at pin #6 is 1/3VCC, the switch is connected to VCC, and the OUTPUT at pin#3 is VCC volts (HIGH). The voltage across a capacitor in a simple RC series circuit will be applied to the THRESHOLD terminal (pin #6) of the 555 to control the state of the OUTPUT. TIME-DELAY CIRCUIT Generally, we think of activating a device or a circuit by closing a switch. Consider the case of “arming” an alarm in your car or home. It is beneficial to provide a time-delay which allows the person arming the system to leave the vehicle or premises without setting off the alarm. In the circuit of Figure 3, a 555 timer is used to close a relay which provides power to a load (simulated by a buzzer) after a certain length of time (the time-delay). OnOff EDR201A12 Key = S 12VRelay RV1 8 Key = A 100kOhm Prim aryPow er 12 V U1 VCC 50% 4 RST 7 DIS 6 THR 2 TRI 5 CON K OUT 3 Buzzer GND LM555CN 1 LoadPow er 12 V 200 Hz C 1uF Figure 3. A time-delay circuit using the 555 timer The circuit operates as follows. When the On/Off switch is closed, the initially uncharged capacitor C will charge towards the 12 volts provided by the Primary Power battery via the potentiometer RV1. The OUTPUT of the 555 will be HIGH (12 volts) and the relay coil will not be energized until the voltage across the capacitor is equal to 8 volts (2/3 of 12 volts). This will occur at approximately 1.1RC seconds (the time-delay) after the switch is closed. The 555 OUTPUT will change to LOW (0 volts) and the relay will be energized (the 12 volt Primary Power battery will now be connected across the coil terminals). The 12 volt Load Power battery will now be connected to the buzzer via the closed relay contact. The time-delay is adjustable by changing the value of either the potentiometer RV1 or the capacitor C (or both). 2 PRELIMINARY WORK /DESIGN Design a time delay circuit using a 555 integrated circuit that will activate (supply 12 volts DC to) a burglar alarm by closing a relay 15 seconds after a key switch is closed. Prior to key switch closure, illuminate a Green LED to indicate that the system is ready to be armed. When the relay closes, turn the Green LED off and illuminate a Red LED to indicate that the system is armed. Use two separate 12 volt power supplies to operate the 555 and the alarm load. Use a 1 kΩ resistor to represent the loading of the alarm circuitry. Include current-limiting resistors to protect the LEDs. Simulate your design in MultiSim and make any modifications that you think are necessary. LABORATORY PROCEDURE / RESULTS Construct the time delay circuit that you designed and simulated in MultiSim. Check that the circuit operates the relay in 15 seconds (more or less). When you are satisfied that your final circuit meets the design specifications, show it to the instructor or TA for their approval. If time permits, investigate the possibility of making the delay time variable from 5 to 30 seconds. 3