The End of the War

The End of the War in
Europe
North Africa
• Struggle for control of the Suez Canal and access to oil from the Middle East and raw materials from Asia
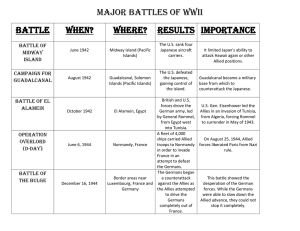
• At the battle of El Alamein (Egypt) in Oct.
1942, the Germans fell short on fuel and ammunition forcing Rommel to retreat to
Tunisia
• George Patton leads troops from the West in
Morocco as Montgomery leads troops from the
East
D-Day (Operation Overlord)
• By mid-1944 early mobilization of manpower and resources in America was beginning to pay off
• By the beginning of June 1944, the United
States and Great Britain had accumulated the largest number of men and the greatest amount of materiel ever assembled to launch and sustain an amphibious attack (3.5 million men)
D-Day
• Three months before D-Day, a strategic air campaign was launched to cripple bridges/railways/airfields near Normandy, France
• The Allies also put into effect a deception plan to lead the Germans to believe that landings would take place farther north of the beaches at Normandy
The Attack
• Despite unfavorable weather forecasts, General
Eisenhower made the decision to attack on June 6, 1944.
• After an intensive air and naval bombardment, assault waves of troops began landing at 0630. More than 5,000 ships and 4,000 ship-to-shore craft were employed in the landings
• U.S. forces in the center (Omaha Beach) met determined opposition.
Result
• Beachheads secured by June 11 th (10,000 Allied
Troops Killed)-----6,000 Americans (est.)
• French and American troops rolled into Paris on
August 25, 1944
Battle of the Bulge
(The Ardennes Offensive)
• Hitler had convinced himself that the alliance between
Britain, France and America was not strong and that a major attack and defeat would break up the alliance
• Hitler’s plan was to launch a massive attack using three armies on the Allies
• Goal: To take the huge port of Antwerp through which a great deal of supplies was reaching the Allies.
The Plan
• Hitler believed that his forces would be able to surround and cut off America’s 1st and 9th Armies and Britain’s Second Army.
• The battle started with a two hour bombardment of the Allies lines that was followed by a huge armored attack (Dec. 16 th , 1944)
The Last Battle
• Despite punching a bulge into the Allies front line, the
Germans could not capitalize on this, and the success lasted 2 days
• By December 22nd, the Allies brought their air power into force
• By mid-January 1945, the effect of lack of fuel was becoming evident as the Germans had to simply abandon their vehicles
Wartime
Agreements
• Unlike WWI, there was no Peace of Paris to reshape Europe.
• Instead, the Yalta agreement of February 1945 , signed by Roosevelt, Churchill, and Stalin, turned the prevailing military balance of power into a political settlement. (Divide Germany into zones of occupation, free elections in Europe)
• Potsdam Conference, in suburban Berlin (July
1945)—Truman, Stalin, Churchill – Finalized plans on
Germany / Truman mentions bomb to Stalin
Outcome
• The one huge problem for the Germans – their inability to keep their armored vehicles supplied with fuel
• Allied bombing of fuel plants in Germany meant that such supplies did not exist
• Hitler's plan that a successful attack would split the Allies was also based on false hope.
• Germany surrenders May 8, 1945 (V-E Day)