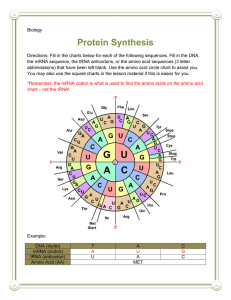
Protein Synthesis PP Notes
advertisement

DNA & RNA Lecture II Using the Code of Life DNA & RNA 1 Two process involve DNA 1. Replication: making an exact copy of DNA purpose: reproduction occurs: nucleus uses: only DNA 2. Protein Synthesis: production of proteins purpose: growth & reproduction occurs: between nucleus & ribosomes uses: both DNA & RNA 2 Replication Making Exact Copies of DNA 3 DNA Unzip 4 Replication of Helix 5 Mechanism of Replication Basics 6 Replication • Creates an exact copy DNA • Steps: 1. DNA unzips 2. “Free-floating” nucleotides in cytoplasm fill slots along existing strand of DNA 3. Two double strands formed. 7 Replication • A more detailed diagram. 8 Comparing DNA & RNA DNA • Double stranded • Deoxyribose Sugar • Phosphate • Nitrogenous bases – – – – Adenine Cytosine Thymine Guanine RNA • Single stranded • Ribose Sugar • Phosphate • Nitrogenous bases – – – – Adenine Cytosine Uracil Guanine 9 Protein Synthesis 10 Why Do We Need Proteins? 1. Cell Structure • Cell = 80% protein Cell membrane 11 Why Do We Need Proteins? 2. Cell Processes • Hormones (signals) • Enzymes (speed up reactions) 12 Why Do We Need Proteins? 3. Membrane Channels (remember transport?) 4. Neurotransmitters (carry nerve/brain messages) 13 What Do We Need For Protein Synthesis? 1. DNA Template for making mRNA during Transcription 14 What Do We Need For Protein Synthesis? 2. RNA a) mRNA — messenger RNA makes & takes copy of DNA to cytoplasm. b) tRNA — transfer RNA Matches w/ mRNA on ribosome. Carries AA to add to protein chain. 15 What Do We Need For Protein Synthesis? 3. Ribosome Reads mRNA Directs tRNA Creates peptide bonds between AAs makes polypeptide (protein) chain 16 What Do We Need For Protein Synthesis? 4. Amino Acids (AAs) • Building blocks of proteins (20 AAs exist) • Protein = AA chain = polypeptide chain • ORDER MATTERS! AA order determines function of protein 17 Amino Acids 18 Steps of Protein Synthesis 1. Transcription (writing the “message”) DNA makes mRNA messenger carries code to cytoplasm 2. Translation (reading the “message”) mRNA and tRNA make protein (AA chain) message translated into a protein 19 Steps of Protein Synthesis 20 Steps of Protein Synthesis (Nucleus) (Cytoplasm) 21 Transcription Transferring the DNA Code to mRNA DNA to mRNA 22 Transcription — Basics 23 Transcription DNA to mRNA Location = nucleus 1. Enzyme binds to DNA, unzips it 2. mRNA makes a copy of gene from DNA template *U replaces T in RNA 24 Transcription 3. A codon is a threeletter “word” of instruction 4. Codons are made of mRNA 25 Transcription 5. They attach to anticodons at ribosomes 6. Anticodons are attached to clover leaf like structures which carry a specific amino acid. 26 Transcription 5. DNA nucleotides (triplet) turn into mRNA codon Codons 27 Transcription 28 Translation Writing the Code to form Amino Acids (Proteins) mRNA to tRNA 29 Translation Decoding (writing) — bonding of amino acids to form proteins mRNA and tRNA make protein (AA chain) Location = cytoplasm 30 Translation — Basic 31 Translation Steps of Translation 1. mRNA moves to cytoplasm, binds to ribosome 2. tRNA anticodon brings AA (amino acid) to mRNA codon on ribosome 32 Translation 3. Ribosome moves down mRNA to next codon 4. tRNA anticodon picks up & attaches next AA with peptide bond 33 Translation 5. tRNA leaves ribosome once AA attached Protein chain AA tRNA mRNA 34 Translation 6. Steps 1-5 repeated, adding Aas until STOP CODON signals end of protein 7. Polypeptide chain (protein) released from ribosome 35 Translation 36 Synthesis Practice DNA Triplet mRNA Codon tRNA Anti-codon TAC GGA CCT TAT ACT 37 Synthesis Practice DNA Triplet mRNA Codon TAC AUG tRNA Anti-codon GGA CCT TAT ACT 38 Synthesis Practice DNA Triplet mRNA Codon tRNA Anti-codon TAC AUG UAC GGA CCT TAT ACT 39 Synthesis Practice DNA Triplet mRNA Codon tRNA Anti-codon TAC AUG UAC GGA CCU CCT TAT ACT 40 Synthesis Practice DNA Triplet mRNA Codon tRNA Anti-codon TAC AUG UAC GGA CCU GGA CCT TAT ACT 41 Synthesis Practice DNA Triplet mRNA Codon tRNA Anti-codon TAC AUG UAC GGA CCU GGA CCT GGA TAT ACT 42 Synthesis Practice DNA Triplet mRNA Codon tRNA Anti-codon TAC AUG UAC GGA CCU GGA CCT GGA CCU TAT ACT 43 Synthesis Practice DNA Triplet mRNA Codon tRNA Anti-codon TAC AUG UAC GGA CCU GGA CCT GGA CCU TAT AUA ACT 44 Synthesis Practice DNA Triplet mRNA Codon tRNA Anti-codon TAC AUG UAC GGA CCU GGA CCT GGA CCU TAT AUA UAU ACT 45 Synthesis Practice DNA Triplet mRNA Codon tRNA Anti-codon TAC AUG UAC GGA CCU GGA CCT GGA CCU TAT AUA UAU ACT UGA 46 Synthesis Practice DNA Triplet mRNA Codon tRNA Anti-codon TAC AUG UAC GGA CCU GGA CCT GGA CCU TAT AUA UAU ACT UGA ACU 47 AMINO ACID FUN!! DNA Triplet: ACC mRNA codon: UGG tRNA anti-codon: ACC Amino acid: Tryptophan Why you sh Tryptophan is in TURKEY – makes you sleepy 48 Protein Synthesis 49 Protein Synthesis Animation http://www.columbia.edu/cu/biology/course s/c2005/images/animtransln.gif 50 List of Condons & Amino Acids 51 List of Amino Acids 52