World War I Cornell Lecture Notes
advertisement
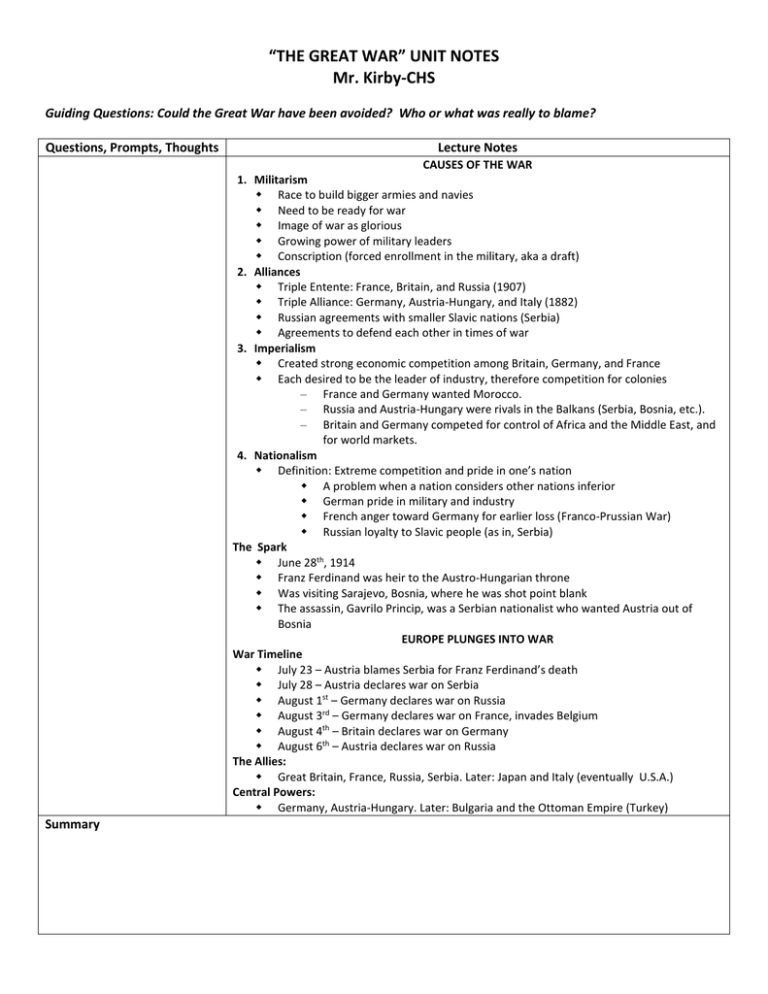
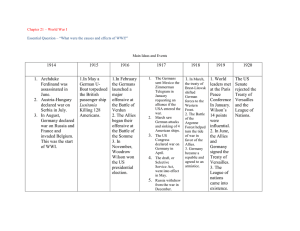
“THE GREAT WAR” UNIT NOTES Mr. Kirby-CHS Guiding Questions: Could the Great War have been avoided? Who or what was really to blame? Questions, Prompts, Thoughts Lecture Notes CAUSES OF THE WAR 1. Militarism Race to build bigger armies and navies Need to be ready for war Image of war as glorious Growing power of military leaders Conscription (forced enrollment in the military, aka a draft) 2. Alliances Triple Entente: France, Britain, and Russia (1907) Triple Alliance: Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy (1882) Russian agreements with smaller Slavic nations (Serbia) Agreements to defend each other in times of war 3. Imperialism Created strong economic competition among Britain, Germany, and France Each desired to be the leader of industry, therefore competition for colonies – France and Germany wanted Morocco. – Russia and Austria-Hungary were rivals in the Balkans (Serbia, Bosnia, etc.). – Britain and Germany competed for control of Africa and the Middle East, and for world markets. 4. Nationalism Definition: Extreme competition and pride in one’s nation A problem when a nation considers other nations inferior German pride in military and industry French anger toward Germany for earlier loss (Franco-Prussian War) Russian loyalty to Slavic people (as in, Serbia) The Spark June 28th, 1914 Franz Ferdinand was heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne Was visiting Sarajevo, Bosnia, where he was shot point blank The assassin, Gavrilo Princip, was a Serbian nationalist who wanted Austria out of Bosnia EUROPE PLUNGES INTO WAR War Timeline July 23 – Austria blames Serbia for Franz Ferdinand’s death July 28 – Austria declares war on Serbia August 1st – Germany declares war on Russia August 3rd – Germany declares war on France, invades Belgium August 4th – Britain declares war on Germany August 6th – Austria declares war on Russia The Allies: Great Britain, France, Russia, Serbia. Later: Japan and Italy (eventually U.S.A.) Central Powers: Germany, Austria-Hungary. Later: Bulgaria and the Ottoman Empire (Turkey) Summary Guiding Questions: Could the Great War have been avoided? Who or what was really to blame? Questions, Prompts, Thoughts Lecture Notes The War Begins Both sides thought it would be a fast war. Both sides were excited to fight. Millions signed up to fight The Schlieffen Plan Germany’s plan just in case there was a two-front war: German army would quickly defeat the French in West. Then race east to defeat the Russians At first it seemed like it would work. 1st Battle of the Marne changed this (Sept. 1914). Germans were defeated and this began stalemate on Western Front (northern France) Western Front- Deadlocked region in northern France Eastern Front -Stretch of battlefield along the German and Russian border where Russians and Serbs battled Germans, Austrians, and Turks Trench Warfare • When soldiers fight each other from trenches. Huge losses of human life and small gains. “No Man’s Land”: Area between two opposing trenches. Occurred mostly on Western Front; stretched for 500 miles. Nicknamed “terrain of death”. Many new weapons slowed down gains in land: machine guns, poison gas, tanks, large artillery. Slow gains: Battle of Verdun – Germany gained 4 miles. Battle of Somme – British gained 5 miles. Trench foot - Common to both sides during WWI, also reemerged during Vietnam Major battles of the Western Front 1st Battle of the Marne Sept. 1914 – Germany loses, beginning of stalemate Battle of Verdun, 1916 – each side lost 500,000 men Battle of the Somme, 1916 – heaviest 1 day loss, lasts 6 months and over 1 million lives lost Eastern Front Russians and Serbs vs. Germans and Austro-Hungarians Russian army not industrialized, lacked food, guns, clothing. Only advantage = numbers Unrestricted submarine warfare kept supplies from reaching Russia Winters particularly deadly Global Conflict Battle of Gallipoli - Ottoman Empire vs. Allies. Allies give up leaving Russia cut off from supplies Japan seizes German colonies in China English and French troops attack German colonies in Africa India provides 1.3 million men to fight with Allies Australia and N. Zealand provide many troops Summary Guiding Questions: Could the Great War have been avoided? Who or what was really to blame? Questions, Prompts, Thoughts Lecture Notes Technology: Industrialization of War • Poison Gas: Introduced by Germans; used by both sides. Some caused blindness, others death by choking. • Machine Gun: 200 bullets per minute • Flame throwers: Made it possible to clear terrain faster • Grenade launchers: But grenades themselves were often unreliable • Krupp’s Big Bertha Gun: Could fire up to 80 miles in distance • British Tank: First used at Battle of Somme 1916; not effective until 1918. Eventually made trenches obsolete in WW2. • Zeppelin: German airship used for transport and bombing of Britain. Also used for reconnaissance. • U-Boat: AKA submarines. Used torpedoes. Unrestricted submarine warfare (sinking without warning) used until Lusitania. Renewed by Germans in 1917. • The Airplane: First used on battlefront in 1915. Famous German Pilot – Red Baron The Home Front WW1 was a total war – meaning all resources (including civilians) were dedicated to the war effort. Factories were converted to munitions factories Many goods were rationed – like butter and leather Propaganda everywhere. Women and the war effort: Many roles, including financing the war, recruited, munitions workers, factory workers, farming, ambulance drivers, Red Cross nurses, soldiers, even spies. Art from the War 1917: AMERICA JOINS AND THE RUSSIAN REVOLUTION America joins the war • 1915 – Sinking of the Lusitania. 1,198 dead, including 128 Americans. After this, Germany stops torpedoing civilian ships. • Jan. 1917 – Germany begins unrestricted submarine warfare again and sinks ships without warning. • Feb. 1917 – Zimmerman note. Germany promises to help Mexico invade the U.S. This is the last straw. America declares war on Germany in April of 1917. Russian Revolution Russia is suffering huge losses; almost 2 million dead Czar Nicholas VERY unpopular. Women rebel over rationing of food, many strikes and riots March 1917 – Czar Nicholas forced to step down Germany transports Communist leader Vladimir Lenin to Russia Nov. 1917 – Lenin seizes power and withdraws troops, offers Germany a truce March 1918 – Treaty of Brest-Litovsk signed between Germany and Russia Germany moves all troops to Western Front Summary Guiding Questions: Could the Great War have been avoided? Who or what was really to blame? Questions, Prompts, Thoughts Lecture Notes THE ALLIES WIN THE WAR The Great War Ends Russia withdraws, leaving Germany in a better position to win. But German soldiers were exhausted from 4 long years of fighting and were no match against fresh American soldiers who had joined France on the Western Front 1918 Flu Pandemic depletes all armies. 19,000,000 die by 1919. 2nd Battle of the Marne – Germans tried one last big attack July 1918 German soldiers too weak against fresh American troops Nov. 9, 1918 - Kaiser Wilhelm steps down Nov. 11, 1918 - Armistice – agreement to stop fighting Legacy of the War 9 million soldiers dead 8 million civilians dead 21 million wounded, including 7 million maimed for life Another 19 million dead due to the flu epidemic An entire generation in Europe is wiped out and the people left behind are called the “Lost Generation” VERSAILLES TREATY Who was there? Treaty was created by: Woodrow Wilson (USA), Georges Clemenceau (Fr), David Lloyd George (GB), Vittorio Orlando (It.) Germany, her allies, and Russia were not present. Wilson’s 14 Points Wilson created a plan for lasting peace called the Fourteen Points. This included: Reduction of military in all countries. An end to secret alliances. Giving colonies freedom. Creating a League of Nations. Versailles Treaty Britain and France hated Wilson’s plan. They wanted to keep their military and get even with Germany. The treaty they created: Said Germany was solely responsible for the war and punished Germany by forcing her to pay for the war. Stripped Germany of all power. The only part of Wilson’s plan they kept was the League of Nations. Results: Left lasting feelings of bitterness in the hearts of Germans Austria-Hungary was split into four countries: Austria, Hungary, Yugoslavia, and Czechoslovakia. Ottoman Empire lost their entire empire to France and Britain Russia lost Poland and Romania The U.S. refused to follow the treaty and refused to join the League of Nations. Therefore the League of Nations was irrelevant since it was missing the most powerful nation in the world. Japan was angry because she did not gain territory for helping the Allies. Leads the way to WW2.