personality
advertisement

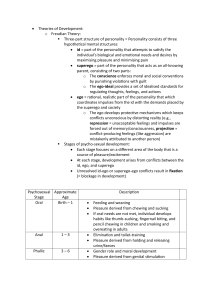
Personality Personality – unique attitudes, behaviors, emotions that characterize a person Key question: stability vs. change Type A vs. Type B (A = competitive, aggressive, volatile) Freudian theory – psychosexual stages Oral – 0-1 year, pleasure from mouth Anal – 1-3 years, pleasure from elimination Phallic – 3-5 years, pleasure from genitals Oedipal complex – boy wants mom, resents dad Castration anxiety Electra complex – girl wants dad, resents mom (not Freud) Penis envy Resolved through identification with same sex parent Latency – 6-puberty, repression of sexual feelings Genital – puberty on, sexual pleasure through relationships Fixations – problem in resolving a stage Oral – overeat, smoke, chew gum Anal – anal retentive (compulsive, overly organized) Anal expulsive (messy, disorganized) Id (pleasure principle) Ego (reality principle) – mediates between id and superego Superego – conscience, mores of society Defense mechanisms Repression Denial Displacement Projection Reaction formation Regression Rationalization Sublimation Criticisms of Freud Feminists (Karen Horney – womb envy) Neo-Freudians Adler – birth order, inferiority complex – drive for superiority Carl Jung – collective unconscious Archetypes – shadow Trait theories Eysenck – stable-instable, introversion-extraversion scale Cattell – 16PF Big 5 – OCEAN (openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, neuroticism) Factor analysis – finding clusters of items that differentiate between traits Other theorists Allport – cardinal dispositions (traits that clearly identify a person) Central dispositions/secondary dispositions Biological theories Temperaments – characteristic way of dealing with the world Hippocrates – four humors (body fluids – blood, yellow bile, black bile, phlegm) Somatotype theory – Sheldon (endomorphs, ectomorphs, mesomorphs) Social-cognitive theories Bandura – reciprocal determinism (traits, environment, behavior) Self-efficacy – making a difference, getting things done Rotter – locus of control (internal vs. external) Humanistic theories People are innately good Self-concept Self-esteem Unconditional positive regard, empathy, genuineness Assessment of personality Projective test – Rorschach, Draw-a-Person, TAT Self-report inventories – MMPI Barnum effect – see self in vague, stock descriptions of personality Astrological sign can fit anyone