Pertemuan 21 Internetworking Matakuliah : H0174/Jaringan Komputer
advertisement

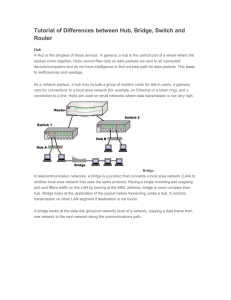
Matakuliah Tahun Versi : H0174/Jaringan Komputer : 2006 : 1/0 Pertemuan 21 Internetworking 1 Learning Outcomes Pada akhir pertemuan ini, diharapkan mahasiswa akan mampu : • Menunjukkan internetworking 2 Outline Materi • Bridge • Router • Switch 3 Internetworking Terms • End System (ES) – Device attached to one of the networks of an internet – Supports end-user applications or services • Intermediate System (IS) – Device used to connect two networks – Permits communication between end systems attached to different networks 4 How Networks Differ 5-43 5 Internetworking Devices Types of devices for interconnecting LAN Bridge Routers Layer 2 switch Layer 3 switch 6 Interconnecting Networks (a) Two Ethernets connected by a switch. (b) Two Ethernets connected by routers. 7 Internetworking Components • Bridge – IS (Intermediate System) used to connect two LANs using similar LAN protocols to expand beyond single LAN – Address filtering- passing on packets to the required network only – OSI layer 2 (Data Link) – Bridge is simple, minimal processing • Router – Connects two (possibly dissimilar) networks – Uses internet protocol present in each router and end system – OSI Layer 3 (Network) 8 Connection of Two LANs 9 Functions of a Bridge • Read all frames transmitted on one LAN and accept those address to any station on the other LAN • Using MAC protocol for second LAN, retransmit each frame • No modification to content or format of frame, no encapsulation (Exact bitwise copy of frame) • May be more than one bridge to cross • May connect more than two LANs • Bridging is transparent to stations 10 Bridge Protocol Architecture • MAC level – Station address is at this level • Bridge does not need LLC layer – It is relaying MAC frames • Can pass frame over external communication system WAN link – Capture frame – Encapsulate it – Forward it across link – Remove encapsulation and forward over LAN link 11 Address Learning • Preload forwarding address database • Learn forwarding address – When frame arrives at port X, it has come from the LAN attached to port X – Use the source address to update forwarding database for port X to include that address – Timer on each entry in database – Each time frame arrives, source address checked against forwarding database 12 Spanning Tree Algorithm • Address learning works for tree layout – i.e. no closed loops • For any connected graph there is a spanning tree that maintains connectivity but contains no closed loops • Each bridge assigned unique identifier • Exchange between bridges to establish spanning tree 13 Router • Complex large LANs need alternative routes – Load balancing – Fault tolerance • Routing selected for each source-destination pair • Routers do all IP-level processing in software • High-speed LANs and high-performance layer 2 switches pump millions of packets per second • Layer 3 switches – Implementpacket-forwarding logic of router in hardware • Two categories: Packet by packet and Flow base 14 Problems with Routers • Routers do all IP-level processing in software – High-speed LANs and high-performance layer 2 switches pump millions of packets per second – Software-based router only able to handle well under a million packets per second • Solution: layer 3 switches – Implement packet-forwarding logic of router in hardware • Two categories – Packet by packet – Flow based 15 Layer 3 Switch • Packet by Packet – Operates insame way as traditional router – Order of magnitude increase in performance • Flow-based switch – Tries to enhance performance by identifying flows of IP packets of same source and destination – Done by observing ongoing traffic – Once flow is identified, predefined route can be established 16